![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oxidation-Fermentation (OF) Test |

|
|
|
Oxidation-Fermentation (OF) Test: Medium Recipe |

|
|
|
Oxidation-Fermentation (OF) Test: Purpose |
The OF test is used to differentiate bacteria based on their ability to oxidize or ferment specific sugars. It allows presumptive separation of the fermentative Enterobaderiaceae from the oxidative Pseudomonas and Bordetella, and the nonreactive Alcaligenes and Moraxella. |
|
|
Oxidation-Fermentation (OF) Test: Visual of Results |

|
|
|
Definition: Fermentation Tests |
Is the metabolic process by which an organic molecule acts as an electron donor (becoming oxidized in the process) and one or more of its organic products act as the final electron acceptor (FEA). Includes hydrolysis of disaccharides prior to the fermentation reaction. Thus, a "lactose fermenter" is an organism that splits the disaccharide lactose into the monosaccharides glucose and galactose and then ferments the monosaccharides. |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth (PR) Test: Purpose |
PR broth is used co differentiate members of Enterobaderiaceae and to distinguish chem from ocher Gram-negative rods. It also is used to distinguish benveen Grain-positive fermenters, such as Streptococcus and Lactobacillus species. |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth (PR) Test: Medium Recipe |

|
|
|
What is Phenol Red? |
Differential test medium prepared as a base to which a carbohydrate is added. |
|
|
Phenol Red Indication:
(A) Yellow (Acid) + Gas (B) Yello (Acid) no Gas (C) Orange (neutral) no gas (D) Red (alkaline) no gas |
(A) Fermentation of Sugar (B) fermentation of Sugar (C) Oxidation of Sugar (D) Oxidation of proteins |
|
|
What causes color change in Phenol Red Broth? |
Acid production from fermentation of the carb lowers the pH below the jeitralnrange if the indicator (Phenol Red) and turns the color Yellow.
Delamination of amino acids supplied by pepitone marks an alkine reaction via the production of NH3. This turns the broth Pink to Magenta. |
|
|
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer (MR-VP) Tests |
It's two tests combined into one: Methyl Red (MR) and Voges Proskauer (VP) |
|
|
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer (MR-VP) Tests: Medium |
Composed of Peptone, Glucose, and Phosphate Buffer.
The Peptone and Glucose supply protein (via Nitrogen) and fermentable carbs.
Potassium phosphate resists pH change in medium. |
|
|
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer (MR-VP) Tests: the MR portion |
Is designed to detect organisms performing mixed acid fermentation which overcomes the phosphate buffer in the medium and lowers the pH. - Red color = (+) results (pH 4.4) - Orange olor = (-) or unconfirmed - Yellow color = (-) |
|
|
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer (MR-VP) Tests: the VP portion |
Detects organims able to ferment glucose. The resulting acid is converted to Acetoin and 2,3-butamediol.
VP reagent oxidizes acetoin and 2,3-butamediol, which in turn reacts with grenadine nuclei from proton to produce a red color.
(+) VP test = Red color (-) VP test = No color change (or development of Copper Color) |
|
|
Catalase Test |
When Hydrogen Peroxide is added to a Catalse-positive culture, oxygen bubbles form immediately. If no bubbles form, then the organism is Catalase-negative. |
|
|
Catalase Test: Results Interpretation (1) |

|
|
|
Catalase Test: Results Interpretation (2) |

|
|
|
Oxidase Test |
Designed to detect the presence of Cytochrome C Oxidase. Chromogenic reducing agents are chemicals that develop color as they become oxidized. |
|
|
Oxidase Test: Results Interpretation |

|
|
|
Oxidase Test: Why must results be read during first 20 sec after application? |
Reagents used for this test are unstable and may oxidize independencly shortly after they become moist. Therefore, it is important to take your readings within the recommended time (usually 20 seconds). |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test: Medium |

|
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test: Results Interpretation |

|
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test: Graphic |
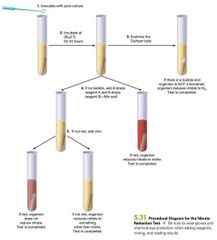
|
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test: Info |
Occurs in two parts, no color indicators are used in first half. If gas forms in tube = (+) result - Signals Nitrate Reductase Activity. If no gas, then add Reagent A and B. - Red Color change = Organism reduced nitrate to nitrite. - No Color change = add Zinc. After Zinc was added - Red Color change = Nitrate was NOT reduced by organism. - No Color Change = organism reduced beyond Nitrite. |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test: Application |
Virtually all members of Enterobacteriaceae perform a one-step reduction of nitrate to nitrite. The nitrate test differentiates them from Gram-negative rods that either do not reduce nitrate or reduce it beyond nitrite to N2 or other compounds. |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test: Symbol |
O-F |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test:
Substrate |
Sugar |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test:
Reaction |
Ferm. Or Oxid. |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test:
Indicator |
Bromothymol Blue |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test: Positive Result |
Ferm. - Yellow Oxid. - Blue |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test:
Negative Result |
Green |
|
|
Oxidation Fermentation Test:
What it Isolates |
Differentiates between Gram (-) aerobic/anaerobic. |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
Symbol |
PRB |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
Substrate |
Sugar |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
Reaction |
Ferm. + Gas |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
Indicator |
Phenol Red |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
Positive Results |
Yellow - Ferm.
Bubble in Durham tube - Gas Prodution |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
Negative Results |
Red- Pink broth; No bubble. |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth:
What it Isolates |
Differentiate between Gram + fermenters. |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
Symbol |
MRVP |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
Substrate |
Glucose |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
Reaction |
Mixed Acid Ferm. |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
Indicator |
None. |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
Positive Results |
MR - Red color; VP - Red Color |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
Negative Results |
No color change. |
|
|
Methyl Red - Voges Proskauer Test:
What it Isolates |
Differentiate between Enterobacteriacaea. |
|
|
Catalase Test:
Symbol |
None. |
|
|
Catalase Test:
Substrate |
H2O2 |
|
|
Catalase Test:
Reaction |
Catalase Enz. Rxn. |
|
|
Catalase Test:
Indicator |
None |
|
|
Catalase Test:
Positive Results |
Bubbles |
|
|
Catalase Test:
Negative Results |
No bubbles |
|
|
Catalase Test:
What it Isolates |
Differentiate Mirococcacus from Streptococcus. |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
Symbol |
None |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
Substrate |
Cytochrome - C Oxidase |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
Reaction |
Reduction |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
Indicator |
None. |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
Positive Results |
Purple - dark blue |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
Negative Results |
No color change. |
|
|
Oxidase Test:
What it Isolates |
ID Neisseria or Moraxella sp. |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
Symbol |
None |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
Substrate |
Nitrate |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
Reaction |
Reduction |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
Indicator |
None. |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
Positive Results |
Red - after reagents; colorless - after zinc. |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
Negative Results |
Colorless - then pink. |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction Test:
What it Isolates |
Differentiate between Enterobacteriacaea |

