![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Resistive Load |
pure power consuming load; voltage and current are in-phase and all Current produces real power |
|
|
|
Real Power |
Power as measured in Watts (or MW for the Bulk Electric System, or BES) |
|
|
|
Reactive Load |
A load that is either capacitive or inductive (as to say that these loads have high magnetic or electric fields) |
|
|
|
Inductive loads |
- Require VARs - Have components that produce a magnetic field, such as a motor |
|
|
|
In inductive loads, the current tends to _______ the voltage by an angle approaching 90° |
Current tends to lag voltage |
|
|
|
Capacitive Load |
- store energy in electric field - Source of VARs |
|
|
|
In capacitive loads, current tends to _______ voltage by an angle approaching 90° |
Current tends to lead voltage |
|
|
|
VARs |
Volt Amperes Reactive |
|
|
|
Inductive loads for MVAR control ... |
- Shunt Reactors - Static VAR Compensators - Loaded transmission lines - Transformers |
|
|
|
Capacitive loads for MVAR control... |
- Synchronous Condensers (unloaded, overexcited generators) - Shunt Capacitors - static VAR Compensators - Lightly loaded transmission lines - Transmission lines open at one end |
|
|
|
Power Triangle |
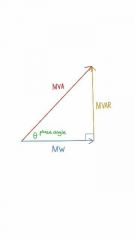
|
|
|
|
Power Factor |
cosine of the phase angle; the ratio of real power (MW) and apparent power (MVA) [pf = MW/MVA].Expressed as a decimal or multiplied by 100 to display a percentage. cosine of the phase angle; the ratio of real power (MW) and apparent power (MVA) [pf = MW/MVA].Expressed as a decimal or multiplied by 100 to display a percentage. |
|
|
|
Apparent Power |
Measured in Volt-amperes (VA); the mathematical Combination of Real & Reactive Power |
|
|
|
Phase Angle |
When one Waveform (current or voltage) leads or lags, or has some angular separation |
|
|
|
Voltage Angle |
Angular difference between a reference voltage sine Wave and another voltage sine wave. (is the phase angle between two voltages; is the same as the power angle and torque angle in a generator) |
|
|
|
Power Angle |
Voltage angle difference between two locations on the poWer system |
|
|
|
MVAR flow is generally from a ( higher / lower ) Voltage to a ( higher / lower ) voltage. |
higher to lower |
|
|
|
Three forms of dynamic reactive sources are... |
Generators, Synchronous Condensers, and Static VAR Compensators |
VAR-001 |
|
|
When you have a 200 mile long transmission line that is open ended with no reactors at the open end, the highest voltage will occur at the (1)_____ end due to the (2)______ rise effect. |
(1) open (2) Ferranti |
VAR-001 |
|
|
So long as power angles are less than (1)____ degrees, power will flow from the (2) higher/lower voltage magnitude to the (3) higher/lower voltage magnitude. |
(1) 10 (2) higher (3) lower |
TOP-004 |
|
|
If the frequency is exactly matched on both sides of an open breaker, then the phase angle across the breaker is... |
Constant.This does not indicate that the phase angle is zero , but that the angle difference that's present will remain constant. |
|
|
|
Line-to-ground voltage is equal to... |
(line-to-ground) / square root of three |
|
|
|
Line-to-line voltage is equal to... |
line-to-ground voltage x Square root of 3 |
|
|
|
Maintaining system frequency requires a balance between load and... |
Real power generation (MW) |
|
|
|
Maintaining system Voltage requires a balance between load and... |
Reactive power generation (MVAR) |
|

