![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 functions of bones |
Support Storage of minerals and lipids blood cell production Protection Leverage |
|
|
Structural classifications of bones |
sutural irregular short flat long sesamoid |
|
|
example of sutural bone |
found between plat bones of skull |
|
|
irregular bone example |
vertebrae pelvis bones in skull |
|
|
short bone example |
carpal/ankle bones |
|
|
flat bone example |
skull bones sternum ribs scapulae |
|
|
example of long bones |
antebrachial brachial femur digits |
|
|
example of sesamoid bone |
patella located in joints |
|
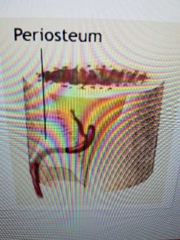
Function of pariosteum |
-membrane that covers outside of bones. -bone growth/repair -route for blood vessels/nerves -isolate bone from surrounding tissue |
|
|
Function of endosteum |
-active during bone growth/repair -covers spongy bone -incomplete layer lines medullary cavity |
|
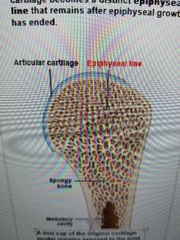
Function of articular cartilage |
prevent damaging in joints from bone to bone contact |
|
|
Describe perforating fibers |
fibers that become incorporated in bone tissue increase strength |
|
|
Describe epihpysis |
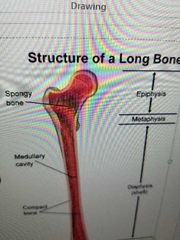
wide part (end) Mostly Spongy Bone |
|
|
Describe diaphysis |
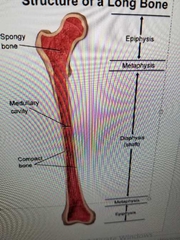
(shaft) wall of compact bone central space contains medullary cavity (marrow) |
|
|
Describe metaphysis |
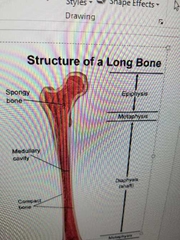
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet |
|
|
desceibe medullary cavity |
where bone marrow is made |
|
|
Locations and function of red bone marrow. |
-between trabeculae -forms red blood cells -contains blood vessels that supply nutrients to osteocytes by diffusion |
|
|
Desceibe yellow bone marrow |
found in spongy bone marrow stores fat |
|
|
Differences in spongey and compact bone. |
Sponge : -No osteons -Red/yellow marrow production -matrix forms an open network of trabeculae-Red/yellow marrow productionCompact: -has osteons-has central canal-has perforating canals-has lamellae Compact: -has osteons -has central canal -has perforating canals -has lamellae
|
|
|
Where would you find spongey bone |
Mostly in Epiphysis and center of bone |
|
|
Where would you find compact bone? |
Mostly in diaphysis and in bone wall |
|
|
Describe mesenchymal cells |
divide to produce osteoblasts assist in fracture repair |
|
|
Define Osteogenesis |
Formation of bone immature cells produce new bone |
|
|
Define ossificiation |
turning into bone or tissue |
|
|
Define Calcification |
Hardening of tissue |
|
|
Describe intramembranous ossification |
-dermal ossification -produce dermal bones like mandible or clavicle -5 step process |
|
|
Describe endochondral ossification |
-how most bones form -primary ossification center -develops inside hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Describe appositional enochondral. one growth |
-growth in width of bone -layers of circumferential lamellae at outer surface. -deepest layers become replaced by osteons -osteoclasts slowly remove bone matrix at inner surface of bone, enlarging medullary cavity. |
|
|
Does bone have a good blood supply? |
Yes, highly vascular |
|
|
Functions of bone remodeling |
-recycling and renewing bone matrix -involves osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts. |
|
|
Are bones removed faster than replaced? |
yes |
|
|
Vitamin D importance |
Use for cholecalciferol. Calcium |
|
|
Vitamin C importance bone |
Stimulate osteoblasts differentiation |
|
|
Vitamin A importance to Bone |
stimulate osteoblasts activity |
|
|
Vitamin K and B12 importance |
Required for synthesis of bone proteins. |
|
|
what effect does mechanical stress have on bone growth? |
Increases strength (osteoblasts) |
|
|
what are fontanels? |
space between fetal skull bone ossification is not complete. |
|
|
How is an infant skull different than an adult? |
No teeth Fontanels instead of sutures |
|
|
Differences in Male and female bone |
Male: Rougher appearance 10% larger granium More sloping forehead Larger Sinus Larger Larger Teeth Larger mandible Larger ribcage Larger collarbones |
|
|
Define Wormian Bones |
small, flat bones found between the flat bones of the skull. |
|
|
Describe sinus |
Chamber within bone normally filled with air. Frontal and sphenoid sinus. |
|
|
what forms has articulation? |
the joints of bone forming the skeleton |
|
|
Describe Intervertebral Foramen |
Gaps between pedicles of adjacent vertebrae For nerve connections to spinal cord |
|
|
Describe vertebral Foramen |
-Encloses the spinal cord -Formed by vertebral framina of successive vertebrae. |
|
|
Describe the atlas vertebrae |
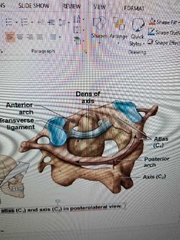
-articulates with occipital of skull -has no body or spinous process -has large anterior and posterior foramen |
|
|
Describe axis |
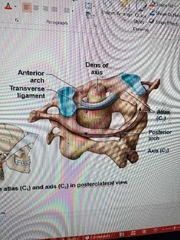
-articulates with the atlas -has heavy spinous process to attach muscles of head and neck |
|
|
Do bodies of axis and atlas fuse during development to form dens? |
Yes |
|
|
what is the only bone that dosent articulate with another bone? |
Hyoid |
|
|
what are the 2 structural features seen in cervical vertebrae and not in other vertebrae? |
Bifida Spinosus Process No spinous process |
|
|
Hiw many phalanges in the hand? |
14 |
|
|
Location and function of calcaneus |
-Transfers weight from Talus to ground -Heel bone |
|
|
Location and function of tarsus |
-transfers weight from tibia across trochlea -ankle bone |
|
|
Describe acetabelum |
spot for head of femur to rest in hip bone. Articulation spot. |
|
|
location and function of doves capitis |
-tip of femur head for ligament insert |
|
|
Function of sella turcica |
holds pituitary gland |
|
|
Location and function of carotid canal. |
passageway in temporal bone for carotid artery. |
|
|
Function and location of jugular foramen. |
passageway between temporal and occipital for jugular vein. |
|
|
Location and function of foramen ovale. |
hole in septum to shunt oxygenated blood from right to left atria. |
|
|
Location and function of foramen rotundum. |
At base of sphenoid greater wing. provides connection between the middle cranial for a and pterygopalatine fossa. |
|
|
Location and function of foramen spinosum. |
Several nerves pass through. |
|
|
Location and function of foramen lacerum. |
Nerve if pterygoid canal and smoke drainage pass through. |
|
|
Function of a joint |
where 2 bones meet where body movements occur |
|
|
Define Synarthrosis |
immovable joint |
|
|
Define apmphiarthrosis |
slightly movable joint |
|
|
define diarthrosis |
freely movable joint |
|
|
Example of suture |
between skull bones |
|
|
Example of gomphosis |
binds teeth to bony sockets |
|
|
Example of synchondrosis |
rigid cartilage between 2 bones |
|
|
example of synotosis |
2 bones fuse metopic suture of frontal bone |
|
|
What is syndesmosis? |
bones connected by a ligament |
|
|
what is symphysis? |
bones connected by fibrocartilage. |
|
|
Function of synovial fluid. |
lubrication nutrient distribution shock absorption |
|
|
Define meniscus. |
Fibrocartilage pad between bones |
|
|
Define bursa. |
small pockets of synovial fluid. |
|
|
what is circumduction? |
a complete circular movement without rotation. |
|
|
what is rotation? |
referance to anatomical position. |
|
|
Define medial rotation. |
internal rotation towards long axis |
|
|
Define lateral rotation. |
external rotation away from body |
|
|
Define gliding |
when two flat surfaces slide past each other. |
|
|
Define flexion |
decreases angle between articulating bones. |
|
|
Define extension |
increases angle between articulating bones. |
|
|
Define abduction |
Move away from longitudinal axis |
|
|
Define adduction. |
movement toward longitudinal axis. |
|
|
Define pronation |
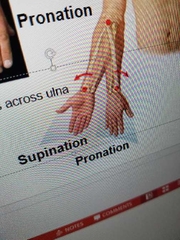
rotates forearm |
|
|
Define supination |
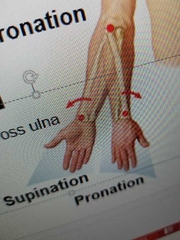
turns palm anteriorly forearm is supinated. |
|
|
Define inversion. |
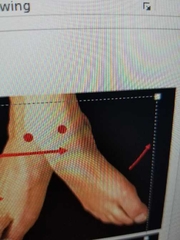
twists sole of foot medially |
|
|
Define eversion |
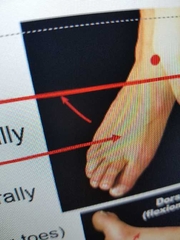
twists sole of foot laterally |
|
|
Define dorsiflexion. |
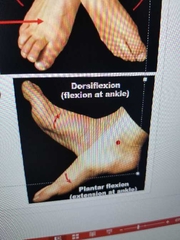
flexion at ankle (lifting toes) |
|
|
Define plantar flexion. |
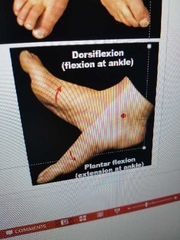
extension at ankle (pointing toes) |
|
|
Define protraction |
anterior movement in horizontal plane (forward) |
|
|
Define retraction |
opposite of protraction (pulling back) |
|
|
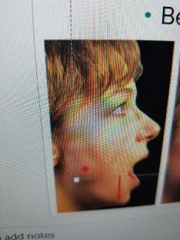
Define elevation |
moving a structure superiorly (up) |
|
|
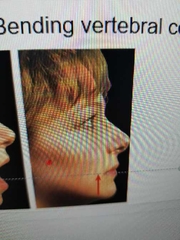
Define depression. |
moving structure inferiorly (down) |
|
|
Define lateral flexion |
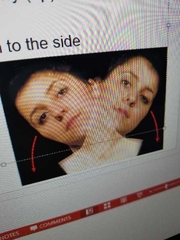
bending vertebral column to both sides. |
|
|
Function of intervertebral disk |
separates vertebral bodies |
|
|
what happens when a disk is herniated? |
compresses spinal nerves |
|
|
Describe motion of Hinge |
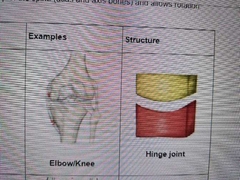
Flexion/Extension |
|
|
Describe motion of pivot |
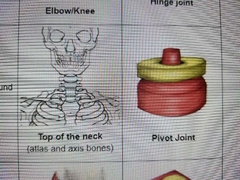
rotation of one bone around another |
|
|
Describe motion of Ball and socket |
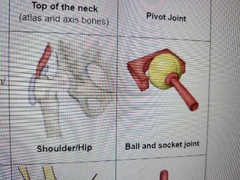
Alot of motions |
|
|
Describe saddle motion |
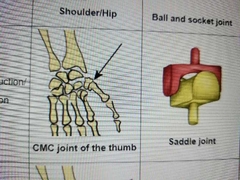
thumb, thumb movements |
|
|
Describe condyloid motion |
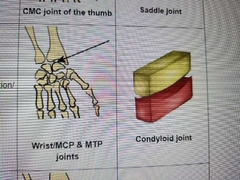
alot |
|
|
Describe gliding motion |
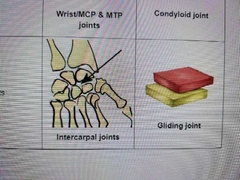
Gliding movements |
|
|
Describe joint types in elbows |
hinge humero-ulnar Humeroradial |

