![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
Study of structures of body and their relationships to one another |
|
|
|
Gross anatomy |
Large structures visible to the naked eye |
|
|
|
Sub divisions of gross anatomy |
1. Surface anatomy 2. Regional anatomy 3. Systemic anatomy |
|
|
|
Microscopic anatomy |
Small structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye |
|
|
|
Cytology (microscopic anatomy) |
Internal structures of cells |
|
|
|
Histology (microscopic anatomy) |
Structure and properties of a collection of cells (=tissues) |
|
|
|
Physiology |
-Study of function -How body structures work and carry out their vital activities -often at cellular level -requires knowledge of physics and chem |
|
|
|
Grand theme of Anatomy and physio |
Structure directly determines function |
A slight change in anatomy can have a significant effect on physiology |
|
|
Life processes |
Movement Growth Responsiveness Metabolism Differentiation Reproduction |
|
|
|
Levels of organization |
1. Chemical level 2. Cellular 3. Tissue 4. Organ 5. Organ system 6. Organism |
|
|
|
Levels of organization |
1. Chemical level 2. Cellular 3. Tissue 4. Organ 5. Organ system 6. Organism |
|
|
|
Chemical level (level of organization) |
Atoms combined to form molecules |
|
|
|
Cellular level (level of organization) |
Cells made of molecules |
|
|
|
Cellular level (level of organization) |
Cells made of molecules |
|
|
|
Tissue level (level of organization) |
Collection of same cells |
|
|
|
Organ level (level of organization) |
Made up of different types of tissues come together to form an organ |
|
|
|
Organ system (level of organization) |
Different organs that work together closely |
|
|
|
Organism (level of organization) |
Made up of many organ systems working together |
|
|
|
Body systems (11) |
1. Endocrine 2. Lymphatic 3. Respiratory 4. Cardiovascular 5. Nervous 6. Urinary 7. Skeletal 8. Muscle 9. Digestive 10. Integumentary 11. Reproduction |
|
|
|
Body systems |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
The internal environment of the body is in a dynamic state of equilibrium Mainly controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems |
|
|
|
Homeostatic control mechanisms |
1. Receptor 2. Control center 3. Effector |
|
|
|
Homeostatic control mechanisms variables are |
Something that changes |
|
|
|
Negative feedback |
End result is opposite of what started with -The output shuts off the original stimulus |
|
|
|
Positive feedback |
The output is adding onto the change that happened -output enhances original stimulus -needed for dangerous or stressful situations Ex) regulation of blood clotting |
|
|
|
Anatomical position |
Body react, feet parallel, slightly apart, arms to the side, palms facing forward, thumbs pointing away from body |
|
|
|
Supine |
Person laying down in anatomical position on posterior part of the body |
|
|
|
Supine |
Person laying down in anatomical position on posterior part of the body |
|
|
|
Prone |
Lying facedown on anterior part of body |
|
|
|
Superior |
Upper half of the body, towards the head |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Lower half of the body, towards the feet |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Back of the hands elbows and fingernails |
|
|
|
Anterior |
Palm of the hand |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Posterior of the body, the back |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Posterior of the body, the back |
|
|
|
Ventral |
Interior of the body, abdomen |
|
|
|
Deep |
Toward interior of the body |
|
|
|
Superficial |
Near surface of the body |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Directional term towards sides of body from the midline |
|
|
|
Medial |
Toward midline of the body |
|
|
|
Distal |
Moving from hip or shoulder down in arm or leg |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Move toward hip or shoulder on arm or leg |
|
|
|
Sectional anatomy (Different planes) |
-sagittal -midsagittal or medial -frontal or coronal -transverse (cross section) -oblique section |
|
|
|
Sectional anatomy (Different planes) |
-sagittal -midsagittal or medial -frontal or coronal -transverse (cross section) -oblique section |
|
|
|
Sagittal (sectional anatomy/planes) |
Cut through the body from front to back so there are right and left side |
|
|
|
Mid sagittal or medial (sectional anatomy/planes) |
Cutthrough medially, dividing body into EQUAL right or left halves |
|
|
|
Mid sagittal or medial (sectional anatomy/planes) |
Cut through medially, dividing body into EQUAL right or left halves |
|
|
|
Frontal or Coronal (sectional anatomy/planes) |
Through so there are front and back halves, result is a vertical plane |
|
|
|
Transverse (cross section) (sectional anatomy/planes) |
Cut across transversely |
|
|
|
Transverse (cross section) (sectional anatomy/planes) |
Cut across transversely |
|
|
|
Oblique section (sectional anatomy/planes) |
at an angle |
|
|
|
Regional landmarks |
Used by anatomists and clinicians to indicate a specific area of the abdominal or pelvic regions By Abdominopelvic regions Abdominopelvic quadrants |
|
|
|
Abdominalpelvic regions (9) |
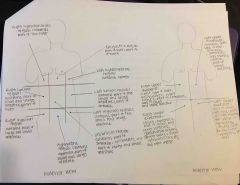
Umbilical, epigastric, hypogastric, right left hypochondriac, right left lumbar, right left iliac |
|
|
|
Organs in abdominopelvic regions |
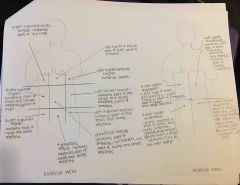
|
|
|
|
Organs in Abdominopelvic quadrants |
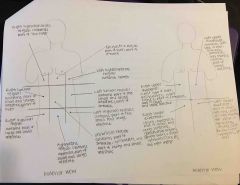
|
|
|
|
Right upper quadrant |
Liver, gallbladder, kidney, stomach, large and small intestine |
|
|
|
Left upper quadrant |
Liver, stomach, pancreas, kidney, spleen, portion of large intestine |
|
|
|
Right lower quadrant |
Cecum, appendix, small intestine, ovary, spermatic cord, right ureter |
|
|
|
Left lower quadrant |
Most of small intestine, large intestine, left ureter, ovary, spermatic cord |
|
|
|
Body cavities |
Cavities are spaces which are closed to the outside
Axial (head, neck, torso -no extremities) portion of the body has two large body cavities |
|
|
|
Two large body cavities |
Dorsal and ventral |
|
|
|
Two large body cavities |
Dorsal and ventral |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
-Protects central nervous system -Toward the back -contains two cavities |
|
|
|
Two large body cavities |
Dorsal and ventral |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
-Protects central nervous system -Toward the back -contains two cavities |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity - 2 cavities within |
Cranial cavity and Vertebral cavity |
|
|
|
Two large body cavities |
Dorsal and ventral |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
-Protects central nervous system -Toward the back -contains two cavities |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity - 2 cavities within |
Cranial cavity and Vertebral cavity |
|
|
|
Cranial cavity of the dorsal body cavity |
Contains the brain enclosed in the skull |
|
|
|
J |
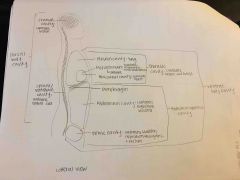
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Vertebral cavity within the dorsal body cavity |
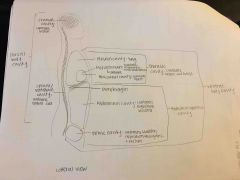
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Ventral body cavity |
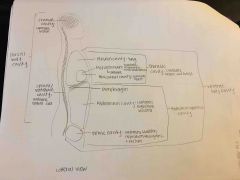
|
|
|
|
Ventral body cavities |
Thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
-Superior cavity -Surrounded by ribs, muscles, diaphragm |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity contains |
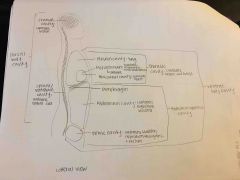
Right and left pleural cavity and mediastinum |
|
|
|
R/L pleural cavity |
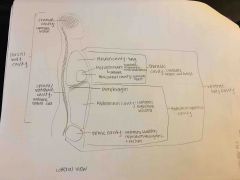
Contains lungs (sides of chest) |
|
|
|
Mediastinum |
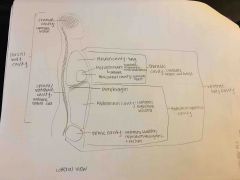
-Center of chest -Contains Pericardial cavity with heart, trachea, esophagus, and major blood vessels |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
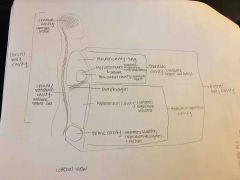
-Below the diaphragm -Enclosed abdominal wall and pelvis -Contains abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity (abdominal cavity of ventral body cavity) |
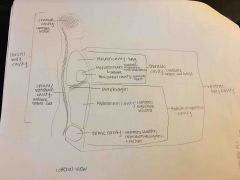
Contains digestive organs and spleen |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity (of abdominopelvic cavity of ventral body cavity) |
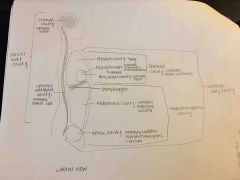
-More inferior, most inferior of torso -Enclosed by true pelvis, contains bladder, reproductive organs and rectum |
|
|
|
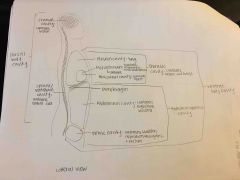
Body cavity summary |

|
|
|
|
Ventral body cavity summary |
Back (Definition) |
|

