![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is urinary incontinence? |
1. Condition where involuntary urinary loss occurs 2. Result of a rise in intravesical pressure that exceeds intraurethral pressure in the absence of a bladder contraction |
|
|
What is the 2nd MCC of urinary incontinence? |
1. Detrusor instability |
|
|
What does abdominal pressure transmission to the urethra depend on? |
1. Support of proximal urethra from surrounding fibrous and muscular tissues |
|
|
What is mixed incontinence? |
1. Combined stress incontinence and detrusor instability |
|
|
What is overflow incontinence? |
1. Defect in urination causing the marked dissension of the bladder 2. Leads to leaking as the pressure eventually overrides an intact sphincter |
|
|
What is a urogenital fistula? |
1. Anatomical defect causing a tract between the urinary system and some other system |
|
|
What are the primary support structures of the urethra? |
1. Arcus tendineus fascia 2. Levator ani |
|
|
What is the MCC of damage to the fibromuscular support to the urethra? |
1. Pregnancy and vaginal delivery |
|
|
What are the MCC of detrusor hyperreflexia? |
1. MS 2. CVA 3. Spinal injuries or tumors 4. Congenital spinal cord abnormalities |
|
|
What should be included in a PE for incontinence? |
1. Lumbosacral neurologic evaluation 2. Urine culture 3. Measurement of residual urine 4. Assessment of urethral mobility |
|
|
What is the use of oral phenazopyridine in incontinence? |
1. Colors the urine orange 2. Can help patients distinguish between urine and vaginal fluids |
|
|
How can an estrogen deficiency contribute to incontinence? |
1. Urethra and trigone are estrogen dependent |
|
|
How can spinal cord lesions lead to genital prolapse? |
1. Can lead to detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia |
|
|
What dermatomes should you specifically test in genital prolapse? |
1. L2-S2 |
|
|
What genital reflex should you test in suspected prolapse? |
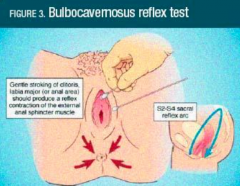
1. Bulbocavernosus reflex test |
|
|
How do you demonstrate the mobility of the urethra? |
1. Q-tip test |
|
|
How do you do the Q-tip test? |
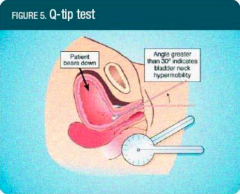
1. Measure resting and straining angles several times 2. Positive for urethral hypermobility when straining angle is >30-35 degrees |
|
|
Is flow pattern or peak flow more important when assessing incontinence? |
1. Flow pattern |
|
|
What are the MCC of intermittent flow patterns? |
1. Urethral atrophy 2. Inflammation 3. Pain 4. Fear |
|
|
What is eyeball cystometry? |
1. Self-retaining catheter is placed transurethrally 2. Bladder progressively filled by sterile water 50 mL at a time 3. Syringe held approximately 15 cm above patient's pubic bone 4. Ask patient 'when is the first strong urge to void?'
|
|
|
What suggests involuntary bladder contractions in eyeball cystometry? |
1. Rising meniscus |
|
|
How do you perform stress testing? |
1. Have patient cough to increase intra-abdominal pressure to reproduce stress incontinence 2. Urination with cough is positive |
|
|
What are the first-line tx for stress incontinence? |
1. Lifestyle--- weight loss, caffeine reduction, fluid management 2. Kegels 3. Biofeedback |
|
|
What are the surgical tx for stress incontinence? |
1. Tension-free transvaginal sling 2. Burch 3. MMK 4. Bulking procedures |
|
|
What is the non-pharmacologic tx for detrusor instability? |
1. Bladder re-training 2. Biofeedback |
|
|
What is the pharmacologic tx for detrusor instability? |
1. Anti-muscarinics-- M2 and M3 2. Tri-cyclic anti-depressants |
|
|
Where is a stress-free vaginal sling anchored? |
1. Obturator internus muscle |
|
|
What is a cystocele? |
1. Prolapse of the bladder |
|
|
What is a rectocele? |
1. Prolapse of the rectum |
|
|
How do you grade prolapses? |
1. Stage 0- no prolapse 2. Stage 1- Leading edge of the prolapse is greater than 1 cm above hymen 3. Stage 2- Leading edge is =/- 1 cm from hyemn 4. Stage III- More than 1 cm below hymen but not the total vaginal length 5. Stage IV- Complete eversion of the vagina |
|
|
What should a PE consist of for prolapse? |
1. Speculum exam 2. Urinary stress test after replacement of prolapse |
|
|
How do you medically tx prolapse? |
1. Pessary- non-surgical supportive or space occupying device to reduce prolapse
|
|
|
How do you surgically tx prolapse? |
1. Hysterectomy with re-suspension 2. Colporraphy |

