![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Km
|
Michaelis constant
The concentration of substrate at Vmax/2 |
|
|
Allostery
|
Multiple binding sites
|
|
|
Apparent Km for allosteric enzymes
|
?
|
|
|
What are the four methods of enzyme regulation?
|
Allosteric modulation
Covalent Modification Activation of Zymogens Control of gene expression (steroid hormones in mammals; operons in bacteria. |
|
|
As a molecule becomes more oxidized, what happens to its energy?
|
Its energy goes down.
Energy is used in oxidizing things. (Trees burning) |
|
|
Does serine have an OH group?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
What are committed steps?
|
Steps in a reaction that cannot be reversed. It is the 'point of no return.'
|
|
|
What is the michaelis menten equation?
|
Ko = Vmax[S]/Km +[S]
|
|
|
Allosteric modulators act by changing the apparent km of an enzyme for it's substrate. True or False
|
I don't know
|
|
|
Isozymes
|
Enzymes that catalyze the same reaction, but differ in structure.
|
|
|
What does a kinase do?
What does a phosphatase do? |
Phosphorylates a molecule.
Dephosphorylates a molecule. |
|
|
What enzyme activates trypsinogen to trypsin?
What enzyme activates prolipase to lipase, chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin, proelastase to elastase, procarboxypeptidase to carboxypeptidase? |
Enteropeptidase
Trypsin |
|
|
What are the differences between andoses and ketoses?
1. Andoses 2. Ketoses |
1.
|
|
|
True or False:
The letters D or L indicate direction of plane polarized light rotation |
FALSE
|
|
|
How do you know the number of stereoisomers of a compound?
|
2 to the n
n = chiral centers |
|
|
What is the structure of pyran?
|
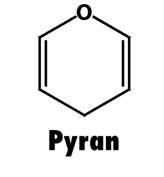
|
|
|
What is the structure of furan?
|

|
|
|
What is an epimer?
|
A diastereomer that differs in respect to only one stereogenic center.
|
|
|
Anomeric carbon
|
Carbon at changing stereogenic center of epimer. In cyclic saccharides - the carbon the alpha or beta oxygen is attached to.
|
|
|
Glycosidic bonds
|
Ethers - link sugar molecules together
|
|
|
What are the structures of sucrose, maltose, and lactose?
|
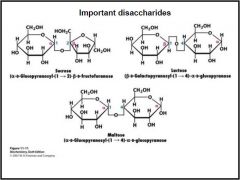
|
|
|
Homopolysaccharides or homoglycans
|
Same repeating sugar unit
|
|
|
Heteropolysaccharides or heteroglycans
|
alternating sugars
|
|
|
What is the storage form of glucose in animals?
What is the storage form of glucose in plants? |
Glycogen
Starch |
|
|
Which type of starch is unbranched?
Which type of starch is branched? |
Amylose. alpha 1-4 linkages
Amylopectin. alpha 1-4 linkages, alpha 1-6 linkages. An alpha 1- linkage for every 30 alpha 1-4 linkages. |
|
|
What are some differences between glycogen and amylopectin?
1. Glycogen 2. Amylopectin |
1. alpha 1-6 linkage every 8-12 alpha 1-4 linkage, so more branched. Storage form of animals.
2. alpha 1-6 linkage every 12-20 alpha 1-4 linkage. Storage form of plants. |
|
|
Which has more glucose units, glycogen or amylopectin?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
1. Reducing end
2. Non-reducing end |
1. The first glucose in a glycogen chain. It has a free aldehyde.
2. The end of a branch on a glycogen molecule. Can react because carbon one is involved with glycosidic bond. |
|
|
What is a name for glycosaminoglycan-protein complexes?
|
Proteoglycans
|
|
|
What are glycosaminoglycans?
|
Unbranched heteroglycans of repeating dissaccharides.
Contains many sulfated hydroxyl and amino groups. Dissacharide components consist of an amino sugar (D-galactosamine or D - glucosamine) and alduronic acid |
|
|
How do proteoglycans provide cushioning?
|
negatively charged GAG's attract water. When tissue is compressed, water is squeezed out, cushioning impact. When compression is released, water rebinds.
|
|
|
Structure of proteoglycan from cartilage.
|
Backbone is hyaluronan, a GAG. Non-covalently bonded to it are multiple proteoglycans called Aggrecan. Aggrecan consists of 3 globular protein domains, and GAG's in between domains two and three. The two GAG's are keratin sulfate and chondroitin sulfate.
|
|
|
Glycoproteins
1. definition 2. kind of linkages 3. Do oligosaccharides have great variability in their makeup? 4. Glycoforms |
1. Proteins that contain covalently bound oligosaccharides.
2. O-glycosidic and N-glycosidic linkages 3. Yes. 4. Glycoproteins that have the same amino acid sequence but different oligosaccharide chain composition. |
|
|
What enzyme catalyzes the the formation of the glycosidic bonds that link monosaccharides?
|
Glycosyltransferases
|
|
|
Blood groups:
1. These catalyze the addition of monosaccharides 2. The A group addition, its enzyme 3. The B group addition, its enzyme 4. The O phenotype occurs because |
1. Glycosyltranferases
2. N-acetylgalactosamine, A type glycosyltransferase 3. Galactose, B type glycosyltransferase 4. it is the result of a mutation that prevents synthesis of type A and B glycosyltransferase. |
|
|
Sugars in glycoproteins are attached in two ways:
1. 2. |
1. the side chain of asparagine to the amide nitrogen, termed an N-linkage.
2. the side chain of serine to the oxygen, termed an O linkage. |
|
|
Where does N linked glycosylation occur?
Where does O linked glycosylation occur? |
Starts in the ER, continues in the golgi apparatus
Exclusively in the Golgi apparatus |
|
|
Peptidoglycans
1. Definition 2. Major component of 3. what is the heteroglycan composed of? 4. What kind of linkages for the sugar units? 5. Penicillin destroys complex by... 6. Lysozyme destroys complex by... |
1. Heteroglycan chains linked to peptides
2. bacterial cell walls 3. alternating GlcNAc and MurNAc 4. B-1-4 5. preventing cross linking of peptides. 6. hydrolyzes polysaccharide |
|
|
Cell wall structure:
1. Sugar portion 2. Pentapeptide 3. Tetrapeptide |
1. Alternating N-acetylglucosamine residue and N-acetylmuramic residue
2. Five glycine residues. Runs below the plane of the sugar and tetrapeptides 3. Amino acid residues. |
|
|
Cross linking of peptides, and prevention
1. Mechanism of peptidoglycan cross linking 2. Catalyzed by 3. Penicillin action |
1. Normally, terminal glycine residue of glycine attacks peptide bond between two D alanine residues in another peptide unit.
2. Glycopeptide transpeptidase 3. Mimics the transition state of R-D-ala-D-ala. Highly reactive peptide bond in beta lactam ring is attacked by the hydroxyl group of serine of glycopeptide transpeptidase. Because peptidase deactivates itself, penicillin acts as a suicide inhibitor. |
|
|
Properties of polysaccharides
|
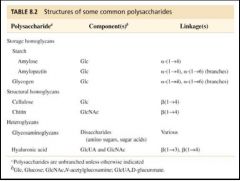
|
|
|
How do you convert alpha anomer to beta anomer? IN a pyranose (like mannose)
|
The linkage is broken to form the open form. Rotation occurs around the c1 and c2 bond. A mixture of isomers results.
|
|
|
Fructose can occur in which two forms?
Heating causes what to happen? |
B-D-pyranose form
B-D-furanose form heat causes the pyranose form to convert to the more stable but less sweet furanose form. |
|
|
What is the purpose of fat? What molecules can be converted into it?
|
Primarily storage. Any molecules can be.
|
|
|
Name the fatty acid with 18 carbons.
Name the fatty acid with 18 carbons and a double bound. Name the fatty acid with 18 carbons and two double bonds. |
Octadecanoic acid.
Octadecenoic acid. Octadecdienoic acid |
|
|
The notation 18:0 describes
The notation 18:1 describes |
Fatty acid with 18 carbons, no double bonds
Fatty acid with 18 carbons, one double bond |
|
|
Do fatty acids contain an even or odd number of carbon atoms?
|
Even number. They are usually synthesized two carbons at a time.
|
|
|
What is the storage form of fatty acids? of oil?
|
Triacylglycerol
|
|
|
What are the three major kind of membrane lipids?
|
Phospholipids
Glycolipids Cholesterol |
|
|
A phospholipid molecule is constructed of four types of molecules:
|
Fatty Acids
Glycerol or Sphingosine Phosphate Alcohol |
|
|
Phospholipids derived from glycerol are called
What is the simplest of the above category? |
phosphoglycerides
phosphatidate |
|
|
What are the five common alcohol moieties of phosphoglycerides?
|
Serine
Ethanolamine Glycerol Choline Inositol Which make Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylinositol |
|
|
Sphingomyelin
1. What is the backbone here? 2. What is the structure of the backbone? 3. How is the fatty acid linked to the backbone? 4. What is the primary hydroxyl group attached to? |
1. Sphingosine
2. Amino alcohol with long, unsaturated carbon chain. 3. By an amide bond 4. phosphorylcholine group by an ester linkage |
|
|
Glycolipids
1. Definition 2. Derived from what, in animal cells? 3. How are they similar to sphingomyelin? 4. How are they different than sphingomyelin? 5. An example? 6. What orientation in the cell? |
1. Sugar containing lipids
2. Sphingosine 3. Sphingosine attached to fatty acid by amide bond 4. Instead of attaching to a phosphorylcholine, it is attached to a sugar unit 5. Cerebroside 6. Extracellular side of the membrane |
|
|
The Km of an enzyme is around the intracellular concentration of its substrate. True or false
|
True
|
|
|
Cosubstrates are recycled/reused by other enzymes, true or false
|
True
|
|
|
What is the anomeric carbon in a sugar?
|
The carbon attached to the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal/hemiketal version of the sugar
|
|
|
Chitin and cellulose are different in that:
|
Chitin contains amino sugars
|
|
|
What is the difference between glycoproteins and gangliosides?
|
Gangliosides are always membrane component. Glycoproteins may or may not be associated with the membrane
|
|
|
Do sphingomyelins contain glycerol?
|
Nooo. Has a different backbone.
|
|
|
What does phospholipase cleave?
|
ester linkage between acyl group and fatty acid
releases fatty acid from phospholipid |
|
|
What is the difference between the glycoproteins, cerebroside and ganglioside?
|
Ganglioside has branched polysaccharides
|
|
|
Typical percentage of proteins to lipids in membranes
|
60% to 40%
|
|
|
Above phase transition temperature:
|
membrane becomes thinner
more fluid/ |
|
|
How does lysozyme work?
|
By hydrolyzing the glycosidic bond
|

