![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. frontalis
2. orbicularis oculi (orbital aspect) 3. orbicularis oculi (palpebral aspect) 4.orbicularis oris 5. platysma 6. frontal occipital aponeurosis 7. auricularis 8. occipitalis 9. zygomaticus major 10. risorius |
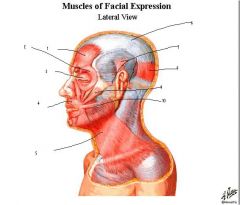
labels?
|
|
|
all the muscles of the face originate and insert into where?
|
originate from skull and insert into the skin
|
|
|
the motor innervation for the muscles of the face is via what nerve?
|
facial nerve (CN VII)
|
|
|
what facial muscle is known for smiling?
|
risorius
|
|
|
what facial muscle assists in opening the jaw?
|
platysma
|
|
|
what facial muscle is used for squinting?
|
orbital portion of orbicularis oris
|
|
|
1.orbicularis oculi
2. levator labii superioris 3. depressor anguli oris 4. depressor labii inferioris 5. procerus 6. zygomaticus minor 7. zygomaticus major 8. risorius 9. mentalis |
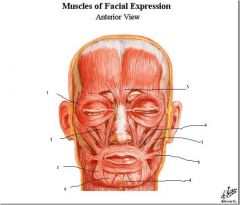
labels?
|
|
|
the buccinator muscle is found deep to what muscle?
|
masseter muscle
|
|
|
the parotid duct pierces what muscle and then opens where?
|
pierces the buccinator muscle and opens in the oral cavity opposite the 2nd upper molar
|
|
|
what is the action of the buccinator muscle?
|
it stabalizes the cheek, for example when you are playing the trumpet
|
|
|
what is the spacial relationship of the parotid duct to the masseter?
|
it runs superficially and transversly over the masseter
|
|
|
the structural elements of the nose are?
|
hyaline cartilage and fibrofatty tissue
|
|
|
what nerve provides cutaneous branches for the face?
|
trigeminal (CN V), which is GSA, note that sympathetic GVE's on skin for sweat glands, etc. join the cutaneous branches of the trigeminal
|
|
|
what branches of the trigeminal exit through small foramen in the viscerocranium to innervate the skin?
|
supraopitcal, infraoptical, and mental nerves.
|
|
|
branches of opthalmic (V1)
1. supraorbital 2. supratrochlear 3. infratrochlear branches of maxillary nerve (CN V2) 4. zygomatical facial 5. infraorbital 6. zygomatical temporal mandibular nerve (CN V3) 7. buccal 8. mental 9. auriculotemporal |
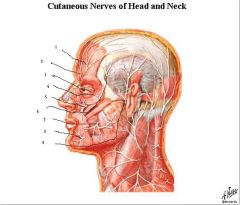
label the nerves and give their orriginating nerves.
|
|
|
earache can be due to pain related to disease distributed along what nerves?
|
CN V, VII, IX, and X
|
|
|
1. posterior auricular
2. main trunk of facial nerve emerging from stylomastoid foramen 3. temporal 4. zygomatic 5. buccal 6. marginal mandibular 7. cervical |
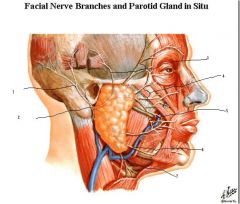
labels?
|
|
|
from internal carotid
1. supratrochlear 2. supraorbital 3. dorsal nasal from the external carotid 4. angular 5. transverse facial 6. facial 7. external carotid 8. internal carotid veins 9. internal jugular 10. retro mandibular 11. external jugular from external carotid 12. posterior auricular 13. occipital 14. superficial temporal |
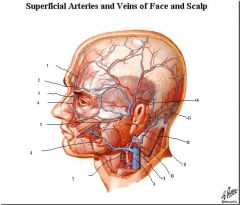
label the vessels and if it is an artery determine whether it came from the internal carotid via the opthalmic artery or if it came from the external carotid
|
|
|
what muscle seperates the external and internal jugular veins?
|
sternocleidomastoid
|
|
|
the mentalis muscle does what?
|
pouts lower lip
|
|
|
what are the 5 layers of the scalp?
|
skin, dense connective tissue, aponeurosis, loose connective tissue, periosteum
|
|
|
what layer of the scalp is highly vascularized and if injured keeps the blood vessels open?
|
dense connective tissue
|
|
|
what layer of the scalp allows infection to spread quickly within that layer?>
|
loose connective tissue
|
|
|
what layer of the scalp allows infection to spread into bone or inside cranial vault via the emissary veins?
|
the periosteum
|
|
|
lymph usually drains following what vein in head in neck into the thoracic duct? what is the other vein it can follow?
|
usually follows the internal jugular vein, but it can also follow the anterior jugular vein.
|
|
|
what are the lymph nodes in the head and neck region (their names correspond to their anatomical locations)?
|
parotid, submental, submandibular, anterior jugular, occipital, mastoid, and deep cervical (main ones palpated).
|

