![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If solute is dissolved, bp? fp? vp? |
Boiling point rises Freezing point lowers Vapor pressure lowers |
|
|
Molality |
Moles solute/kg solvent |
|
|
Xsolute |
Moles solute/total moles |
|
|
The speed of rxn depends on |
Catalyst and reactants |
|
|
Vapor Pressure Equation |
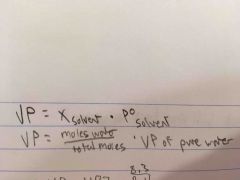
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Boiling Pt |
Change in Temp = K x Molality |
|
|
Rank Vapor Pressure |
Pure water will be highest Multiply molality by # of ions, biggest # is lowest |
|
|
Find Mole fraction |
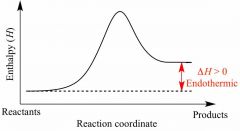
Mass percent = grams Convert to moles Divide thing by total moles |
|
|
Catalyst increases rxn speed by |
Lowering activation energy (Ea) |
|
|
Endothermic |
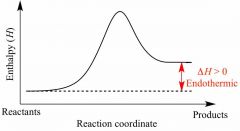
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Activation energy |
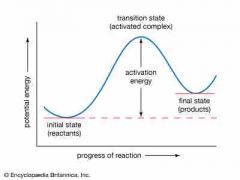
Back (Definition) |
|
|
If temp increases, kinetic energy curve shifts |
Right |
|
|
Find Partial order |
Look @ data, choose 2 where concentration changed and everything else constant. Rate 2/Rate 1 = ([A2] / [A1])^m Ex: 0.2/0.05 = (0.2/0.1)^m 4 = 2^m m = 2 |
|
|
Find rate of change |
Proportion of rate and coefficient in balanced equation |
|
|
Least soluble |
Closer together and higher up |
|
|
Most soluble gas |
Polar gas (uneven molecular structure) |

