![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Patients presents with dwarfism, short limbs, but head and trunk are normal size. What molecule is defective?
|
Achondroplasia
Defect in FGF receptor |
|
|
LoH, which disease manifests?
|
Rb = retinoblastoma
What is LoH? When there's a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene, the complementary allele must be deleted/mutated before cancer develops. |
|
|
Pt. presents with acute loss of central vision. Her mom had it too. What is disease mode of inheritence?
|
Dx. Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy
Mode of inheritence : Mitochondrial inheritance |
|
|
See genu varus, what is disease mode of inheritance?
|
Bow legged ==> Ricket's, so X-linked DOMINANT
|
|
|
Patients presents with dwarfism, short limbs, but head and trunk are normal size. What molecule is defective?
|
Dx: Achondroplasia
Defect in FGF receptor |
|
|
What is Be Wise Fool's GOLD Heeds Silly Hope?
|
X linked recessive disorders:
B= bruton's agammaglobinemia W= wiskott-aldrich ( triad: eczema, thrombocytopenia,immunodeficiency) F = Fabry's dz G = G6PD deficiency O = ocular albinism L = Lesch-Nyhann D = Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy HS = Hunter's Syndrome H = Hemophilia A and B |
|
|
What are the nucleotide repeats for the following trinucleotide repeat disorders?
1. Huntington's Disease 2. Myotonic Dystrophy 3. Fragile X syndrome 4. Friedrich's Ataxia |
1. CAG
2. CTG 3. CGG 4. GAA ( GAAAA, my ataxia!) |
|
|
What two diseases are Down's kids most likely to get?
|
1. ALL ( MAJOR $$)
2. Alzheimer's |
|
|
What are the findings in a Down's positive pregnancy screen?
|
A, B , E, I
down ,up, down, up alpha- feto protein ( AFP ) low Beta- hCG ( high) estriol ( low) inhibin A ( high) |
|
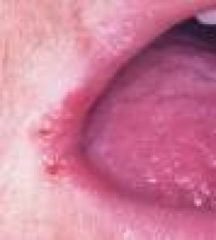
Patient presents with lesions on lips, and also corneal vascularizaiton. What vitamin is this person deficient in?
|
Vitamin B2
( B2, 2 syllables ( Ri-Bo), and 2 C's = Cheliosis and Corneal vascularization, FADH2**). |
|
|
Patient presents with skin lesions, diarrhea, and confusion. What amino acid is deficient?
|
Patient has pellagra
Niacin is deficient vitamin ( need tryptophan to make NAD+, NADP+ from niacin). Low Tryptophan absorption = Hartnup disease High metabolism of tryptophan = carcinoid syndrome (FA 302) Another cause could be INH, which blocks vitamin B6. B6 is necessary for the synthesis of niacin from tryptophan |
|
|
Patient presents with fatigue, + Schilling test, and see macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia. What enzyme is non-functional?
|
Dx: Pernicious anemia
Lack of IF, and lack of B12 B12 is Cofactor for Homocysteine methyltransferase. FA 92 |
|
|
What's the difference between megaloblastic anemias between B12 deficiency and Folate deficiency?
|
Folate deficiency has no NEURO symptoms. FA 92
|
|
|
Deficiency in Vit E, can cause demyelination in which part of the spinal cord?
|
posterior column and spinocerebellar tracts FA 93
|
|
|
Patient has AGMA, breath smells sweet, seems intoxicated. What is the antidote?
|
He has ethylene glycol poisoning
Antidote: Fomepizole |
|
|
Patient develops vomiting, has rice water stools, and a tinge of garlic smelling breath. The toxin suspected acts to block which factor?
|
Arsenic Poisoning:
Headache, confusion, diarhhea rice water stools, vomiting, lactic acidosis. Arsenic blocks Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex which has 3 enzymes, 5 cofactors: TPP- pyrophosphate ( B1- Thi) FAD ( B2- Ri-BO) NAD ( B3- NI- A- CIN) CoA ( B5- pantothenate) Lipoic acid Arsenic blocks LIPOIC ACID ( answer) |
|
|
How do you great PDH deficiency?
|
Increase intake of ketogenic amino acids:
( Lysine and Leucine) |
|
|
Patient has hx of hepatitis, he presents with tremor, slurred speech, vomiting, blurry vision. What is the treatment to alleviate his symptoms?
|
Dx:He has hyperammonemia
Sx: Tremor, slurred speech, somnolence, vomiting, cerebral edema, blurred vision Liver disease or Urea Cycle enzyme deficiency can cause this. Hyperammonemia increases NH4+ and depletes alpha-ketoglutarate, which blocks the TCA cycle Tx: Decrease protein intake, + Benzoate and phenylbutyrate to lower ammonia levels. |

