![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Biomechanics |
A branch of physics that applies the laws of mechanics to live in creatures. Examines the action of forces on the body at rest or in motion Researchers of this field discover how people get injured and develop strategies to prevent injuries in the future |
|
|
|
Base of support |
The foundation on which a body rests or stands. When a person is standing the feet and the space between the feet constitute that person's base of support. |
|
|
|
Center of gravity |
Hypothetical Point around which all mass appears to be concentrated. Gravitational forces appear to act on the entire body from the specific point |
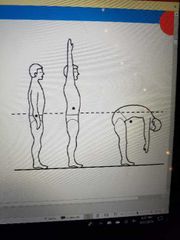
|
|
|
Mobility muscles |
Muscles that are found in the four extremities and are designed for movement. Example includes the biceps and hamstring muscles |
|
|
|
Stability muscles |
Muscles that support the Torso and are designed to provide posture stability. Examples include the erector spinae and the rectus abdominis muscles |
|
|
|
Orthostatic hypotension |
A sudden drop in blood pressure in the brain when a person stands up quickly from sitting or Supine position. When the oxygen in the brain drops, the person becomes dizzy and is prone to fall. Symptoms of this include dizziness, fainting, blurred vision, and slurred speech |
|
|
|
Immobilization |
Act of rendering immoveable |
|
|
|
Restraint |
Hindrance of an action (movement) |
|
|
|
Simple immobilization techniques |
Involve the use of a positioning sponge to support the anatomic area of Interest or gently laying a sandbag across a patient's forearm to minimize shaking caused by patient anxiety |
|
|
|
Involved immobilization techniques |
More complex techniques might involve completely wrapping an infant or small child in a sheet or securing a trauma patient to a backboard to facilitate transport and minimize the possibility of more severe complications |
|
|
|
Communication |
One of the most effective ways to reduce motion |
|
|
|
Rapport |
Relation of Harmony and Accord between two persons |
|
|
|
Empathy |
Recognition of and entering into the feelings of another person |
|
|
|
Positioning sponges |
A common method of reducing patient motion involves the use of these. They allow for increased accuracy by supporting the patient for anatomic area of Interest |
|
|
|
Sandbags |
Radiopaque, extremely helpful in reducing voluntary motion |
|
|
|
Head clamps |
Design strictly for use in positioning various projections of the skull |
|
|
|
Velcro straps |
Can be effective as restraining or positioning devices and are radiolucent |
|
|
|
Ambulatory |
Ability to walk |
|
|
|
Axial projection |
Any projection not at right angle to the long axis of an anatomic structure |
|
|
|
Flexion |
Act of bending or condition of being bent |
|
|
|
Trauma applications |
Immobilization is one of the most critical considerations when working with serious injured patients |
|
|
|
Trauma |
Wound or injury |
|
|
|
Spinal trauma |
The most common ____ traction device is a cervical collar. The cervical collar must stay on until the physician has declared it safe to remove. A backboard is used when multiple injuries in addition to this are present |
|
|
|
Anteroposterior (AP) |
Direction of X-ray beam from front to back |
|
|
|
Head trauma |
Radiographer must become versatile in the production of skull images. Instead of being able to position the patient correctly, the radiographer must be able to manipulate the radiographic equipment to compensate for the patients lack of Mobility |
|
|
|
Extremity trauma |
May involve traction devices, particularly for the lower extremities. In these cases the traction devices are in the form of splints, most often inflation or traction splints. Satisfactory initial image can be obtained with a splint in place |
|
|
|
Pediatric application |
Many methods and devices are available to facilitate pediatric radiography, perhaps the most overlooked aspect of positioning and immobilizing children are communication and establishing a rapport |
|
|
|
Pediatric |
Pertaining to the branch of medicine that treats children |
|
|
|
Neonates |
Newborn infants |
|
|
|
Sheet restraints |
Sheets or blankets can be used in many ways for immobilizing infants and small children. Mummy wrapping an infant is one way |
|
|
|
Commercial restraints |
Usually take one of two forms, upright restraint devices or restraint boards. Two common upright restraint devices are the Pigg o stat & pediaposer pediatric position chair |
|
|
|
Artifacts |
Substances or structures not naturally present but of which an authentic image appears on an image |
|
|
|
Non-commercial restraints |
Plexiglass paddle, velcro straps, tape or stockinette are all inventive ways of immobilizing pediatric patients |
|
|
|
Geriatric |
Pertaining to the treatment of the Aged |
|
|
|
Routine applications |
Sponges. Sandbags. Head clamps. Velcro straps. Stability bar.
|
|
|
|
Special applications |
Trauma applications.Pediatric applications.Geriatric applications. |
|

