![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Homeostasis |
Constancy in the internal environment of the body, naturally maintained by adaptive responses that promote healthy survival |
|
|
|
Body temperature |
Measurement of the degrees of heat of the deep tissues of the human body |
|
|
|
Diaphoresis |
Profuse sweating |
|
|
|
Oral Axillary Tympanic Temporal Rectal |
Ways you can measure body temperature |
|
|
|
Hyperthermia |
Abnormally high body temperature, especially that induced for therapeutic purposes |
|
|
|
Fibrile |
Pertaining to or characterized by fever |
|
|
|
Hypothermia |
Low body temperature |
|
|
|
Normal body temperature range |
97.6 - 100 |
|
|
|
98.6° |
Average oral temp |
|
|
|
Average Tympanic temp |
97.6° |
|
|
|
100° |
Average Temporal artery |
|
|
|
99.6° |
Average rectal temp |
|
|
|
97.6° |
Average Axillary |
|
|
|
Tidal volume |
Volume of air inhaled during one respiratory cycle |
|
|
|
Ventilation |
Mechanical movement of air into and out of the lungs |
|
|
|
Respiratory Measurement |
In healthy adults a single respiration consists of an inspiration phase in an expiration phase. Respirations are counted by observing the movement of the abdomen |
|
|
|
Tachypnea |
Abnormal Rapid breathing |
|
|
|
Bradypnea |
Abnormal slowness of breathing |
|
|
|
Dyspnea |
Difficult or labored breathing |
|
|
|
Orthopnea |
Difficulty breathing when laying down |
|
|
|
Apnea |
Cessation of spontaneous ventilation |
|
|
|
Adult: 12 - 20 per min Child: 20 - 30 per min |
Normal respiration rates for adult and child |
|
|
|
Pulse |
A rhythmical throbbing of arteries as blood is propelled through them |
|
|
|
Auscultation |
Listening to sounds of the body, typically through the use of a stethoscope |
|
|
|
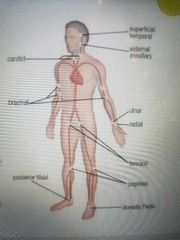
Radial artery on the lateral side of the wrist Brachial artery found in the antecubital fossa or upper arm in infants Carotid artery in the neck |
Pulse measurement locations |
|
|
|
Pulse oximeter |
Photoelectric device used for determining the oxygen saturation of the blood. 95% or greater oxygen saturation is considered a normal range |
|
|
|
Tachycardia |
Rapidity heart action. Usually defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute |
|
|
|
Bradycardia |
Slowness of the heartbeat as evidenced by slowing of the pulse rate to less than 60 beats per minute |
|
|
|
Adult: 60 -100 Child: 70 - 120 |
Normal pulse ranges in adults and children |
|
|
|
Blood pressure |
The pressure of the blood in the circulatory system, often measured for diagnosis since it is closely related to the force and rate of the heartbeat and the diameter and elasticity of the arterial walls |
|
|
|
Diastolic |
Pertaining to the dilation, or a period of relaxation of the heart, especially of the ventricles |
|
|
|
Systolic |
Pertaining to the tightening, or period of contraction of the heart, especially of the ventricles |
|
|
|
Systolic pressure |
When taking blood pressure, the initial sound of blood flow is the ___ observed on the manometer |
|
|
|
Diastolic pressure |
When taking blood pressure, when the sound of blood can no longer be heard the ____ will be observed on the manometer |
|
|
|
Sphygmomanometer and stethoscope |
Blood pressure readings are obtained with the use of.. |
|
|
|
Sphygmomanometer |
Instrument for measuring blood pressure. Consists of a cuff, tubing, a valve, a ball, and a manometer. |
|
|
|
Stethoscope |
A medical instrument for listening to the action of someone's heart or breathing, typically having a small disk-shaped resonator that is placed against the chest and two tubes connected to ear pieces |
|
|
|
Hypertension |
Persistently High arterial blood pressure |
|
|
|
120 -139 / 80-89 |
Prehypertension range |
|
|
|
140-149 / 90-99 |
Stage 1 hypertension range |
|
|
|
>160 / >100 |
Stage 2 hypertension range |
|
|
|
Hypotension |
Abnormally low blood pressure |
|
|
|
<95 / <60 |
Hypotension range |
|
|
|
<120 / <80 |
Normal blood pressure |
|
|
|
Oxygen therapy |
Also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as a medical treatment |
|
|
|
Hypoxemia |
Decreased oxygen concentration in the blood |
|
|
|
Hypoxia |
Reduction of oxygen supply in the tissue |
|
|
|
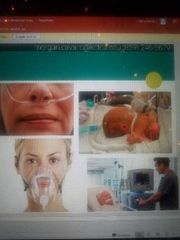
Nasal cannula Masks Tent and Oxyhood Ventilators |
Types of oxygen devices |
|
|
|
Endotracheal tubes |
Used to manage a variety of respiratory complications |
|
|
|
Intubation |
Insertion of a tubular device into a canal, Hollow organ, or cavity |

|
|
|
Atelectasis |
Absence of gas from part or the whole of the lungs, as a result of failure of expansion or reabsorption of gas from the alveoli |
|
|
|
Thoracostomy tubes |
AKA chest tubes, are used to drain the intrapleural space and the mediastinum |
|
|
|
Pneumothorax |
Presence of air or gas in the pleural cavity |
|
|
|
Pleural effusion |
Increased amounts of fluid within the pleural cavity, usually the result of inflammation |
|
|
|
Central venous lines |
Catheters that are inserted into a large vein. ____ are used to administer a variety of drugs, manage fluid volume, serve as a conduit for blood analysis and transfusions, and monitor cardiac pressures |
|
|
|
Cardiac output |
Amount of blood ejected from the ventricles each minute. Calculated as the product of stroke volume times heart rate |
|
|
|
Electrocardiogram |
Device used to assess the heart's ability to perform its vital function of producing adequate cardiac output |
|
|
|
EKG |
Abbreviated term commonly used to describe the electrocardiogram, based on the Greek term kardia meaning heart |
|
|
|
ECG |
Abbreviated term commonly used to describe the electrocardiogram, based on the English term cardia meaning heart |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle |
Events that occur from the beginning of the ventricle contraction (systole) until the beginning of another |
|
|
|
Arrhythmia |
Irregularity of cardiac actions associated with physiologic or pathologic interruptions of the neuro conductive tissues of the heart (AKA dysrhythmia) |
|
|
|
Depolarization |
Myocardial cells are stimulated to contract |
|
|
|
Repolarization |
Myocardial cells relax |
|
|
|
Automaticity |
Process whereby cardiac cell membrane spontaneously depolarize at recurrent periods |
|
|
|
Action potential |
Processes of depolarization and repolarization of the cardiac membrane 1. The resting cell membrane is positively charged on the outside and negatively charged on the inside 2. After stimulation, positive ions enter the cell, reversing this polarity 3. This process continues until the entire cell membrane is depolarized 4. Ions return to their normal location, and the cell repolarizes to its normal resting potential |
|
|
|
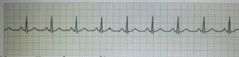
Normal electrocardiogram |
|
|
|
|
Sinus Bradycardia |
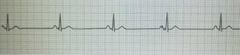
|
|
|
|
Sinus Tachycardia |
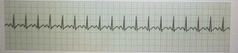
|
|
|
|
Atrial Fibrillation |
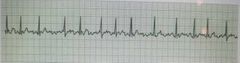
|
|
|
|
Ventricular Fibrillation |
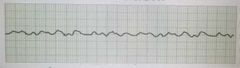
|
|
|
|
Asystole |
|
|
|
|
Fibrillation |
Quivering contraction of the cardiac muscle fibers |
|
|
|
Asystole |
There is no evidence of any cardiac neuro conductive activity (full cardiac arrest) |
|
|
|
Cardiac pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) |
Implantable device used to treat arrhythmias and often bradycardia |
|
|
|
Atria depolarization |

P wave |
|
|
|
Ventricle depolarization |
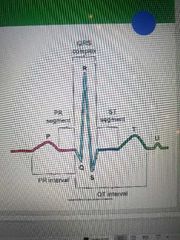
Q wave |
|
|
|
Ventricle repolarization |
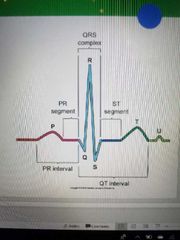
T wave |
|

