![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
Symbol |
LIA. |
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
Substrate |
Lysine, Sulfer. |
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
Reaction |
Decarb.; Deamin., Red. |
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
Indicator |
Bomcresol Purple; Ferric Amm. Citrate. |
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
(+) Results |
Color change - 4 possible combinations. |
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
(-) Results |
No color change. |
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar:
Used to Isolate... |
Differentiate between Enterobacteriacaea. - differentiate enterics based on their ability to decarboxylate or deaminate lysine and produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S). |
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
Symbol |
None. |
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
Substrate |
Skim Milk (contains lactose [for fermentation] and Caesin [protein]). |
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
Reaction |
(1) Fermentation of Lactose
(2) Reduction of Linnus
(3) Coagulation of Casein
and (4) Hydrolysis of Caesin (or, F.R.C.H.) |
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
Indicator |
Azolitmin
- its pink at pH 4.5 and blue at pH 8.3. Between these extremes it is light purple. |
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
(+) Results |

|
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
(-) Results |
No changes. (Light purple in color) |
|
|
Litmus Milk Medium:
Used to Isolate... |
Used primarily to differentiate members within the genus Clostridium.
Enterobacteriaceae from other Gram Negative bacilli (based on the ability of enterics to reduce litmus).
Litmus milk cultivates and maintains cultures of lactic acid bacteria. |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
Symbol |
None. |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
Substrate |
Antibiotics. |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
Reaction |
Bacitracin - peptide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by interfering with transport of peptidoglycan subunits across the cytoplasmic membrane.
Novobiocin - interferes with ATPase activity associated with DNA gyrase, an enzyme necessary during DNA replication.
Optochin - derived from quinine that interferes with ATP synthase activity and ATP production in susceptible bacteria. |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
Indicator |
None. |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
(+) Results |
Growth next to the small circular piece of paper (6mm) that contains antibiotics. (Which means the organism is resistant to thebantibiotic) |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
(-) Results |
B - any zone of clearing 10 mm or greater around the disk is interpreted as bacitracin susceptibility. N - a 5 µg disk (6mm in diameter) should produce a zone of clearing 16 mm or more for the organism to be considered novobiocin susceptible. O - a 5 µg disk (6mm in diameter) should produce a zone of inhibition 14 mm or more for the organism to be considered optochin susceptible. |
|
|
Bacitracin, Novobiocin, and Optochin Susceptibility Tests:
Used to Isolate... |
B - differentiate/identify beta-hemolytic group A streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes-bacitracin susceptible) from other beta-hemolytic streptococci (bacitracin resistant). Differentiates the genus Staphylococcus (resistant) from the susceptible Micrococcus.
N - differentiate coagulase-negative staphylococci. Used to identify the novobiocin-resistant Staphylococcus Saprophyticus.
O - differentiate Streptococcus pneumoniae from other a-hemolytic streptococci. (It kills S. Pneumoniae) |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
Symbol |
None. |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
Substate |
Blood Plasma. |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
Reaction |
Coagulation. |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
Indicator |
None. |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
(+) Results |
Agglutination. |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
(-) Results |
No agglutination. |
|
|
Coagulate Tests:
Used to Isolate... |
Pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus. |
|
|
Motility Test:
Symbol |
None. |
|
|
Motility Test:
Substrate |
None. |
|
|
Motility Test:
Reaction |
None. |
|
|
Motility Test:
Indicator |
Tetrazolium Salt (TTC). |
|
|
Motility Test:
(+) Results |
Red hazy media. |
|
|
Motility Test:
(-) Results |
Red only around stab. |
|
|
Motility Test:
Used to Isolate... |
Detect bacterial motility. |
|

Litmus Results Visual |
left to right:
alkaline reaction (K);
uninoculated control;
alkaline reaction (K);
digestion reaction (D);
acid clot production, gas production, and reduction reaction (ACGR);
acid reaction (A);
acid reaction, curd production (with whey, the clear liquid, on the surface.)
The clear liquid on the surfaces of the (D) and (ACGR) tubes is mineral oil to promote anaerobic growth. |
|

Litmus Chart if Results |

|
|

Bacitracin |
The organism above has no clear zone and is resistant (R); the organism below has a clear zone larger than 10 mm and is susceptible (S). (The disks themselves are usually 6 mm.) |
|

Novobiocin |
A novobiocin-resistant organism (R) is on the left; a susceptible organism (S) is on the right. |
|

Optochin |
The zone of inhibition surrounding the disk indicates susceptibility to optochin and presumptive identification of S. pneumoniae. |
|

Lysine Visual Results |
Left to Right:
R/A;
K/A, H2S, (note the small amount of black precipitate near the middle and the gas production from glucose fermentation at the base);
uninoculated control;
K/K (obscured by the black precipitate), H2S. |
|

Lysine Results Chart |
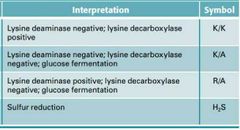
|

