![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The organ in an animals body that is the primary site of extravascular hemolysis is the |
Spleen |
|
|
Which of the following is a reasonable number for RBC count in a horse? |
8,400,000 per microliter (cu mm) |
|
|
Maternal Ab obtained by foal from colostrum provide |
Passive immunity |
|
|
Which of these is produced through the breakdown of heme from old RBC's? |
Bilirubin |
|
|
Yellow bone marrow is composed primarily of |
Fat cells |
|
|
Where would you look for the thymus in a young animal? |
Cranial thorax |
|
|
One hemoglobin molecule can carry how many molecules of oxygen? |
4 |
|
|
An NRBC (nucleated RBC) is ______ a mature erythrocyte |
Less mature than |
|
|
A senescent erythrocyte is a/an _______ erythrocyte |
Aged |
|
|
When monocytes enter tissue they become |
Macrophages |
|
|
Polychromasia seen erythrocytes is a sign of -dehydration -immaturity -acid/base imbalance -cell death |
Immaturity |
|
|
If immature neutrophils are observed in peripheral blood, the condition is called a -leukopenia -left shift -right shift -leukemia |
Left shift |
|
|
The normal reference range for the hematocrit in an adult dog is 37%-55%. Allover, an adult Golden Retriever, has a hematocrit of 15%. This is an indication that Allover might |
Be anemic |
|
|
Cell mediated immunity is a function of -T lymphocytes -B lymphocytes -cytokines -neutrophils |
T lymphocytes |
|
|
The rate of erythropoietin is controlled by erythropoietin, which is a/an -hormone produced by the kidney -enzyme produced by the spleen -hormone produced by the spleen -enzyme produced by the kidney |
Hormone produced by the kidney |
|
|
What is true of vaccinations? -the provide passive immunity -the expose animal too antibody produced by the pathogen -the expose animal to antigen produced by the pathogen -the elicit only a non-specific immune response |
They expose animal to antigen produced by the pathogen |
|
|
Which organ is capable of storing blood that can be released into circulation when the animal needs it? |
Spleen |
|
|
Which mature blood cell is described as a non-nucleated biconcave disc? -monocyte -lymphocyte -thrombocyte -erythrocyte |
Erythrocyte |
|
|
Which set of vessels may contain one-way valves to prevent backflow? |
Veins and lymph vessels |
|
|
You would most likely see postprandial lipemia |
Shortly after an animal has eaten |
|
|
In a 3-year-old sheep most leukocyte production takes place in the |
red bone marrow |
|
|
Hematopoiesis is the formation of |
RBC's, WBC's and platelets |
|
|
Which of these is considered a PMN? -lymphocyte -monocyte -neutrophil -eosinophil |
Neutrophil |
|
|
Which of the following cells is most primitive? -megakaryoblast -pluripotential stem cell -megakaryocyte -unipotential stem cell |
Pluripotential stem cell |
|
|
Red blood cells normally mature in |
The bone marrow |
|
|
EDTA is a/an |
Anticoagulant |
|
|
Lymph from the digestive tract is called |
Chyle |
|
|
An irregular dark patch in skin or mucous membranes caused by hemorrhage -epistaxis -ecchymosis -thrombocytopenia -petechia -thrombopathia |
Ecchymosis |
|
|
Coagulation disorder due to abnormal platelet function -epistaxis-ecchymosis-thrombocytopenia-petechia-thrombopathia |
Thrombopathia |
|
|
Bleeding from the nose -epistaxis-ecchymosis-thrombocytopenia-petechia-thrombopathia |
Epistaxis |
|
|
Pinpoint red spots on mucous membranes or skin caused by submucosal or intradermal hemorrhage -epistaxis-ecchymosis-thrombocytopenia-petechia-thrombopathia |
Petechia |
|
|
Abnormally low number of platelets -epistaxis-ecchymosis-thrombocytopenia-petechia-thrombopathia |
Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
You are looking at a stained smear of horse blood and you see a leukocyte with large red granules in its cytoplasm. What cell are you most likely seeing? |
Eosinophil |
|
|
Stercobilinogen is a breakdown product of -globin -heme -amino acids -liver cells |
Heme |
|
|
Which of the leukocytes is most prevalent in sheep? -neutrophils -monocytes -lymphocytes -basophils |
Lymphocytes |
|
|
Which of these cells can become an Antigen Presenter Cell? -neutrophil -T lymphocyte -B lymphocyte -maceophage |
Macrophage |
|
|
There are 13 clotting factors. What is the minimum number of factors that can be deficient or absent and blood will still clot? |
0 |
|
|
Which of the following leukocytes will be found in large numbers at the site of a bite wound with bacterial contamination? -erythrocytes -B lymphocytes -basophils -neutrophils |
Neutrophils |
|
|
A megakaryocyte will eventually produce -erythrocytes -neutrophils -thrombocytes -monocytes |
Thrombocytes |
|
|
If an anticoagulant is used when collecting a blood sample, the fluid obtained from the sample after it has been centrifuged is |
Plasma |
|
|
Which vessel carries lymph into a lymph node? -afferent lymph vessel -thoracic duct -lymph artery -efferent lymph vessel |
Afferent lymph vessel |
|
|
The process by which neutrophils engulf invading foreign microorganisms is called |
Phagocytosis |
|
|
White blood cells use peripheral blood for |
Transportation |
|
|
Jaundice (icterus) could be a result of -decreased intravascular hemolysis -decreased amounts of conjugated bilirubin -excessive amounts of unconjugated bilirubin -excessive amounts of glucuronic acid |
Excessive amounts of unconjugated bilirubin |
|
|
This granulocyte's granules contain heparin -basophils -eosinophil -lymphocyte -neutrophil |
Basophil |
|
|
Along with tissue macrophages, which leukocytes make up the mononuclear phagocyte system? -eosinophils -monocytes -lymphocytes -neutrophils |
Monocytes |
|
|
During hemostasis which process occurs first? |
Platelet adhesion |
|
|
If you counted 95% neutrophils on a cow's differential white blood cells count and the normal range is 15% to 33%, this would be classified as a |
Neutrophilia |
|
|
Tonsils differ from lymph nodes in that they |
Are not encapsulated |
|
|
How many heme molecules are contained in one hemoglobin molecule? |
4 |
|
|
One antibody type has thousands of antigen receptors on its cell surface. How many types of antigens will typically fit these receptors? |
1 |
|
|
Which one of the following blood tests would measure the average size of an erythrocyte in a blood sample? -mean corpuscular hemoglobin conc -red cell distribution width -reticulocyte count -mean corpuscular volume |
Mean corpuscular volume |
|
|
The process by which blood is prevented from leaking out of damaged blood vessels is -hematocytosis -hemolysis -hematopoiesis -hemostasis |
Hemostasis |
|
|
The organ that is made up of white pulp and red pulp is the |
Spleen |
|
|
Mature platelets contain mitochondria but mature erythrocytes do not. Based on this information, which cell activities would you expect to occur in platelets but not erythrocytes? |
Aerobic respiration |
|
|
The lymph nodes caudal to the stifle are normally palpable in dogs.. these are the |
Popliteal l.n. |
|
|
An immature neutrophils with a horseshoe-shaped nucleus is called a |
Band cell |
|
|
Oxygen carried in a hemoglobin molecule is bound to a/an |
Iron atom |
|
|
Lymph passes through the ______ just before returning to blood circulation -pulmonary vein -portal vein -mesenteric artery -thoracic duct |
Thoracic duct |
|
|
What is the minimum number of nuclear lobes seen in a hypersegmented neutrophil? |
6 |
|
|
An example of an agranulocytic leukocyte is a/an -neutrophils -erythrocyte -lymphocyte -basophil |
Lymphocyte |
|
|
The PCV is determined using -whole blood with an anticoagulant added -whole blood with no anticoagulant -serum only -plasma only |
Whole blood with an anticoagulant added |
|
|
You have just identified large numbers of Ancylostoma caninum on a fecal exam on a sick puppy, so you are not surprised by this finding on the CBC -anemia -polycythemia -increased number of eosinophils -A & C |
A & C |
|
|
The process by which a neutrophil squeezes between the cells of the endothelium to leave a blood vessel and enter tissue is called |
Diapedesis |
|
|
The most common immunoglobulin produced after an animal has been exposed to a pathogen for a long time is -IgM -IgG -IgE -IgA |
IgG |
|
|
Any organism that is capable of causing disease is considered a/an |
Pathogen |
|
|
What type of immunologic cell can protect an animal from a pathogen after the animal's initial exposure and during a subsequent exposure? |
Memory B cell |
|
|
Natural killer cells are part of -the adaptive immune system only -the innate immune system only -both the innate and adaptive immune systems -not part of the immune system |
Both the innate and adaptive immune systems |
|
|
Helper T cells help the immune response by secreting ____ into the surrounding tissue -toxins -hydrogen peroxide -antibodies -cytokines |
Cytokines |
|
|
Adaptive immunity -is associated with erythrocytes -is nonspecific -is associated with memory cells -is quick to respond to an invading organism |
Is associated with memory cells |
|
|
An immunoglobin is also known as a/an |
Antibody |
|
|
External innate immunity depends on |
Intact skin |
|
|
An attenuated vaccine contains |
Modified live virus |
|
|
The innate immune system -is fast to respond to foreign invaders -develops as the animal matures -is dependent on the production of antibodies -discriminates against certain types of foreign invaders |
Is fast to respond to foreign invaders |
|
|
Transplacental antibody transfer from mother to fetus is an example of |
Passive immunity |
|
|
What cell is responsible for immunity against intracellular pathogens? -T lymphocytes -B lymphocytes -monocytes -plasma cells |
T lymphocytes |
|
|
Chemotaxis is the process of |
Attracting phagocytes to a site of injury |
|
|
When an animal receives a vaccine, about how long will it take before the animal's immune system will protect the animal from disease? |
2 weeks |
|
|
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia results from a Type ____ reaction |
Type II reaction |
|
|
An animal's first line of defense against potential disease-causing organisms is the |
Skin |
|
|
Another name for programmed cell death is caused by NK cells is |
Apoptosis |
|
|
Where on the animal would you look for the popliteal lymph node? |
Caudal aspect of the hamstring muscles |
|
|
The first immunoglobulin produced by newborn animals is |
IgM |
|
|
The complement system can alter a microbial cell membrane through a process of ______ that makes the microbe more 'visible' to a phagocyte -opsonization -exocytosis -chemotaxis -leukopoiesis |
Opsonization |
|
|
Which blood cells becomes a macrophage when it enters tissue? |
Monocyte |
|
|
If you see a lymphocyte on a stained blood smear, it is most likely what type of lymphocyte? -Kupffer cell -T cell -dendritic cell -B cell |
T cell |
|
|
Lysosomes in the cytoplasm of a phagocyte contain |
Digestive enzymes |
|
|
The type of hypersensitivity reaction that can be associated with a severe allergic reaction from a second exposure to an Antigen is |
Type I reaction |
|
|
The immunoglobulin that protects body surfaces such as mucosal surfaces from foreign microorganisms us -IgA -IgM -IgG -IgE |
IgA |
|
|
The type of cytokine that is produced by virus-infected cells and attaches to the cell membranes of nearby cells is a/an -interferon -chemokine -opsonin -interleukin |
Interferon |
|
|
The two most important functions of the complement system are to alter microbial cell membranes and |
Initiate an inflammatory response |
|
|
Where do T lymphocytes mature? -thymus -spleen -lymph nodes -thyroid |
Thymus |
|
|
A dendritic cell is a macrophage found in -liver -bone -lymph nodes -nerve tissue |
Lymph nodes |
|
|
What type of cell will inhibit helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells? |
Regulatory T cells |
|
|
The virulence of a pathogen refers to |
The relative strength of the pathogen |
|
|
What cell is responsible for production, storage, and release of antibodies? -T lymphocyte -B lymphocyte -parietal cell -plasma cell |
Plasma cell |
|
|
Which specific type of immunity is involved in antibody production? -cell-mediated -adaptive -humoral -innate |
Humoral immunity |
|
|
Redness, swelling, heat, and pain are the four cardinal signs of inflammation. A fifth sign that is frequently added is |
Loss of function |
|
|
The type of immunoglobulin produced through intranasal vaccination is |
IgA |
|
|
When an animal receives a vaccine, about how long will it take before the animal's immune system will protect the animal from disease? |
2 weeks |
|
|
Excessive numbers of chylomicrons in blood can cause -lipemia -hemodilution -leukopenia -hemolysis |
Lipemia |
|
|
What cell is responsible for immunity against intracellular pathogens? -T lymphocytes -monocytes -B lymphocytes -plasma cells |
T lymphocytes |
|
|
External innate immunity depends on |
Intact skin |
|
|
An attenuated vaccine contains |
Modified live virus |
|
|
Which valves produce the second heart sound when they snap shut? -aortic and mitral -tricuspid and pulmonary -pulmonary and aortic -mitral and tricuspid |
Pulmonary and aortic valves |
|
|
The right atrium pumps blood into the |
Right ventricle |
|
|
Cardiac output is determined by |
Stroke volume and heart rate |
|
|
Another name for the left atrioventricular valve is the |
Mitral valve |
|
|
Chordae tendineae are found in the -auricles -ventricles -interatrial septum -atria |
Ventricles |
|
|
Which is true of the pulmonary circulation? -it carries deoxygenated blood to the L atrium -it operates at a higher pressure than systemic circulation -blood coming from the pulmonary circulation enters the R atrium -none |
None |
|
|
Arterioles are |
Small muscular arteries |
|
|
The _____ represents the strength of a heartbeat |
Stroke volume |
|
|
The mediastinum -is the sac surrounding the heart -contains the heart, thymus, and other structures -is formed by an I folding of the parietal peritoneum -is the space containing the heart and lungs |
Contains the heart, thymus, and other structures |
|
|
Systolic blood pressure measures -the force by which blood is ejected from the left ventricle during systole -the force by which blood is ejected from the right ventricle during systole -the pressure remaining in the aorta during left ventricular diastole -the pressure remaining in the aorta during right ventricular diastole |
The force by which blood is ejected from the left ventricle during systole |
|
|
The fibrous sac that enclosed the heart is the |
Pericardium |
|
|
The apex of the heart is made up of the |
Wall of the left ventricle |
|
|
Diastolic blood pressure is -the pressure in the venous system -the pressure in the arteries just before the ventricles contract -the pressure in the arteries just after ventricles contract -the average pressure in the arteries and veins |
The pressure in the arteries just before the ventricles contract |
|
|
Which chamber of the heart sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation when it contracts? |
Right ventricle |
|
|
The heart is located in the thoracic cavity in the space between the two lungs. This space is called the |
Mediastinum |
|
|
Which of these would slow heart rate? -sympathetic stimulation -increased vagus nerve activity -release of epinephrine from the adrenal gland -all of the above |
Increased vagus nerve activity |
|
|
Which vein can be used for venipuncture in nearly all species of animals? |
Jugular vein |
|
|
The ductus arteriosus in a fetus allows blood to flow -directly into the ven cava from the pulmonary vein -directly from the left atrium into the right atrium -directly from the right atrium to the left atrium -directly into the aorta from the pulmonary artery |
Directly into the aorta from the pulmonary artery |
|
|
What type of muscle is found in the middle layer of a muscular artery's wall? -involuntary, striated muscle -involuntary, nonstriated muscle -voluntary, striated muscle -voluntary, nonstriated muscle |
Involuntary, nonstriated muscle |
|
|
Which diagnostic test is typically required for identifying arrhythmia? |
ECG |
|
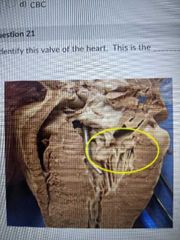
Identify this valve of the heart |
Mitral valve |
|
Blood found in this structure is oxygenated or deoxygenated? |
Oxygenated |
|
Blood found in this structure is oxygenated or deoxygenated? |
Deoxygenated |
|
Blood found in this structure is oxygenated or deoxygenated? |
Oxygenated |
|
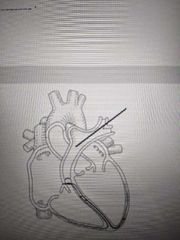
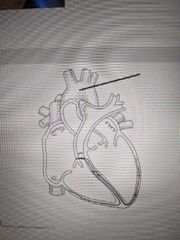
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Pulmonary artery |
|
|
The QRS complex on the ECG represents -atrial depolarization -ventricular repolarization -ventricular depolarization -nerve stimulation of the ventricles |
ventricular depolarization |
|
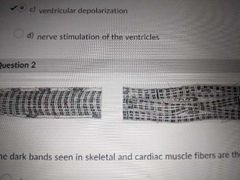
The dark bands seen in skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers are the |
A bands of sarcomeres |
|
|
The impulse created by the natural pacemaker of the heart travels |
Across both atria-atrioventricular septum-interventricular septum-heart apex-heart base |
|
|
Which of the following arteries is most commonly used to check the pulse on the cat? -mandibular -posterior digital -coccygeal -femoral |
Femoral artery |
|
|
The pulmonary circulation begins when deoxygenated blood passes through the ______ into the pulmonary circulation -mitral valve -tricuspid valve -left semilunar valve -right semilunar valve |
Right semilunar valve |
|
|
The largest elastic artery in an animals body is the |
Aorta |
|
|
Which of these is least likely to pass out of the capillaries and into the interstitial space? -water -calcium ions -glucose -albumin |
Albumin |
|
|
Cardiac muscle can generate its own contractions and relaxations and is therefore called |
Autorhythmic muscle |
|
|
The structures that make up the primary cardiac conduction, in order that the impulse travels through them, are the |
SA node-AV node-bundle of His-Purkinje fiber system |
|
|
Deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation enters the heart at the |
Right atrium |
|
|
A heart murmur is a sound produced by |
Turbulent blood flow |
|
|
Onan ECG reading of one cardiac cycle, the contraction of the main mass of the ventricles is represented by |
The R wave |
|
|
The majority of exchange of gases and nutrients between blood and tissue takes place at the ______ level |
Capillary bed |
|
|
Contraction of a heart chamber is called |
Systole |
|
|
The ductus arteriosus -is open in the fetus and closed in the adult -is closed in the fetus and open in the adult -allows blood to move from pulmonary vein to L atrium -A & C |
Is open in the fetus and closed in the adult |
|
|
Oxygenated blood is carried from the mother to a fetus through the -placental vein -umbilical vein -placental artery -umbilical artery |
Umbilical vein |
|
|
The type of blood vessel that usually carries oxygenated blood away from the heart is a/an |
Artery |
|
|
The atria of the heart sit at the _____ of the heart |
Base |
|
|
Which one of the following arteries is most commonly used to check the pulse on a horse? -coccygeal -aorta -mandibular -carotid |
Mandibular |
|
|
Another name for the right semilunar valve is the |
Pulmonary valve |
|
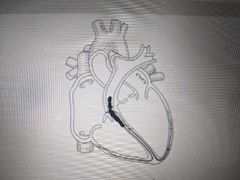
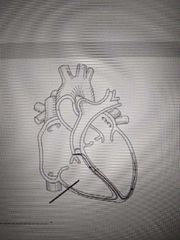
The picture shows blood passing through the ________ valve |
Pulmonary |
|
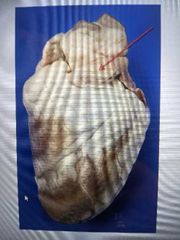
This vessel carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart. This is the |
Pulmonary artery |
|
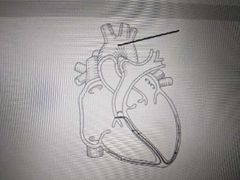
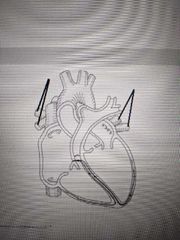
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Aorta |
|
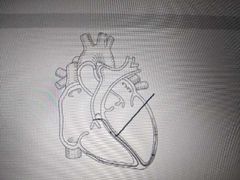
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Interventricular septum |
|
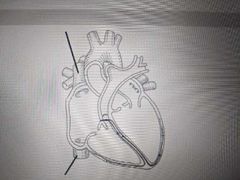
Blood found in this structure is oxygenated/deoxygenated |
Deoxygenated |
|
|
Which type of blood vessel has one-way valves in its lumen? |
Veins |
|
|
Tricuspid valve stenosis results when the tricuspid valve |
Doesn't open completely during a trial systole |
|
|
When looking at a standing animal from the side, you would locate the heart |
Between it's right and left olecranon processes |
|
|
The impulse to begin each heartbeat of the heart comes from the |
Sinoatrial node |
|
|
The interventricular septum is a continuation of the |
Interatrial septum |
|
|
In domestic animals, the _______ of the heart rests on the sternum |
Apex |
|
|
Resting membrane potential in nerve cells, the skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells is maintained by |
Sodium-potassium pump |
|
|
The interarterial septum is a continuation of the |
Myocardium |
|
|
The membrane that lines the chambers of the heart is the -endocardium -myocardium -pericardium -epicardium |
Endocardium |
|
|
The largest vein in an animals body is the |
Vena cava |
|
|
The natural pacemaker of the heart is the |
SA node |
|
|
Osmosis -causes solute to move down the concentration gradient -requires a semipermeable membrane -causes water to move from an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity |
B and C |
|
|
Which chamber of the heart sends oxygenated blood to systemic circulation when it contracts? |
Left ventricle |
|
|
A small amount of pericardial fluid is normally found in the pericardial space between |
The visceral pericardium and parietal pericardium |
|
|
The large blood vessel that brings deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation is the |
Vena cava |
|
|
Which of these vessels carries oxygenated blood? -caudal vena cava -femoral vein -pulmonary vein -pulmonary artery |
Pulmonary vein |
|
|
What event is associated with the first heart sound? - closing AV valves -opening AV valves -onset if diastole -atrial depolarization |
Closing AV valves |
|
|
The outermost layer of the heart itself is the |
Epicardium |
|
|
The inner layer of a blood vessel is the -epithelium -endocardium -endomysium -endothelium |
Endothelium |
|
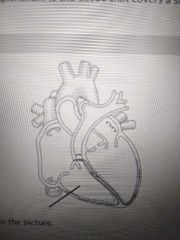
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Right ventricle |
|
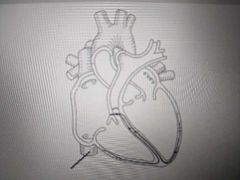
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Caudal vena cava |
|
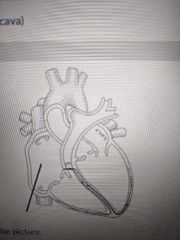
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Right atrium |
|
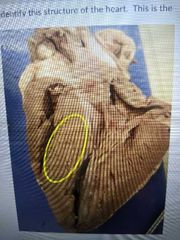
Identify this structure of the heart |
Interventricular septum |
|
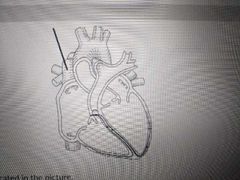
Name the structure indicated in the picture |
Cranial vena cava |

