![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skin layers/stratums
|
Stratum corneum/granulosum/spinosum/basale | Dermis
|
|
|
skin immune defenses
|
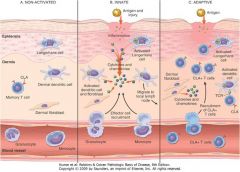
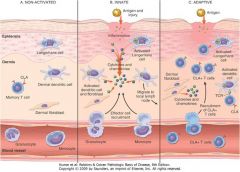
Barrier with innate defenses: salt, sebum, defensins, normal flora
Keratinocytes secrete proinflammatory (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-a) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-b) that modulate immune responses Antigen/injury causes recruitment of phagocytes (neutrophils, monocytes) and activation of dendritic cells (Langerhans cells* are dendritic cells of epidermis; other dendritic cells are also present in dermis), which travel to regional lymph nodes to initiate immune responses CLA+ effector and memory T cells (both CD4+ and CD8+) travel back to dermis to produce local adaptive cellular immune responses* |
|
|
CLA
|
Cutaneous lymphocyte associated antigen; molecule that directs these cells to "home" back to the skin
|
|
|
NK-T cells
|
share both NK and T cell characteristics (both innate and adaptive); express alpha beta TCR of limited diversity; some recognize lipid antigens
|
|
|
Wiskott Aldrich Syndrome
|
X-linked immunodeficiency; recurrent infections w encapsulated bacteria w thrombocytopenia and eczema;
WASP mutation so receptors on skin are defective; antibody responses poor (especially to polysaccharides); Progressive T cell loss pts develop EBV related B cell lymphoma (non Hodgkin), autoimmune dz, other cancers |
|
|
WASP
|
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein; links membrane receptors (ag receptors) to cytoskeleton; defective receptors/signaling
|
|
|
Hereditary angionerotic edema
|
Autosomal dominant C1 inhibitor deficiency (C1 INH, also known as serpin or C1 esterase inhibitor) binds to C1r and C1s and dissociates them from C1q thereby inhibiting their protease activity; C1 INH also inhibits coagulation (Factor XII) and kinin (kallikrein) systems
Unregulated activation leads to increase in vasoactive peptides (like bradykinin) Episodes of edema of skin (dermis and subcutaneous fat) and mucosal surfaces (larynx, GI tract)* after minor trauma or emotional stress Serum C3 levels usually normal; C4 levels usually decreased |
|
|
ataxia telangiectasia
|
Autosomal recessive defect in DNA repair (ATM gene)
Oculocutaneous telangiectasias and progressive cerebellar ataxia Moderate reduction in T cells with deficiency of IgA, IgE and some IgG subclasses* Radiation hypersensitivity causes extreme susceptibility to cancer |
|
|
Scleroderma
|
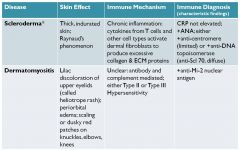
|
|
|
Dermatomyositis
|
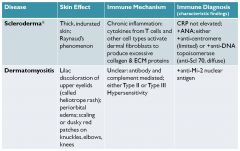
|
|
|
Discoid Lupus (often has skin problems)
|
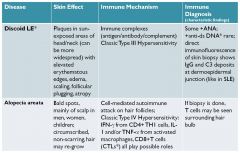
note direct immunofluoresence; antibodies deposited into skin
|
|
|
alopecia areata
|
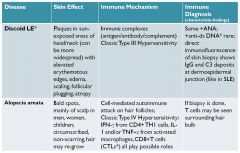
bald spots on scalp; type IV hypersensitivity
|
|
|
Pemphigus vulgaris
|
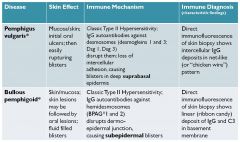
demosomes disrupted; lose intracellular adhesion; get blisters between the basal layer and dermis
|
|
|
bullous pemphigold
|
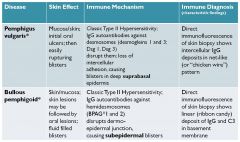
ab against hemidesmosomes; disruptes dermo-epidermal junction; the hemidesmosomes keep the two layers together so ab deposit along the layer junction
|
|
|
dermatitis herpatiformis
|
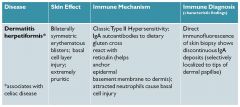
IgA ab cross rx with reticulin, which anchors epidermal basement membrane to dermis; only localized to tips of the dermal layer
|
|
|
lab findings in discoid LE vs SLE
|
+ANa and +anti-ds DNA more characteristic of SLE, less of DLE (+anti-ds DNA rare in DLE)
|
|
|
how does skin biopsy immunoflourescence in dLE compare with SLE
|
same
|
|
|
hypersensitivity type of DLE and SLE
|
Type III
|
|
|
Indirect immunofluroescence in DLE
|
blood draw to detect ANA in tissue
|
|
|
direct immunofluesence in DLE
|
detects IgG
|
|
|
atopic
|
tendency to be allergic; multifactorial causes of hypersensitivity to Type I reactions
|
|
|
Utricaria (hives)
|
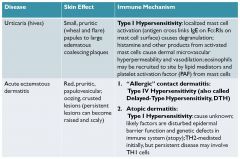
wheel and a bump; histamine and fluid in the bump; flare is red; vasodilation
|
|
|
acute eczematous dermatitis
|
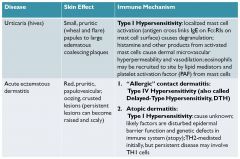
scarly raised red lesions;
classic: allergic contact dermatitis (type IV hypersensitivity/delayed tpe hypersensitivity) |
|
|
erythema multiforme
|
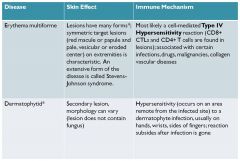
eroded center = target, on extremities, steven johnson syndrome = extreme form of dz; type IV hypersensitivity
|
|
|
dermatophytid
|
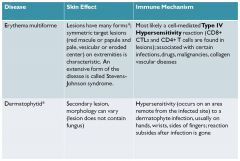
hypersensitivity to a fungal infection
|
|
|
Psoriasis
|
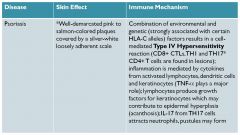
well demarcated pink to salmon colored plaques; environmental/genetic factors;
|
|
|
4-year-old Stephen was breast fed exclusively until 6 months of age when he received his first bottle of cow’s milk formula, at which time he immediately developed urticaria and wheezing. Specific IgE (sIgE) testing revealed sIgE of 12U/ml to cow’s milk and 0.01 U/ml to soya.
What are this patients food allergy symptoms? |
wheezing, utricarica
|
|
|
4-year-old Stephen was breast fed exclusively until 6 months of age when he received his first bottle of cow’s milk formula, at which time he immediately developed urticaria and wheezing. Specific IgE (sIgE) testing revealed sIgE of 12U/ml to cow’s milk and 0.01 U/ml to soya.
what type of T cell initiated this response |
CD4+ TH2 cells
|
|
|
4-year-old Stephen was breast fed exclusively until 6 months of age when he received his first bottle of cow’s milk formula, at which time he immediately developed urticaria and wheezing. Specific IgE (sIgE) testing revealed sIgE of 12U/ml to cow’s milk and 0.01 U/ml to soya.
activation of which cell type was responsibl efo rtihs child's immediate reaction |
mast cell
|
|
|
4-year-old Stephen was breast fed exclusively until 6 months of age when he received his first bottle of cow’s milk formula, at which time he immediately developed urticaria and wheezing. Specific IgE (sIgE) testing revealed sIgE of 12U/ml to cow’s milk and 0.01 U/ml to soya.
what actiaved these mast cells? |
cross linking of milk antigen specific IgE on Fc-epislon-RIs on mast cell surface by polyvalent milk antigen
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with pruritic papules and plaques on his backs, elbows and knees. The lesions are salmon-colored and covered with loosely adherent silver-white scale. Histologic examination of an established lesion on his back revealed overlying parakeratotic scale and marked epidermal thickening (acanthosis) with downward elongation of rete ridges. Neutrophils were evident in the superficial epidermal layers.
|
psoriasis
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with pruritic papules and plaques on his backs, elbows and knees. The lesions are salmon-colored and covered with loosely adherent silver-white scale. Histologic examination of an established lesion on his back revealed overlying parakeratotic scale and marked epidermal thickening (acanthosis) with downward elongation of rete ridges. Neutrophils were evident in the superficial epidermal layers.
acute or chronic? |
chronic
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with pruritic papules and plaques on his backs, elbows and knees. The lesions are salmon-colored and covered with loosely adherent silver-white scale. Histologic examination of an established lesion on his back revealed overlying parakeratotic scale and marked epidermal thickening (acanthosis) with downward elongation of rete ridges. Neutrophils were evident in the superficial epidermal layers.
what type of hypersensitivty is this an example of |
most likely type IV (cell mediated)
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with pruritic papules and plaques on his backs, elbows and knees. The lesions are salmon-colored and covered with loosely adherent silver-white scale. Histologic examination of an established lesion on his back revealed overlying parakeratotic scale and marked epidermal thickening (acanthosis) with downward elongation of rete ridges. Neutrophils were evident in the superficial epidermal layers.
what types of lymhocytes are found in the lesions? |
TH1 and TH17 CD4+ T cells, CD8+ CTLs
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with pruritic papules and plaques on his backs, elbows and knees. The lesions are salmon-colored and covered with loosely adherent silver-white scale. Histologic examination of an established lesion on his back revealed overlying parakeratotic scale and marked epidermal thickening (acanthosis) with downward elongation of rete ridges. Neutrophils were evident in the superficial epidermal layers.
genetic association? |
HLA-C; (ABC are 1, 2 is ARDD)
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with pruritic papules and plaques on his backs, elbows and knees. The lesions are salmon-colored and covered with loosely adherent silver-white scale. Histologic examination of an established lesion on his back revealed overlying parakeratotic scale and marked epidermal thickening (acanthosis) with downward elongation of rete ridges. Neutrophils were evident in the superficial epidermal layers.
Whya re neutrophils present? |
IL-17
|
|
|
A 28-year-old female physician who was performing yard work recognized poison ivy plants within her work area. 48 hours later, she noted a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on her arms and neck.
acute or chronic? |
acute
|
|
|
A 28-year-old female physician who was performing yard work recognized poison ivy plants within her work area. 48 hours later, she noted a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on her arms and neck.
first time she was exposed? |
no; she must be sensitized. rarely individuals are sensitized via cashews or mangos
|
|
|
A 28-year-old female physician who was performing yard work recognized poison ivy plants within her work area. 48 hours later, she noted a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on her arms and neck.
what type of hypersensitivity |
IV
|
|
|
A 28-year-old female physician who was performing yard work recognized poison ivy plants within her work area. 48 hours later, she noted a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on her arms and neck.
what is the immune system recognizing? |
either self MHC molecules or peptides that have been altered by cointact allergen
|
|
|
A 28-year-old female physician who was performing yard work recognized poison ivy plants within her work area. 48 hours later, she noted a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on her arms and neck.
Are B cells and antibodies involved |
no, this is a cell mediated response
|
|
|
A 28-year-old female physician who was performing yard work recognized poison ivy plants within her work area. 48 hours later, she noted a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on her arms and neck.
can you get contact dermatitis if you were only exposed to the allergen just one time? |
yes, if over a week later the allergen is still present on your skin or clothes (wash and use soap_
|
|
|
tuberculoid leprosy
|
less severe; localized flat lesions; lepromin skin test positive; strong THI predominant response. macrophages activated by IFN-gamma from TH1 cells can kill m. leprae
|
|
|
lepromatous leprosy
|
more severe; foamy macrophages w lots of acid fast bacilli; STRONG TH2 predominant response; lepromin skin test negative (anergic); so w/o TH1 response lacking IFN-gamma to activate macrophages, cant kill m. leprae
|
|
|
A 75-year-old man presents with year-long history of a nonpruritic rash on his upper body. The patient had lived in India for several years. He lived in the US for over a year prior to the onset of the rash. Physical exam reveals multiple plaques and patches dispersed on his chest, back and upper extremities. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a punch biopsy skin specimen showed a normal epidermis above a dermal infiltrate of inflammatory cells that extended down to involve the small nerves present in the biopsy specimen. Fite staining revealed macrophages containing numerous small, filamentous, acid-fast organisms.
dx? |
lepromatous leprosy
|
|
|
A 75-year-old man presents with year-long history of a nonpruritic rash on his upper body. The patient had lived in India for several years. He lived in the US for over a year prior to the onset of the rash. Physical exam reveals multiple plaques and patches dispersed on his chest, back and upper extremities. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a punch biopsy skin specimen showed a normal epidermis above a dermal infiltrate of inflammatory cells that extended down to involve the small nerves present in the biopsy specimen. Fite staining revealed macrophages containing numerous small, filamentous, acid-fast organisms.
type of immune response? |
Strong CD4+ TH@ predominant immune response
|
|
|
A 75-year-old man presents with year-long history of a nonpruritic rash on his upper body. The patient had lived in India for several years. He lived in the US for over a year prior to the onset of the rash. Physical exam reveals multiple plaques and patches dispersed on his chest, back and upper extremities. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a punch biopsy skin specimen showed a normal epidermis above a dermal infiltrate of inflammatory cells that extended down to involve the small nerves present in the biopsy specimen. Fite staining revealed macrophages containing numerous small, filamentous, acid-fast organisms.
most characteristic histologic feature? |
acid fast bacilli
|
|
|
A 75-year-old man presents with year-long history of a nonpruritic rash on his upper body. The patient had lived in India for several years. He lived in the US for over a year prior to the onset of the rash. Physical exam reveals multiple plaques and patches dispersed on his chest, back and upper extremities. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a punch biopsy skin specimen showed a normal epidermis above a dermal infiltrate of inflammatory cells that extended down to involve the small nerves present in the biopsy specimen. Fite staining revealed macrophages containing numerous small, filamentous, acid-fast organisms.
what microorganism causes this disease? |
myobacterium leprae
|
|
|
A 75-year-old man presents with year-long history of a nonpruritic rash on his upper body. The patient had lived in India for several years. He lived in the US for over a year prior to the onset of the rash. Physical exam reveals multiple plaques and patches dispersed on his chest, back and upper extremities. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a punch biopsy skin specimen showed a normal epidermis above a dermal infiltrate of inflammatory cells that extended down to involve the small nerves present in the biopsy specimen. Fite staining revealed macrophages containing numerous small, filamentous, acid-fast organisms.
why cant the macrophage skill these microorganisms? |
no TH1/IFN-gamma to activate macrophages
|
|
|
A 75-year-old man presents with year-long history of a nonpruritic rash on his upper body. The patient had lived in India for several years. He lived in the US for over a year prior to the onset of the rash. Physical exam reveals multiple plaques and patches dispersed on his chest, back and upper extremities. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a punch biopsy skin specimen showed a normal epidermis above a dermal infiltrate of inflammatory cells that extended down to involve the small nerves present in the biopsy specimen. Fite staining revealed macrophages containing numerous small, filamentous, acid-fast organisms.
Which type of CD4+ T cell makes IFN-gamma |
TH1
|

