![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The gonads are structurally different by the ____ week of development; external genitalia by the ____ week of development.
|
gonads = 7th week of development
external genitalia = 12th week of development |
|
|
What female structures develop from the mullerian (akak parmesonephric) ducts?
|
The fallopian tubes, uterus, upper vagina.
The lower vagina develops from the sinovaginal bulbs of the urogenital sinus. |
|
|
The upper part of the vagina and the lower part of the vagina develop from different embryologic precursors. Which?
|
Upper vagina develops from the mullerian ducts (as does the fallopian tubes and uterus).
Lower vagina develops from the sinovaginal bulbs of the urogenital sinus. |
|
|
Skin incisions are cosmetically better if made along the lines of tension called __________.
|
Langer's lines
|
|
|
What are the components of the femoral triangle (anatomical landmarks to make the triangle itself) and what are contents found within the triangle?
|
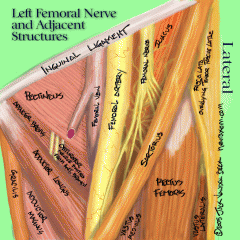
Anatomic boundaries: inguinal liagemtn (superiorly and medially), sartorius muscle (laterally), adductor longus muscle (medially).
Contents: from medial to lateral is "VAN" - femoral Vein, femoral Artery, and femoral Nerve. |
|
|
What are the components of the urogenital triangle? What are the components of the anal triangle?
|
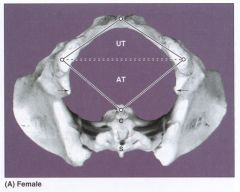
Urogenital triangle: ischial tuberosities and pubic symphysis
Anal triangle: ischial tuberosities and coccyx |
|
|
Regarding the clitoris, what is the :
A. supplying artery B. innervating nerve C. lymphatic drainage to |
Regarding the clitoris
A. artery: dorsal clitoral artery from the internal pudendal artery B. nerve: terminal branch of pudendal nerve C. lymphatics: primariliy to bilateral superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
|
|
True or False:
Bartholin glands are the sites of most adenocarcinomas of tue vulva. |
TRUE
|
|
|
True or False:
The vaginal canal is normally collapsed upon itself and is H-shaped in cross section. |
TRUE
|
|
|
Regarding the vagina, what is the
A. supplying artery B. innervating nerve C. lymphatic drainage to |
Regarding the vagina, what is the
A. supplying artery = vaginal artery (from internal iliac, sends branches to uterus and joins branches from uterine artery to form azygos artery of vagina) B. innervating nerve = uterovaginal portion of hypogastric plexus C. lymphatic drainage to = upper, middle portion of vagina drains to external internal and common iliac nodes. lowest portion of vagina drains to superficial inguinal nodes, vulvar drainage is to superficial inguinal nodes |
|
|
What do the following ligaments connect or specify where about the uterus they are located.
A. cardinal ligament B. uterosacral ligament C. broad ligament D. round ligament |
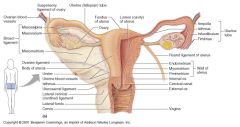
A. cardinal ligament: lateral condensations of endopelvic fascia that suspend cervix and lateral vaginal walls to the fascia overlying the sidewalls and levator ani
B. uterosacral ligament: posterior condensations of endopelvic fascia that suspend cervic by encircling upper cul de sac and attaching to deep fascia over sacrum C. broad ligament: attach fundus to fascia overlying pelvic sidewall musculature D. round ligament: fibrous cords that pass from superior lateral border of uterus beneath anterior surface of broad ligament thru inguinal ligaments to anchor in labia majora |
|
|
Which ligaments do what?
[ Broad , Cardinal, Round, Uterosacral ] A. Help prevent uterine and vaginal prolapse B. help keep fundus anterior and prevent prolapse C. stabilize uterus in transverse plane and contain uterine arteries |
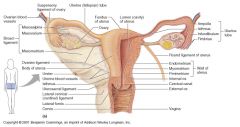
A. Help prevent uterine and vaginal prolapse = cardinal ligaments
B. help keep fundus anterior and prevent prolapse = uterosacral ligaments C. stabilize uterus in transverse plane and contain uterine arteries = broad ligament |
|
|
Regarding the cervix, what is the
A. supplying artery B. innervating nerve C. lymphatic drainage to |
Regarding the cervix, what is the
A. supplying artery: uterine from anterior division of internal iliac, lower portion B. innervating nerve: uterovaginal portion of hypogastric plexus C. lymphatic drainage to: cervix to external, internal, and common iliac nodes. |
|
|
Regarding the fallopian tubes, what is the
A. supplying artery B. innervating nerve C. lymphatic drainage to |
Regarding the fallopian tubes, what is the
A. supplying artery: branches from joining of ovaian adn uterine arteries B. innervating nerve: hypogastric and ovarian plexuses C. lymphatic drainage to: ovarian and uterine drainage |
|
|
Regarding the ovaries, what is the
A. supplying artery B. innervating nerve C. lymphatic drainage to |
Regarding the ovaries, what is the
A. supplying artery: ovarian arteries course in the infundibulopelvic ligament then anastamose with uterine arteries B. innervating nerve: from hypogastric and ovarian plexuses C. lymphatic drainage to: follow ovarian artery to enter lateral adn preaortic nodes Veins: bilateral pampiniform plexus to ovarian veins with R ovarian vein terminating in vena cava and L ovarian vein terminating in left renal vein |
|
|
Pelvic diaphragm is made of....
|
paired and posteriorly fused levator ani muscles with their superior and inferior fascia.
The most important structure providing support for the internal pelvic organs is this pelvic diaphragm. |
|
|
Regarding pregnancy changes of uterine enlargement, the fundus is palpable abdominally after ______ weeks of gestation.
|
10-12 weeks
|
|
|
Match the nerve injuries resulting from pelvic surgery.
1. Common peroneal 2. Sciatic A. due to entrapment of nerve by suture lateral to pubic tubercle, may cause pain in medial groin, labia or inner thigh B. due to hyperflexion of hips stretching nerve against medial aspect of knee may cause burning or aching pain in medial calf C. due to compression or direct injury at undersurface of pubic ramus may cause weakness of ipsilateral thigh adduction D. due to pressure against sciatic notch or stretching during hip flexion may cause weakness during knee flexion or loss of common peroneal or tibial nerve function E. due to compression between fibular neck and leg brace may cause foot drop |
1. common peroneal: E. due to compression between fibular neck and leg brace may cause foot drop
2. sciatic: D. due to pressure against sciatic notch or stretching during hip flexion may cause weakness during knee flexion or loss of common peroneal or tibial nerve function |
|
|
Match the nerve injuries resulting from pelvic surgery.
1. saphenous 2. obturator A. due to entrapment of nerve by suture lateral to pubic tubercle, may cause pain in medial groin, labia or inner thigh B. due to hyperflexion of hips stretching nerve against medial aspect of knee may cause burning or aching pain in medial calf C. due to compression or direct injury at undersurface of pubic ramus may cause weakness of ipsilateral thigh adduction D. due to pressure against sciatic notch or stretching during hip flexion may cause weakness during knee flexion or loss of common peroneal or tibial nerve function E. due to compression between fibular neck and leg brace may cause foot drop |
1. saphenous: B. due to hyperflexion of hips stretching nerve against medial aspect of knee may cause burning or aching pain in medial calf
2. obturator: C. due to compression or direct injury at undersurface of pubic ramus may cause weakness of ipsilateral thigh adduction |

