![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
top-down processing |
a hierarchial model of pattern recognition in which info at higher levels of mental processing can also influence lower, "earlier" levels in the processing hierarchy |
|
|
bottom-up processing |
a hierarchial model of pattern recognition in which data are relayed from one level of mental processing to the next, always moving to a higher level of processing |
|
|
signal detection theory (SDT) |
a theory of perception based on the idea that the detection of a faint stimulus requires a judgement-- it is not an all-or-none principle |
|
|
sensory adaptation |
a decrease in sensitivity to a constant level of stimulation |
|
|
sensation |
the sense organs' detection of external stimuli, their responses to the stimuli and the transmission of these responses to the brain |
|
|
perception |
the processing, organization and interpretation of sensory signals; it results in an internal representation of the stimulus |
|
|
transduction |
a process by which sensory receptors produce neural impulses when they receive physical or chemical stimulation |
|
|
plasticity |
a property of the brain that allows it to change as a result of experience, drugs or injury |
|
|
dizygotic twins |
(fraternal twins) twin siblings that result from two separately fertilized eggs and therefore are no more similar genetically than nontwin siblings |
|
|
monozygotic twins |
(identical twins) twin siblings that result from one zygote splitting in two and therefore share the same genes |
|
|
pituitary gland |
a gland located at the base of the hypothalamus; it sends hormonal signals to other endocrine glands, controlling their release of hormones |
|
|
hormones |
chemical substances released from endocrine glands, that travel through the bloodstream to targeted tissues; the tissues are subsequently influenced by hormones |
|
|
gonads |
the main endocrine glands involved in sexual behavior: in males, the testes; in females, the ovaries |
|
|
endocrine system |
a communication system that uses hormones to influence thoughts, behaviors and actions |
|
|
sympathetic division |
a division of the autonomic nervous system; it prepares the body for action |
|
|
parasympathetic division |
a division of the autonomic nervous system; it returns the body to its resting state |
|
|
somatic nervous system |
a component of the peripheral nervous system; it transmits sensory signals and motor signals between the CNS and the skin, muscles, and joints |
|
|
autonomic nervous system (ANS) |
a component of the peripheral nervous system; it transmits sensory signals and motor signals between the CNS and the body's glands and internal organs |
|
|
parietal lobes |
regions of the cerebral cortex--in front of the occipital lobes and behind the frontal lobes--important for the sense of touch and for conceptualizing the spatial layout of an environment |
|
|
temporal lobes |
regions of the cerebral cortex--below the parietal lobes and in front of the occipital lobes--important for processing auditory info, for memory and for object and face perception |
|
|
frontal lobes |
regions of the cerebral cortex--at the front of the brain--important for movement and higher level psychological processes associated with the prefrontal cortex |
|
|
prefrontal cortex |
the frontmost portion of the frontal lobes, especially prominent in humans; important for attention, working memory, decision making, appropriate social behavior and personality |
|
|
amygdala |
a brain structure that serves a vital role in our learning to associate things with emotional info |
|
|
basal ganglia |
a system of subcortical structures that are important for the production of planned movement |
|
|
cerebral cortex |
the outer layer of brain tissue which forms the convoluted surface of the brain |
|
|
occipital lobes |
regions of the cerebral cortex--at the back of the brain-- important for vision |
|
|
hypothalamus |
a brain structure that is involved in the regulation of bodily functions, including body temp, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels; it also influences our basic motivated behaviors |
|
|
thalamus |
the gateway to the brain; it receives almost all incoming sensory info before that info reaches the cortex |
|
|
hippocampus |
a brain structure that is associated with the formation of memories |
|
|
brain stem |
an extension of the spinal cord; it houses structures that control functions associated with survival, such as breathing, swallowing, vomiting, urination and orgasm |
|
|
cerebellum |
a large, convoluted protuberance at the back of the brain stem; it is essential for coordinated movement and balance |
|
|
Broca's area |
a small portion of the left frontal region of the brain, crucial for the production of language |
|
|
Common Neurotransmitters and their Major Functions |
1. Acetylcholine: motor control over muscles; learning, memory, sleeping and dreaming 2. Epinephrine: energy 3. Norepinphrine: arousal and vigilance 4. Serotonin: emotional states and impulsiveness; dreaming 5. Dopamine: reward and motivation; motor control (voluntary movement) 6. GABA (gamma-aminobutynic acid): inhibition of action potentials; anxiety reduction; intoxication 7. Glutamate: enhancement of action potentials; learning and memory 8. Endorphins: pain reduction; reward 9. Substance p: pain perception; mood and anxiety |
|
|
reuptake |
the process whereby a neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic terminal buttons, thereby stopping its activity |
|
|
agonists |
drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters |
|
|
antagonists |
drugs that inhibit the actions of neurotransmitters |
|
|
receptors |
in neurons, specialized protein molecules on the postsynaptic membrane; neurotransmitters bind to these molecules after passing across the synaptic cleft |
|
|
neurotransmitters |
chemical substances that carry signals from one neuron to another |
|
|
all-or-none principle |
the principle whereby a neuron fires with the same potency each time, although frequency can vary; a neuron either fires or not--it cannot partially fire |
|
|
action potential |
the neural impulse that passes along the axon and subsequently causes the release of chemicals from the terminal buttons |
|
|
dendrites |
branchlike extensions of the neuron that detect info from other neurons |
|
|
cell body |
site, in the neuron, where info from thousands of other neurons is collected and integrated |
|
|
axon |
a long narrow outgrowth of a neuron by which info is transmitted to other neurons |
|
|
terminal buttons |
small nodules, at the ends of axons, that release chemical signals from the neuron into the synapse |
|
|
synapse |
the site at which chemical communication occurs between neurons |
|
|
synaptic cleft |
the gap between the axon of a "sending" neurons and the dendrites of a "receiving" neuron; it contains extracellular fluid |
|
|
myelin sheath |
a fatty material made up of glial cells, that insulates the axon and allows for rapid movement of electrical impulses along the axon |
|
|
nodes of Ranvier |
small gaps of exposed axon, between the segments of myelin sheath, where action potentials are transmitted |
|
|
resting membrane potential |
the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active |
|
|
sensory neurons |
one of three types of neurons; these afferent neurons detect info from the physical world and pass that info to the brain |
|
|
motor neurons |
one of three types of neurons; these efferent neurons direct muscles to contract or relax, thereby producing movement |
|
|
interneurons |
one of three types of neurons; these neurons communicate only with other neurons |
|
|
neurons |
the basic units of the nervous system cells that receive, integrate and transmit info in the nervous system; they operate through electrical impulses, communicate with other neurons through chemical signals and form neural networks |
|
|
central nervous system (CNS) |
the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
all nerve cells in the body that are not part of the CNS; includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems |
|
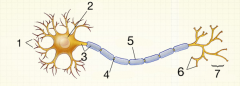
|
1. dendrite 2. cell body 3. axon 4. nodes of Ranvier 5. myelin sheath 6. terminal buttons 7. synapse (synaptic cleft) |
|

|
1. frontal 2. parietal 3. temporal 4. occipital |

