![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What happens during the hydration of ethene? |
Steam is added to an alkane under high temperature and pressure and a phosphoric acid catalyst. |
|
|
|
What are the uses of ethanol? |
Alcoholic drinks, fuel, methylated spirits and methanol |
|
|
|
What is the mp and BP like for alcohols |
Higher than alkanes because of hydrogen bonds |
|
|
|
Are alcohols soluble? |
Yes they are ... in polar solvents like water because the polar OH groups form H bonds with water molecules |
|
|
|
What happens to solubility as chain length increases? |
Solubility decreases as chain length increases as a larger part of the molecule is made up of the non polar hydrocarbon tail |
|
|
|
Explain combustion |
Alcohols can completely combust under lots of oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water Alcohols can partially combust under limited oxygen to form carbon monoxide and water |
|
|
|
Explain oxidation |
Oxidation of alcohols occurs by K2Cr2O7/ H2SO4 They can form different products based on whether the alcohol is primary or secondary |
|
|
|
What happens during the oxidation of primary alcohols |
Aldéhydes are produced if distillation occurs, carboxyllic acids are produced if reaction is refluxed |
|
|
|
What happens during the oxidation of secondary alcohols |
A ketone is produced as the alcohols is put under reflux |
|
|
|
What is reflux |
The continuous boiling and condensing of a reaction mixture to ensure that the reaction takes place without the contents of the flask boiling dry |
|
|
|
What are the uses of halogenalkanes |
As a refrigerant, aerosol propellants, degreasing agents or dry cleaning solvent |
|
|
|
Why do halogen alkanes attract nucleophiles |
Because the carbon halogen Bond is polar with the carbon being partially positive and the halogen being partially negative |
|
|
|
Explain what hydrolysis reactions are |
It's a reaction with water aqueous hydroxide ions that breaks the chemical compound into two compounds |
|
|
|
Which is more important Bond enthalpy or Bond polarity |
Bond enthalpy is more important. The carbon to iodine bond has the lowest Bond enthalpy and so it most readily accepts nucleophiles compared to fluorine |
|
|
|
What is PTFE |
Polytetrafluoroethene |
|
|
|
Ozone |

|
|
|
|
What's the general formula of an alcohol |
Cn H2n+1 OH |
|
|
|
Why are alcohols polar? |
Because oxygen is more electro negative than hydrogen |
|
|
|
Why are alcohols polar? |
Because oxygen is more electro negative than hydrogen |
|
|
|
What is the colour change when a primary alcohol is oxidised |
The quality is from Orange to green because they call me and is reduced from +6 to +3 |
|
|
|
What happens during the elimination of an alcohol |
A h2O molecule is eliminated from the alcohol to form an alkene |
|
|
|
What are the conditions required for the elimination of an alcohol? |
You need a concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst or a phosphoric acid catalyst and a high temperature |
|
|
|
What happens during the substitution of an alcohol |
A hyodrgigen halide replaces the OH group forming a water molecule |
|
|
|
What are the conditions needed for the substitution of an alcohol |
Has to be in the presence of an acid (e.g NaBr/ H2SO4) since this provides another H atom |
|
|
|
Explain why the oxidation of alcohols cannot be carried out in an open round bottomed flask |
Because alcohols are volatile and would therefore escape |
|
|
|
How can distillation be summed up? |
It's basically the separation of a liquid from a solution by vapourisation followed by condensation to a different container |
|
|
|
Diagram of reflux |
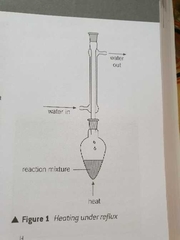
|
|
|
|
Diagram of distillation |
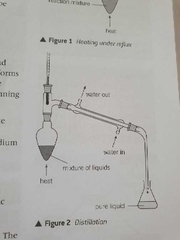
|
|
|
|
What does immiscible mean? |
Whe liquids stay separated and don't mix (e.g water and oil) |
|
|
|
How do you separate immisble liquids? |
By using a separating tap. More dense layer is at bottom |
|
|
|
What anhydrous salts can be used to dry an organic product? |
Anhydrous magnesium sulfate or anhydrous calcium chloride |
|
|
|
Alkanes to haloalkanes |
UV radiation and a halogen under high temperature and pressure |
|
|
|
Alkenes to alkanes |
Hydrogen and a nickel catalyst |
|
|
|
Alkenes to alcohols |
Phosphoric acid catalyst and water |
|
|
|
Alkenes to polyalkenes |
Addition polymerisation |
|
|
|
Alkenes to haloalkanes |
Halogens or hydrogen halides... simply shake! |
|
|
|
Alcohols to haloalkanes |
Sodium halide and sulfuric acid (acidified halide) |
|
|
|
Alcohols to alkenes |
Concentrated sulfuric acid (gets rid of water) |
Elimination |
|
|
Secondary alcohols to ketones |
Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and reflux |
|
|
|
Primary alcohols to aldehyde |
Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and distil |
|
|
|
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids |
Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and reflux |
|
|
|
What is the molecular ion peak in mass spectroscopy |
The highest m/z on the right |
|
|
|
Why does the M+1 peak exist? |
It exists because 1.1% of the carbon is present as the carbon-13 isotope |
|
|
|
What do covalent bonds in molecules naturally do? |
They vibrate |
|
|
|
What do covalent bonds in molecules naturally do? |
They vibrate |
|
|
|
What do bonds do in the presence of infrared radiation |
They vibrate more |
|
|
|
What is the region of an IR spectrum between 400cm-¹ and 1500cm-¹ known as |
The fingerprint region |
|
|
|
At As level what should you be able to identify in IR spectroscopy |
• the O-H group in alcohols • the C=O group in aldehydes and ketones • the COOH in carboxylic acid |
|
|
|
Applications of IR spectroscopy |
Monitoring of gases that cause air pollution, or in breathalysers |
|

