![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the function of cornary arteries? Vessels? |
Arteries: supply the myocardium with blood Vessels: take the deoxygenated blood away from the myocardium |
|
|
What supplies the heart with fresh blood? |
left cornary artery, right cornary artery |
|
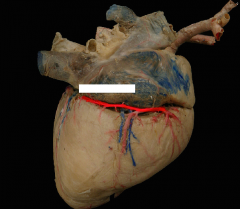
|
Right coronary artery. It encircles the right side of the heart in the coronary groove. It will often extend to the subsinosal interventricular groove VISIBLE FROM RIGHT SIDE |
|
|
What is the left coronary artery? |
A little stump that leaves the left sinus and immediately branches to form the circumflex branch and the paraconal interventricular branch. A final branch comes ff in the subsinuosal groove: the subsinuosal interventricular groove |
|
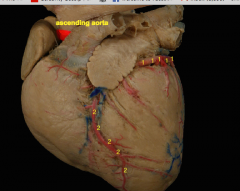
|
1= Circumflex branh of the lefrt coronary artery (lives in coronary groove) 2= paraconal interventricular branch of the l coronary artery (Lives in the paraconal groove) |
|
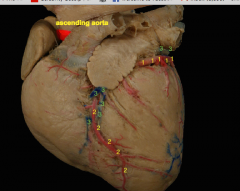
3 |
Great cardiac vein |
|
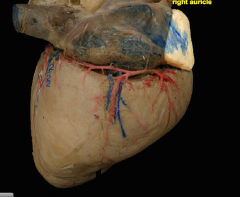
|
1 = subsinuosal artery (come off of the left coronary branch) 2= middle cardiac vein |
|
|
How does blood get into the atrium? |
Blood from the head comes in from the cranial vena cava Blood from the body comes from the caudal vena cava Blood from the heart comes in through the coronary sinus |
|
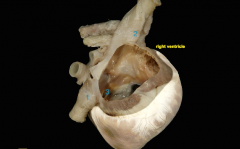
|
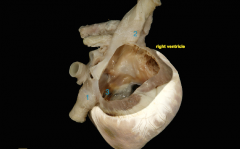
1. Caudal vena cava 2. Cranial vena cava 3. cornary sinus |
|
|
Trace the flow around the coronary arteries |
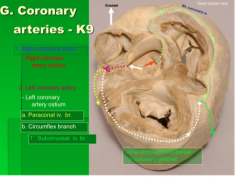
|
|
|
How does does the RA communicate with the rigth ventricle |
Right A-V value (tricuspid |
|
|
What happens to the great cardiac vein as it enters the right atrium? |
it loses its smooth muscle and becomes the coronary sinus |
|
|
GSE |
General somatic efferent motor |
|
|
GSA |
general somatic afferrent sensory |
|
|
How is the cervical region going to get sympathetic nerves? Is it going to jsut be piped into the spinal nerves |
NO NO NO NO NO NO NO. The Cervical nerves are autonomic deprived (they do not have either parasympathetic OR sympathetic). please figure this out |
|
|
Where does the verberbral nerve run |
It orginates at the cervicothoracic ganglion and runs with the vertebral artery _+figureoutwhere up |
|
|
What is unique about the thorcaolumbar region? |
Only region to have autonomics directly piped into their branches |
|
|
What is the tricky thing about nerve fibers? |
they can never split in go in two different directions. They have to pull a U turn. |
|
|
WHen stuff goes out of the ventral root of the thoracolumbar spinal cord what happens? |
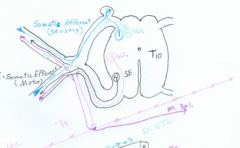
The SE travels on its own little happy logical route. Its the autonomic fibers that are tricky. They go through the spinal nerve with their friends but are worthless and must synapse before they can do anything.
They have the option of going down and synapsing very close to the spinal cord (in the sympathetic chain ganglion). OR IT CAN GO SOMEWHERE ELSE AND SYNAPSE THIS IS WHAT HAPPENS WITH THE CERVICAL REGION AND THE AUTONOMICS |
|
|
How does the cervical region get autonomics (FINAL ANSWER) |
T1-T3 has their preganglionic fibers travel to the cerivothoracic ganglion where they synapse. The entire post ganglionic nerve is called the vertebral nerve, it travels through the transverse foramen they will supply each cervical nerve |
|
|
What vertebrae's autonomic supply will be used to supply the head and neck? |
C8? (we dunno) - about T3 |
|
|
How does the vagus get down from the head? |
In the vagosympathetic trunk - you cannot separate them |
|
|
What happens to the vagus once it hits the thoracic inlet? |
It meets up with the sympathetic trunk via the ansa subclavia and the vagus nerve continues indepedently being just the vagus nerve (the sympathetic outputs go off and do their own thing leaving just the vagus) |
|
|
Where are the cell bodies for the vagus nerve? |
In the brain stem |
|
|
What is the main control of parasympathetic in all of the body? |
vagus = cranial nerve x |
|
|
How does the vagus get out of the brain? |
Carotid sheath |
|
|
What kind of imput is the vagus? |
general efferents |
|
|
What does the vagus supply? |
Thoracic and abdominal cavities |
|
|
What happens to the vagus as it hits the heart |
The left vagus at the level of the aortic arce the let recurrent laryngeal nerves leaves the vagus curvces medially arround the ligamentum and the arch of the aorta and goes back up. Here it reaches the larynx
The right vagus: the right recurent laryngeal nerve leaves bagus, curves around right subclavian artery and reaches the surface of the trachea.
each vagus nerve keeps trucking down the heart |
|
|
Where do vagal nerves synase on organ? |
inbetween the inner circular and outer longitudinal layers. The ganglionic cells of the myenteric plexus |
|
|
Where are the nerve cell bodies for the sympathetic system? |
In the grey horn |
|
|
What are gangalion? |
groups of cell bodies outside of spinal cord |
|
|
Where does the sympathetic trunk lie? |
ventral to the head of the ribs. At intercostal spaces T4 - L5 all of these ganglion are there *sympathetic) this allows fibers to synapse near the cord and then jump back into the branches |
|
|
What is the steallate/cervicothoracic ganglion |
A huge ganglion since so many fibers need to go to head and neck |
|
|
What happens to the vagus when it reaches the base of the heart |
The right splits into dorsal and ventral The left splits into dorsal and ventral
After about 2-3 cm the right and left dorsal branches join and the right and left ventral branches join forming new Dosral and ventral vagal trunks |
|
|
Who gets blood first? |
The heart |
|
|
Who gets blood second? |
The brain |
|
|
What defines the subclavian artery> |
When vessels come off the heart they are the brachiocephalic trunk. The first branch off is the common carotid artery. After this point it is the subclavian artery |

