![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
diseases |
Deviations from or interruptions of the normal structure or function of any part, organ, or system of the body that are exhibited by characteristic set of symptoms and signs |
|
|
|
Microorganism |
Microscopic organisms, those of medical interests include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa |
|
|
|
Infection |
Invasion and multiplication of microorganisms in body tissue that may be clinically inapparent or may result in local cellular injury as a result of competitive metabolism, toxin, intracellular replication, or antigen-antibody response |
|
|
|
Pathogens |
Disease producing microorganisms. Most often ____ have the ability to do one of three functions extremely well. 1. Multiply in large numbers and cause obstructions.2. Cause tissue damage.3. Secrete organic substances called exotoxins |
|
|
|
Exotoxins |
Can produce certain side effects such as an extremely high body temperature, nausea, vomiting, or shock |
|
|
|
Bacteria |
Prokaryotic, ubiquitous, single-celled organisms |
|
|
|
Prokaryotes |
Cellular organisms that lack a true nucleus |
|
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Organisms whose cells have a true nucleus |
|
|
|
Viruses |
Any group of minute infectious agents not resolved in the light microscope, and characterized by a lack of independent metabolism and by the ability to replicate only within living host cells |
|
|
|
Virion |
Complete viral particle found extracellularly and capable of surviving in crystalline form and infecting a living cell; comprises the nucleoid and the capsid; also called viral particle |
|
|
|
Fungi |
General term used to denote a group of eukaryotic protist - including mushrooms, yeast, rust, molds, and smuts - latter characterized by the absence of chlorophyll and by the presence of a rigid cell wall |
|
|
|
Dimorphic |
Occurring in two distinct forms, either as a single-celled yeast or as mold |
|
|
|
Protozoa |
Subkingdom comprising the simplest organisms of the animal kingdom, consisting of unicellular organisms that range in size from submicroscopic to macroscopic. Most are free-living, but some lead commensalistic, mutualistic, or parasitic existences |
|
|
|
Six steps in the establishment of infectious disease |
Encounter. Entry. Spread. Multiplication.
Damaged. Outcome. |
|
|
|
Encounter |
The first step in the establishment of infectious disease.Involves the Infectious organisms coming into contact with the host Involves the Infectious organisms coming into contact with the host Involves the Infectious organisms coming into contact with the host |
|
|
|
Entry |
Second step in establishment of infectious disease Much of the body is in contact with the external environment. And infectious microbe can gain entrance into the human body by either ingestion or penetration |
|
|
|
Spread |
Third step in the establishment of infectious disease The breeding of the Infectious organism, which can take place before or after multiplication |
|
|
|
Multiplication |
Fourth step in the establishment of infectious disease The number of microbes that gain entrance into the host is usually much too small to cause the symptoms of a disease. They must multiply for their impact to be recognized |
|
|
|
Damage |
Fifth step in the establishment of infectious disease Infectious agents can ___ the host in numerous ways. This can either be direct or indirect |
|
|
|
Outcome |
6th and last step to the establishment of infectious disease An encounter with an infectious agent can result in one of three of these.. 1. The host gains control of the infection and eliminates it. 2. The infection overcomes the host immunities to cause disease. 3. The hosts and infectious agent compromise and live in a state of symbiosis |
|
|
|
Host |
Animal or plant that harbors or nourishes another organism |
|
|
|
Infectious microorganism |
Include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa |
|
|
|
Mode of transmission |
Microorganisms can be transmitted through either direct or indirect host-to-host contact |
|
|
|
Vector |
Carrier, especially an animal, that transfers and infective agent from one host to another |
|
|
|
Fomite |
Object, that is not in itself harmful but is able to harbor pathogenic microorganisms and thus may serve as an agent of transmission of an infection |
|
|
|
Reservoir |
Alternate or passive host or carrier that harbors pathogenic organisms, without injury to itself, and serves as a source from which other individuals can be infected |
|
|
|
Health Care-Associated Infections |
(HAIs) Infections that patients acquire while they are receiving treatment for another healthcare issue |
|
|
|
Nosocomial |
Pertaining to or originating in the hospital, said of an infection not present before admittance to the hospital |
|
|
|
Latrogenic |
Resulting from the activities of Physicians |
|
|
|
Compromised patients |
Many patients have weakened resistance to infectious organisms because of they're admitting illness. AKA immunosuppressed |
|
|
|
Bloodborne pathogens |
Disease-causing microorganisms that may be present in human blood |
|
|
|
Constitutive defenses of the body |
Mechanical. Chemical. Cellular |
|
|
|
Flora |
Microbial Community found on or in a healthy person |
|
|
|
Chemotherapy |
Treatment of disease by chemical agents |
|
|
|
Immunization |
The use of vaccine to induce active immunity |
|
|
|
Vaccine |
Suspension of killed microorganisms administered for the prevention, Improvement, or treatment of infectious disease |
|
|
|
Immunity |
Security against a particular disease |
|
|
|
Asepsis |
Freedom from infection |
|
|
|
Surgical asepsis |
Procedure used to prevent contamination by microbes and endospores before, during, or after surgery using sterile technique |
|
|
|
Sterilization |
Complete destruction or elimination of all living microorganisms, accomplished by physical methods (dry or moist heat), chemical agents (alcohol), radiation (ultraviolet, cathode), or mechanical methods (filtration) |
|
|
|
Medical asepsis |
Reduction in numbers of infectious agents, which, in turn, decrease the probability of infection but does not necessarily reduce it to zero |
|
|
|
Disinfectants |
Chemicals used to free an environment from pathogenic organisms or to render such organisms inert, especially as applied to the treatment of inanimate materials to reduce or eliminate infectious organisms |
|
|
|
Autoclave |
Device that uses steam under Pressure to create moist heat |
|
|
|
Standard precautions |
Precautions to prevent the transmission of disease by body fluids and substances.
Includes
hand washing. Gloving. Personal protective equipment. Needle recapping. Bio spills |
|
|
|
Transmission-based precautions |
Applied whenever a patient is infected with a pathogenic organism or a contagious disease |
|
|
|
Airborne precautions |
Patient should be in a negative pressure isolation room with the door closed. If the patient must be moved they should wear a mask that filters expired are. The health care worker should wear a mask that filters inspired air |
|
|
|
Airborne pathogens |
Pathogenic organisms that remain suspended in the air for long periods. Tuberculosis Vercella (chicken pox) Rubeola (measles) |
|
|
|
Droplet precautions |
Patient should be placed in a private room or with another patient who has the same disease and the door can remain open. If the patient must be moved they should wear a mask. Health care workers should also wear a mask when interacting with these patients |
|
|
|
Droplet pathogens |
Pathogenic organisms that typically travel 3 ft before dropping to the ground.
Rubella. Mumps. Influenza. Adenovirus. |
|
|
|
Contact precautions |
Must be used when caring for a patient with a severe or harmful pathogen that spreads by direct contact or by indirect contact with a contaminated object. Patient should be placed any private room or with another patient who has the same disease. When these patients are transported to the radiology department, Department should be notified before receiving the patient.
MRSA. Hepatitis A. Impetigo. Vercella.
|
|
|
|
MRSA. Hepatitis A. impetigo. Varicella. |
conditions requiring contact precautions |
|
|
|
Neutropenic precautions |
AKA reverse isolation, meaning precautions take to protect a patient from germs that staff or visitors could be caring. This is applied to a patient with a compromised immune system, such as those on chemotherapy or a burn victim |

|
|
|
Aseptic |
Describes a product or method that is free of microbiological organisms |
|
|
|
Microorganisms |
Microscopic organisms, those of medical interests include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa |
|
|
|
Sanitize vs. Disinfect |
Means to eliminate microorganisms to a safe level vs. Removing most microorganisms but not highly resistant ones |
|
|
|
Surgical asepsis vs. Medical asepsis |
Is the creation of a sterile environment versus the creation of a clean environment |
|
|
|
Sterile |
Aseptic, free of living microorganisms |
|
|
|
Contaminated |
Presence or the reasonably and anticipated presence of blood or other potentially infectious materials on a item or surface |
|
|
|
Myelography |
X-ray examination of the spinal canal, a contrast agent is injected through a needle into the space around the spinal canal, and nerve roots on the X-ray. The purpose of this is to evaluate the spinal cord and / or nerve roots for suspected compression |
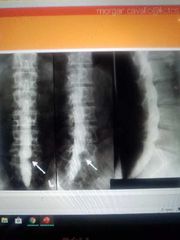
|
|
|
Arthrography |
Examination of a joint using x-ray after the injection of opaque contrast material |
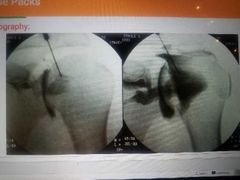
|
|
|
Angiography |
Radiographic procedure used to visualize blood vessels after the introduction of contrast media |
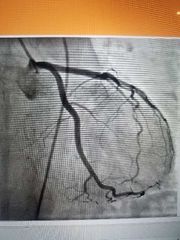
|
|
|
dressing changes |
The Physician is responsible for ordering these. Dressings are best changed in a team setting with another healthcare worker |
|
|
|
Purulent |
Consisting of or containing pus |
|
|
|
Tracheostomy |
Surgical creation of an opening into the trachea through the neck, used to insert a tube to relieve upper Airway obstruction and facilitate ventilation |
|
|
|
Manual Resuscitator (Ambu Bag) |
A handheld device commonly used to provide positive pressure ventilation to patients who are not breathing or not breathing adequately |
|
|
|
Suction |
To minimize the possibility of infection a tracheostomy must be suctioned often to remove secretions Sterile procedure |
|
|
|
Foley catheter |
Sterile procedure Indwelling catheter retained in the bladder by a balloon inflated with air or fluid. Urinary catheters are used to
Empty the bladder. Relieve retention of urine or bypass obstruction. Irrigate the bladder or introduced drugs. Permit accurate measuring of urine output. Relieve incontinence |
|
|
|
voiding cystourethrogram |
Radiographic procedure obtained by the use of fluoroscopy and a contrast agent introduced through a catheter in the bladder. Images are obtained before, during, and after voiding the bladder, urethra, and kidneys
Sterile procedure |
|
|
|
Lithotomy position |
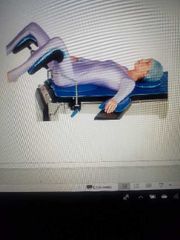
|
|
|
|
Voiding cystourethrogram x-ray |
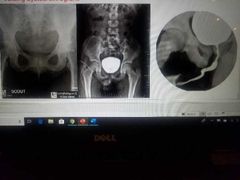
|
|
|
|
Swan-Ganz |
Sterile procedure Catheter provides right heart diagnostic information to rapidly determine hemodynamic pressures, cardiac output, and mixed venous blood sampling. AKA as a Palmieri artery catheter (PAC) or right heart catheter
Trendelenburg position |
|
|
|
Surgical and portable radiography |
Radiography in the surgical environment requires strict attention to sterile technique. Specific guidelines are difficult to give because procedures vary greatly among surgeons and Facilities |
|
|
|
C-arm |
A highly complex piece of equipment that uses X-rays and produces a live image feed that is displayed on a television screen |
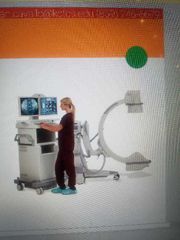
|
|
|
use of the c-arm in surgery |
Requires increased attention to maintain a sterile field. The surgical draping of this and the patient is performed by the surgical team. Three approaches can be used to maintain a sterile field 1. Snap cover.2. Shower curtain.3. Drape the site with an additional sterile cloth |
|
|
|
Nonaseptic techniques |
Include the use of
nasogastric tubes. Urinals. Bedpans. Enemas. Colostomies. |
|
|
|
Nasogastric tubes (NG) |
Tubes of soft rubber or plastic inserted through a nostril and into the stomach. Radiographs are often taken to check for ____ placement. ____ are used to instill liquid food or other substances or for removal of flatus (gas or air) and fluid buildup caused by obstructions |
|
|
|
Lumen |
Cavity or Channel within a tube or tubular organ |
|
|
|
Nemesis Basin |
Kidney-shaped vessel for the collection of vomit |
|
|
|
Urinal |
Vessel or receptacle for urine |
|
|
|
Bedpan |
Vessel for receiving the urinary and fecal discharges for a patient unable to leave his or her bed |
|
|
|
Enema |
Liquid injected or to be injected into the rectum |
|
|
|
Colonoscopy |
Endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a camera on a flexible tube. Biopsies can be performed during the procedure. Excellent method to identify small polyps or masses |
|
|
|
Virtual colonoscopy |
It is performed on a multi slice CT scanner that takes up to 600 2D and 3D images of the colon and approximately 30 seconds |
|
|
|
Sigmoidoscopy |
Procedure used to see inside the sigmoid colon and rectum with a flexible tube that has a camera on the end |
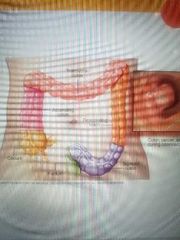
|
|
|
Barium |
Bulky, fine white powder, without odor or taste in free of grittiness. Used as a contrast medium in radiography of the digestive tract |
|
|
|
Standard enema preparation |
Low-residue diet.
Purgation.
Hydration. |
|
|
|
low-residue diet |
Diet that gives the least possible fecal residue. Patient should consume a clear liquid diet for 24 hours before enema examination |
|
|
|
Purgation |
Using a variety of laxatives to evacuate the bowel prior to enema procedure. Then the patient must remain NPO after midnight |
|
|
|
Hydration |
Enema preparation Post-procedure instruct patient to drink plenty of fluids because Barry intends to make patients constipated |
|
|
|
Cleansing enema |
used to promote defecation. The fluid instilled in a cleansing enema breaks up fecal matter, stretches the rectal wall, and initiates the defecation reflex. For any examination that evaluates the colon, the bow should be clear. And most cases the patient can administer a cleansing enema at home |
|
|
|
Barium sulfate vs. water soluble iodine compounds |
Is used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and intestines when bowel perforation is not suspected vs. When a perforation is suspected |
|
|
|
Barium Enema |
To administer a barium sulfate solution into the rectum and through the colon. A larger catheter is required than the one used for a cleansing enema because of barium high viscosity |
|
|
|
Viscosity |
Physical property of liquids that determines the internal resistance to shear forces. State of being thick, sticky, and semifluid in consistency, due to internal friction |

|
|
|
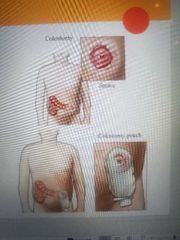
Colostomy |
Surgical creation of an opening between the colon and the surface of the body |
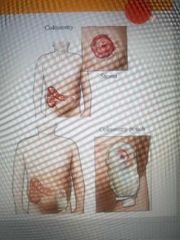
|
|
|
Stoma |
Opening established in the abdominal wall by colostomy, ileostomy, and so forth |
|
|
|
Osteomate |
One who has undergone enterostomy or ureterostomy |
|
|
|
loopogram |
The radiographic evaluation of the small and large bowel that has been connected to the skin surface as a substitute for the urinary bladder with an ostomy |
|
|
|
Enterostomal Therapist |
Health professional (usually a nurse) with special training and certification in the care of ostomies and related concerns |
|
|
|
Aseptic technique must be used |
Tracheostomies.
Chest tube.
Urinary catheters.
Intravenous and intra-arterial lines.
Pacemakers.
Surgery.
NICU.
Some ED patients, inpatient, and ICU patients |
|
|
|
Nonasceptic technique must be used |
NG tubes. Urinals. Bedpans. Enemas. Colostomies. |
|

