![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fungi
|
*detritovores / carnivores
*heterotrophs *nutrients from absorbtion |
|
|
Hyphae
|
thin multicellular filaments that make up fungi
|
|
|
Mycelia
|
network of branched hyphae adapted for absorbtion
|
|
|
Yeasts
|
singled celled fungi
|
|
|
Reproduction of Fungi
|
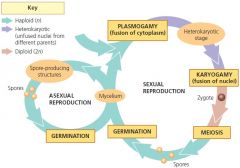
Mainly haploid organism.
|
|
|
Plasmogamy
|
union of cytoplasms but not nuclei
|
|
|
Heterokaryotic stage or dikaryotic
|
*a fused mycelium with two geneticaly diff. nuclei
*non fused nuclei divide without fusing |
|
|
Karyogamy
|
fusion of nuclei after heterokaryotic stage
|
|
|
Molds
|
Asexual fungi that form haploid spores by mitosis
|
|
|
Clade Chytrids/chytridiomycota
|
fruiting bodies , banched hyphe or single celled, primitive fungal group
flagellated spores |
|
|
Clade Zygomycetes
|
food fungi, decomposers
resistand zygosporangium as sexual stage |
|
|
Clade Glomeromycetes
|
aka. abuscular mycorrhizae formed with plants/ plant fungi
mutualistic relationships |
|
|
Clade Asomycetes
|
sac fungi
marine fresh water and terrestrial habitat asci= saclike structure of sexual spore production fruiting bodies called sexual ascocarps |
|
|
Clade Basidiomycetes
|
Decomposers and ectomycorrhizal
club fungi fruiting bodies called mushrooms (dikaryotic) |
|
|
Lichen
|
symbiotic association btw photosynthetic microorg and fungus
often ascomycete, basidiomycetes, glomeromycete |

