![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diels-Alder Reaction |
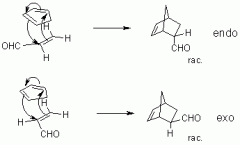
|
|
|
Amino Acids make up ____% of the human body (excluding water) |
75 |
|
|
Amino Acid Functions |
-95% of hormones -100% of proteins -Energy generation -Neurotransmitters -Nitric Oxide (NO) production -MSG - Monosodium glutamate -Nutritional Supplements -Drugs |
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia: approximately ____ US births/yr |
2000 |
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia: approximately ____ US citizens have it |
2 million |
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia: mutation of _____ to _____ in the ______ _______. |
Glutamate, Valine, Hemoglobin, Beta-chain |
|
|
Glutamate is _______ while Valine is _________. |
hydrophilic, hydrophobic |
|
|
Amino acid structure |
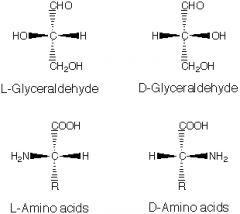
|
|
|
The chiral carbon in an amino acid is the _______ |
alpha-carbon |
|
|
Only _____ amino acids are found in proteins. |
L-configuration |
|
|
Atomic priority (chirality) |
I > Br > Cl > S > O > N > C > H |
|
|
Amphoteric |
Contains acidic and basic groups |
|
|
At pH __ amino acids form a _____ ion |
7, dipolar (zwitterion) |
|
|
The acidic group of an amino acid |
COO- |
|
|
The basic group of an amino acid |
NH3+ |
|
|
At a low pH, both amino acid groups are ________ |
protonated |
|
|
At a high pH, both amino acid groups are ______ |
deprotonated |
|
|
At a low pH, the amino acid has a net _____ charge |
positive |
|
|
At a high pH, the amino acid has a net ______ charge |
negative |
|
|
the L and D configurations are called |
stereoisomers |
|
|
Properties of Amino Acids |
-Size -Charge -Hydrophilicity -Hydrophobicity -Hydrogen-bonding capacity -Side-chain reactivity |
|
|
The pKa of the carboxyl group of amino acids |
2.2 |
|
|
The pKa of the amino group of amino acids |
9.4 |
|
|
Families of Amino Acids |
-acidic -basic -uncharged polar -nonpolar |
|
|
Glycine |
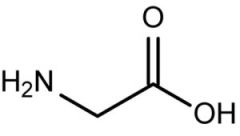
(Gly, G) Nonpolar |
|
|
Alanine |
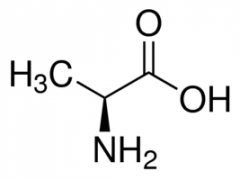
(Ala, A) Nonpolar |
|
|
AA with simple nonpolar side chains: |
Glycine, Alanine |
|
|
AA with complex nonpolar side chains: |
Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine |
|
|
AA with cyclic side chain |
Proline |
|
|
AA with nonpolar side chains: |
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Cysteine |
|
|
Valine |
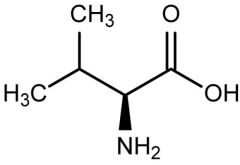
(Val, V) Nonpolar |
|
|
Leucine |
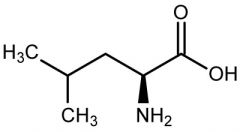
(Leu, L) Nonpolar |
|
|
Isoleucine |
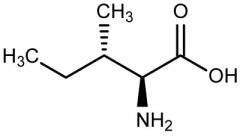
(Ile, I) Nonpolar |
|
|
Methionine |
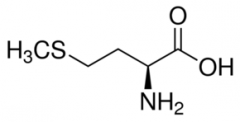
(Met, M) Nonpolar |
|
|
Proline |
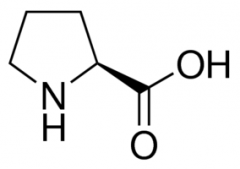
(Pro, P) Nonpolar |
|
|
AA with aromatic nonpolar side chains: |
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan |
|
|
Phenylalanine |
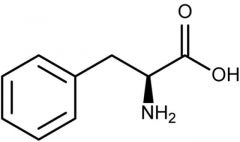
(Phe, F) Nonpolar |
|
|
Tyrosine |
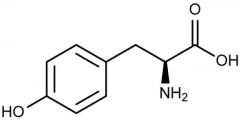
(Tyr, Y) Nonpolar |
|
|
Tryptophan |
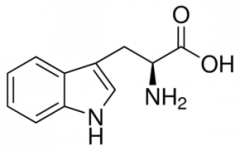
(Trp, W) Polar |
|
|
AA with uncharged polar side chains |
Serine, Threonine, Asparagine, Glutamate, Tyrosine |
|
|
Serine |
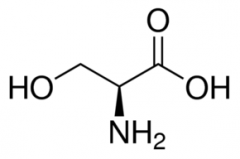
(Ser, S) Uncharged Polar |
|
|
Threonine |
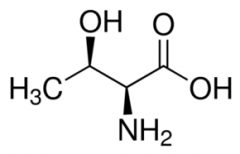
(Thr, T) Uncharged Polar |
|
|
Cysteine |
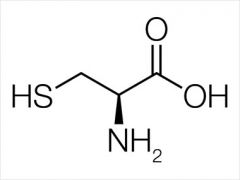
(Cys, C) Nonpolar |
|
|
AA with positive polar side chains |
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine |
|
|
Ionization of histidine |
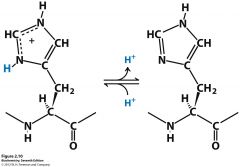
|
|
|
Lysine |
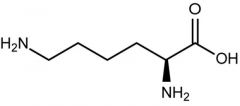
NH3 with + charge
(Lys, K) Positive Polar |
|
|
Arginine |
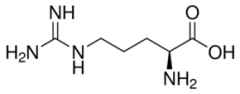
Partial double bond between double bond to N's with positive charge on carbon (Arg, R) Positive Polar |
|
|
Histidine |
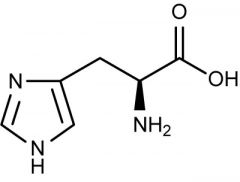
(His, H) Positive Polar |
|
|
AA with Polar negative side chains: |
Aspartate (Aspartic Acid), Glutamate (Glutamic Acid) |
|
|
Acidic Amino Acids: |
Aspartate (Aspartic Acid), Glutamate (Glutamic Acid) |
|
|
Asparagine |
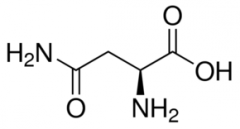
(Asn, N) Uncharged Polar |
|
|
Glutamine |
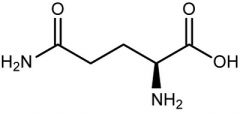
(Gln, Q) Uncharged Polar |
|
|
Aspartate (Aspartic Acid) |
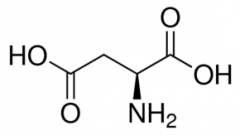
Partial double bond between O's (no H) with negative charge (Asp, D) Negative Polar |
|
|
Glutamate (Glutamic Acid) |
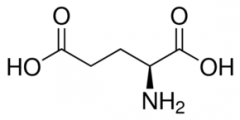
Partial double bond between O's (no H) with negative charge
(Glu, E) Negative Polar |
|
|
AA with 2 Carbons |
Glycine |
|
|
AA with 3 Carbons |
Alanine, Serine, Cysteine |
|
|
AA with 4 Carbons |
Threonine, Aspartate, Asparagine |
|
|
AA with 5 Carbons |
Valine, Methionine, Proline, Glutamate, Glutamine |
|
|
AA with 6 Carbons |
Leucine, Isoleucine, Lysine, Arginine, Histidine |
|
|
AA with Sulfur in side chain |
Methionine, Cysteine |
|
|
AA with 9 carbons |
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine |
|
|
AA with 11 carbons |
Tryptophan |
|
|
AA with oxygen in side chain |
Tyrosine, Serine, Threonine, Aspartate, Glutamate, Asparagine, Glutamine |
|
|
AA with nitrogen in side chain |
Tryptophan, Lysine, Arginine, Histidine, Asparagine, Glutamine |
|
|
Asparagine or Aspartic Acid |
Asx, B |
|
|
Glutamine or Glutamic Acid |
Glx, Z |
|
|
pH = |
-log10[H+] |
|
|
pKa = |
-logKa=log(1/Ka) |
|
|
pKa of a _____ acid is the pH at which _____ |
weak, it is half dissociated |
|
|
Ka = |
([A-][H3O+])/([HA][H2O]) |
|
|
Buffers are: |
An acid base conjugate pair |
|
|
Buffer Function |
resist changes in pH |
|
|
Maximal buffering capacity occurs at ______ |
pH = to pKa |
|
|
at ___ pH unit above or below ____ the buffering capacity is ____ |
1, pKa, 10% |
|
|
major extracellular buffer system |
HCO3-/CO2 |
|
|
major intracellular buffer system |
H2PO4-/HPO42- |
|
|
intracellular buffering system pKa |
6.86 |
|
|
Henderson-Hasselbach Equation |
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]) |
|
|
Titration curve |
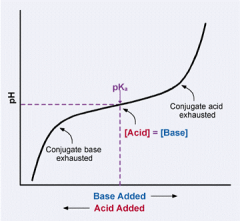
|
|
|
Amino Acids with 3 pKa |
Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid, Lysine, Arginine, Histidine |
|
|
Amino Acids with pKa2 above 10 |
Proline |
|
|
Amino Acids with pKa3 above 10 |
Lysine, Arginine |
|
|
Amino Acids with pI (isoelectric point) below 4 |
Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid |
|
|
Amino Acids with pI (isoelectric point) above 7 |
Histidine, Lysine, Arginine |
|
|
pKa1 refers to |
alpha-carboxyl group |
|
|
pKa2 refers to |
alpha-NH3+ ion |
|
|
pKa3 refers to |
side chain group |
|
|
Terminal alpha-carboxyl group pKa |
3.1 |
|
|
Terminal alpha-amino group pKa |
8.0 |
|
|
Typical pKa1 values for AA |
1.8-2.8 |
|
|
Typical pKa2 values for AA |
8.0-9.7 |
|
|
Typical pI values for AA |
5.0-6.5 |
|
|
Titration curve for Glycine |
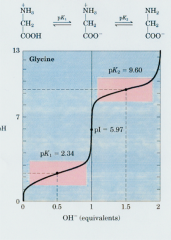
|
|
|
Isoelectric point (pI) |
pH which gives zero charge |
|
|
pI = |
(pK1+pK2)/2 |
|
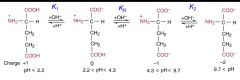
What is the pI of glutamic acid? |
pI = (pK1+pKR)/2 |
|
|
pKa can _____ in a protein due to the ______ |
vary greatly, environment |
|
|
Elution profile to determine amino acid composition (increasing pH) |
D T S E P G A C V M I L Y F K H NH3 R |
|
|
______ react with _____ to give a colorized product |
amines, ninhydrin |
|
|
ninhydrin can be used _______ or ________ |
qualitatively, quantitatively |
|
|
alpha-amino acids typically give a ______ product (reaction with ninhydrin) |
blue-purple |
|
|
_____ gives a ________ product (reaction with ninhydrin |
proline, yellow-orange |
|
|
ninhydrin can be used for visualization of _____ |
fingerprints |
|
|
ninhydrin reaction with amino acids |
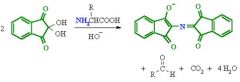
|
|
|
These amino acids absorb strongly near ______ |
280 nm, (Tryptophan, Tyrosine) |
|
|
Amino Acids can be detected and sequences using the ________ |
Edman degradation |
|
|
Labeling compound used in Edman Degradation |
Phenyl isothiocyanate |
|
|
Edman degradation |
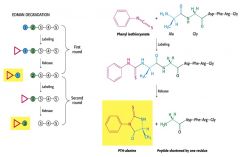
|
|
|
Edman Degradation: After labeling and release, ________ can be rapidly separated by ________ |
PTH-amino acids, high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) |
|
|
The linking of 2 amino acids is called a: |
peptide bond |
|
|
Peptide bond formation |
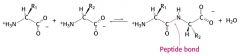
|
|
|
Peptides have a _______ terminus and a ______ terminus |
carboxyl, amino |
|
|
Polypeptide chain |
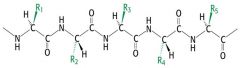
|
|
|
2 _____ residues can form a ________ bond |
cysteine, disulfide |
|
|
The formation of a disulfide bond is a _______ reaction |
oxidation |
|
|
Removal of a disulfide bond is a _______ reaction |
reduction |
|
|
Oxidation is the _____ of electrons |
loss |
|
|
Reduction is the _____ of electrons |
gain |
|
|
Disulfide bonds can link together two ______ or two _______ |
amino acids in one peptide, peptides |
|
|
Selenocysteine |
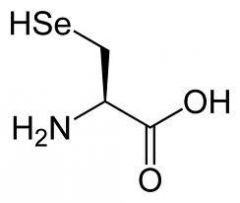
(Sec, U) Codon UGA |
|
|
Selenocysteine is present in _______ enzymes |
eukaryotic |
|
|
There are ______ selenoproteins in the human genome |
25 |
|
|
Selenium (Se) is a ______ in animals and humans |
vital nutrient |
|
|
Health effects of Selenium deficiency |
hypothyroidism, myocardial necrosis, cartilage degeneration |
|
|
Selenium is found in ______ (food) |
broccoli |
|
|
Pyrrolysine |
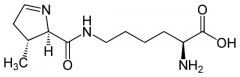
(Pyl, O) Codon UAG |
|
|
Pyrrolysine is found in proteins of _________ __________ |
methanogenic archaebacteria |
|
|
Non-protein Amino Acids |
5-Hydroxylysine, 4-Hydroxyproline, Ornithine, Penicillamine, Thyroxyine, GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), gamma-carboxyglutamic acid |
|
|
Non-protein amino acids in collagen |
5-Hydroxylysine, 4-Hydroxyproline |
|
|
Non-protein amino acid that plays a role in urea cycle |
ornithine |
|
|
non-protein amino acid used as a form of immunosuppression to treat arthritis |
penicillamine |
|
|
non-protein amino acid that is a major hormone secreted by thyroid |
thyroxyine |
|
|
non-protein amino acid that is a neurotransmittter |
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) |
|
|
non-protein amino acid that is found in blood clotting factors |
gamma-carboxyglutamic acid |
|
|
Formation of a peptide bond is a _____ reaction |
condensation |

