![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
physical properties |
1. C=O is polar 2. bp higher than in alkanes 3. bp lower than alcohols/carboxylic acids 4. IR absorption = 1700 cm-1 |
|
|
aldehyde/ketone --> hemiacetal |
1. nucleophilic addition 2. alcohol, H2SO4 |
|
|
aldehyde/ketone --> acetal |
1. nucleophilic addition x2 2. [ alcohol, H2SO4 ] x 2
aldehyde/ketone --> hemiacetyl --> acetyl |
|
|
aldehyde/ketone --> hemiaminal |
1. nucleophilic addition 2. amine (primary or secondary) |
|
|
aldehyde/ketone --> imine |
1. nucleophilic addition x2 2. primary amine x 2
aldehyde/ketone --> hemiaminal --> imine |
|
|
aldehyde/ketone --> enamine |
1. nucleophilic addition x2 2. secondary amine x 2
aldehyde/ketone --> hemiaminal --> enamine |
|
|
halogenation |
halogen attached to the alpha carbon on a ketone/aldehyde |
|
|
ketone/aldehyde ---> haloform |
1. H20 (OH-) 2. result: halogenized ketone/aldehyde 3. H20 (OH-) 4. result: haloform + carboxylate |
|
|
aldol condensation |
acetaldehyde ---> aldol ----> condensed acidic alpha hydrogen |
|
|
acetaldehyde --> aldol --> condensed |
1. 2 acetaldehyde needed 2. OH- attacks one --> alpha H becomes H20 3. negative carbon attacks second acetylaldehyde 4. aldol 5. water leaves 6. condensed |
|
|
1,3 - dicarbonyl |
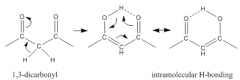
internal H-bonding |
|
|
tautomerism |
causes one of the carbonyls in 1,3 - dicarbonyl to switch to an enol |
|
|
enol form |
carbonyl with the alcohol |
|
|
keto form |
1. carbonyl with the ketone 2. more stable |
|
|
keto - enol tautomerism |

|
|
|
organometallic reagents |
1. Li or BuLi 2. make R- 3. purpose: to make carbon-carbon bonds |
|
|
Alkyl halide ----> organometal (R-Li) |
1. Li ; by-product: LiX OR 2. BuLi; by-product: Bu-X |
|
|
orangometal (R-Li) ----> alcohol |
carbonyl group |
|
|
Wolff-Kishner reaction |
1. reduces C=O to --CH2-- 2 carbonyl --> hydrozone --> diazene --> elemental nitrogen + alkane |
|
|
carbonyl --> alkane |
1. use Wolff-Kishner reaction 2. carbonyl --amine--> hydrozone --> diazene --H2O--> N2 + alkane |
|
|
Gringard reagents |
R--Mg--Br |
|
|
Gringard reaction |

|
|
|
alcohol/ketone ---> alcohol |
use Gringard reaction 1. HBr, R-Mg-X 2. result: alcohol + MgBr2 |
|
|
reactivity |
decreases with more substitutents |
|
|
alpha proton |
1. acidic 2. resulting carbanion is stabilized by resonance |
|
|
alpha, beta - unsaturated carbonyl |
1. resonance structure of beta carbonyl 2. nucleophilic attack on beta unsaturated carbonyl 3. tautomerizes the original carbonyl |

