![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two processes that release energy from glucose are _________ and __________
|
cellular respiration and fermentation
|
|
|
________ must be present for _______ or cellular respiration to take place.
|
Oxygen, aerobic
|
|
|
……………………….. …………………. is produced by …………………… bacteria at landfill sites. It can be used to produce …………………………….
|
Methane gas, anaerobic, electricity
|
|
|
____________are negatively affected when pH of water drops below 5.5 while ________ are least affected by a drop in pH.
|
Clams and snails, frogs
|
|
|
Plants prepare ……………………….. during photosynthesis and yet they rely on ………………………. …………………………. to release the energy in glucose.
|
glucose, cellular respiration
|
|
|
Green house gases are………………….. …………………., ………………….. ……………… and ……………………… gas. These reduce the loss of heat from the earth’s …………………………….
|
Carbon dioxide, water vapour, and methane gas, atmosphere.
|
|
|
……………………. …………………….is when gases prevent loss of heat.
|
greenhouse effect
|
|
|
Burning …………………… ……………………. is similar to cellular respiration.
|
Fossil Fuels
|
|
|
9. Burning fossil fuels produces gases such as nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide which combine with rain water to form ……………….. …………… and …………………. ………………………...
|
nitric acid, sulferic acid
|
|
|
What is the difference between the greenhouse effect and the enhanced greenhouse effect?
|
Greenhouse effect is when naturally occurring gases keep the earth’s atmosphere warm while enhanced green house effect is the increased concentration of greenhouse gases as a result of man’s activities resulting in global warming.
|
|
|
What is the difference between cellular respiration and fermentation?
|
Cellular respiration is releasing energy from glucose in presence of oxygen gas. Much energy [ 36 ATP ] is produced and glucose is completely oxidized.
Fermentation is incomplete oxidation of glucose resulting production of less energy [2 ATP] and methane gas is produced. |
|
|
What is the Kyoto protocol?
|
The Kyoto protocol is an agreement between more than 180 countries to reduce greenhouse gases by planting more trees.
|
|
|
What are the effects of acid rain?
|
Acid rain reduces nutrients from soil as these dissolve in rain water.
Acid rain increases concentration of aluminum that reduces absorption of nutrients from soil. Acid rain causes greatest effect on aquatic ecosystems as aquatic organisms are unable to tolerate lowering of pH of the water. |
|
|
All activities utilize …………… that originally comes from the …………..
|
energy, sun
|
|
|
Energy in the sun is produced by nuclear reactions called …………. …………….
|
nuclear fusion
|
|
|
Much energy reaches the earth, but most of it is ……….…… to the atmosphere.
|
lost back
|
|
|
Only ……….. ….…….. can absorb radiant energy of the sun and change it to …………. …… …………in carbohydrates.
|
green plants, chemical energy (food)
|
|
|
…………………….. is the carbohydrate produced during photosynthesis.
|
glucose
|
|
|
………………………. is the process by which green plants absorb water and carbon dioxide, and using energy from the sun prepare food which is ………………………. ……………………….
|
photosynthesis, chemical energy
|
|
|
……………. gas is also produced which is used by all living organisms for respiration.
|
oxygen
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide is absorbed through openings called ………………………….
|
stomata
|
|
|
Photosynthesis takes place mostly in the leaves as …………………. ………………… in the leaf contain much chloroplast.
|
palisade cells
|
|
|
……………………. is the green pigment that helps plants to absorb light energy.
|
cholorpyll
|
|
|
Not all ecosystems produce the same amount of …………………………
|
oxygen
|
|
|
…………………… ……………….. and …………………. ecosystems produce most oxygen.
|
tropical forests and oceans
|
|
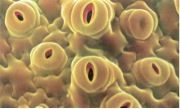
Identify the cells and state their function:
|
• Cells are guard cells that form openings called stomata.
• Stomata allow air exchange and loss of water by transpiration. |
|
|
13. Write the equation for photosynthesis.
|
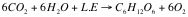
|
|
|
Identify the raw materials and products of photosynthesis.
|
Raw materials are water and carbon dioxide and products are sugar and oxygen.
|
|
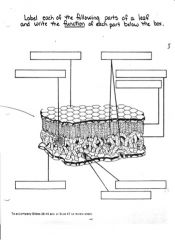
Label the structure of the leaf and state the function of each part.
|
1. cuticle prevents loss of water from plant surface
2. Chloroplast contain chlorophyll pigment which absorbs light energy and changes to chemical or food energy. 3. Palisade cells contain much chloroplast and are on upper surface to get maximum light energy. 4. Palisade mesophylls cells are irregularly placed to allow circulation of air within the plant body 5. Guard cells regulate the opening of the stoma 6. Stoma is the opening through which gaseous exchange and water loss takes place. 7. Lower epidermis contains lots of stomata for exchange and forms a protective coat. |
|
|
The third trophic level consists of organism which are____________
|
secondary consumers
|
|
|
The last organisms in a food chain are the ………………………….
|
decomposers
|
|
|
Pyramids of ……………………….. are similar to pyramids of numbers.
|
numbers
|
|
|
In food chains, ………………….. is recycled but …………………… is never recycled.
|
mater, energy
|
|
|
Why are food chains short?
|
food chains are short because there is a small percentage of energy that is transferred through the food chain that becomes smaller and smaller, so if they were extended there would be not enough energy to sustain a further predator.
|
|
|
Explain how energy passes through food chain.
|
-Only about 10% of energy passes from organism to organism in food chains
-much of the energy is lost as heat energy, -predator may not consume the entire plant, -predators may not be able to digest fur and bones -they creates waste. |
|
|
Explain the difference between bioaccumulation and biomagnification using specific examples.
|
bioaccumulation- when more of a toxin is ingested than eliminated
-ex. monarch butterfly eats poisonous milkweed when caterpillar -toxins stored in tissues in butterfly where butterfly cannot be harmed -it ingests toxins at a greater rate then it elimates them Biomagnification- when the concentration of a toxin is increased as it moves from one trophic level to the next. -ex. insecticide DDT entered environement from runoff in north america -algae ingested it, then miscroscopic animals ate algae, then small fish -concentration became higher and higher -preregrine falcons were affected, they could not longer produce -almost went extinct -humans captivated young birds and raised them in boxes on nesting cliffs or tall downtown buildings until strong adults |
|
|
……………………… is a group of organisms belonging to the same species living in the same place at the same time and can reproduce successfully
|
a population
|
|
|
……………………. ………………. is characterized by a J shaped curve.
|
exponential growth
|
|
|
When will the population of a species increase exponentially?
|
Population of a species will increase exponentially if conditions are ideal; plenty of resources, less competition, higher birth rate than death or emigration, protection by law.
|
|
|
What caused the decline of the wild turkey in Ontario?
|
Human activities such as deforestation and hunting decreased the population of the wild turkey to extinction.
|
|
|
Define limiting factors and suggest some examples of these?
|
Limiting factor is defined as the factor that limits the growth and distribution of a population in an ecosystem. Limiting factors may be biotic [ prey as source of food, mating partners] or abiotic [ nutrients, light, space, water, light].
|
|
|
………………………….is the size of the population that an ecosystem can support indefinitely with its resources.
|
carrying capacity
|
|
|
When a population is supported at an ecosystem’s carrying capacity, the size of the population reaches its …………………………….
|
equilibrium
|
|
|
8. What would happen if the population increased beyond carrying capacity or a resource were removed when the population was at equilibrium?
|
If population is increased beyond carrying capacity, the ecosystem will not be able to sustain for a long time the new population and the population will drop to the original equilibrium.
If a resource is removed, then the population will drop to a new equilibrium. If a resource is increased, the population will get a new high equilibrium. |
|
|
Suggest an example of human activity which may increase carrying capacity.
|
Creating of landfill sites may increase carrying capacity for scavengers and bacteria as there may be a lot of energy in biomass of garbage. Irrigating dry areas may increase carrying capacity for plants which in turn will attract animals.
Construction of roads, dams, buildings may decrease carrying capacity. |
|
|
10. What is urban sprawl? How has it decreased carrying capacity of the streams in the golden horseshoe region of Ontario?
|
Urban sprawl is when an urban region gradually begins to expand outwards into its boundary areas by having new construction.
Urban sprawl resulted in the removal of the overhanging vegetation which kept the waters of streams cool, an ideal condition for the redside dace. With increase in temperature of the water, the population of this fish decreased. |
|
|
……………………….. is the process of building new homes within the boundary of the urban region and preventing urban sprawl.
|
intensification
|
|
|
………………………… and …………………………. are two examples of biotic factors that can reduce carrying capacity.
|
competition and parasitism
|
|
|
…………………. …….. ………………….. partners and ………………………. are biotic factors that can increase carrying capacity.
|
availability of mating, symbiosis
|
|
|
………………………….. is defined as the way that an organism occupies a position in an ecosystem, its biotic and abiotic factors.
|
ecological niche
|
|
|
Describe the ecological niche of the brown bat.
|
Biological or biotic niche is food it eats: insects: competitors that eat insects too and occupy same nesting sites, :common night hawk and its predators. Abiotic niche is airspace, places where it roosts, hibernates, temperature range, water, etc.
|
|
|
Name three ecological services an organism provides to the ecosystem in which it lives.
|
Three ecological services that species provide are control population of organisms , matter cycling and energy flow
|
|
|
Explain why no two species may occupy the same ecological niche?
|
No two species occupy the same ecological niche as no two species behave in exactly the same way. Some services may overlap but each species has its own unique ecological niche.
|
|
|
Why do pitcher plants and sundew need to feed on insects?
|
These plants live in bogs where the soil is poor in nitrogen containing compounds. They feed on insects to obtain their protein.
|
|
|
Explain the concept of bottom up population control and top down population control.
|
Bottom up control is when the population of prey decreases resulting in decrease in the population of predator.
Top down population control is when the number of prey increases resulting in increase in population of predator. This then decreases the population of prey followed by decrease in population of predator. The cycle of events produces graphs that show fluctuation in population of prey and predator. |
|
|
What does research studies on relation between wolf and moose population indicate?
|
It indicates that there are other factors that determine population of species rather than only prey – predator relationship. These are climate changes, infestations of parasites, human activities etc
|
|
|
How does competition affect population size?
|
When organisms are under stress of competition, much energy is spent in competing and less on growth and reproduction. Birds are seen to lays fewer eggs, rabbits give birth to dead offspring’s .
|
|
|
Define the two kinds of symbiosis [ interaction between two members of different species].
|
Mutualism: A relationship where both members benefit.
Parasitism: A relationship where a parasite depends on a large host for food and sometimes protection. Parasites usually harm the host to some extent. |
|
|
Explain how global warming has affected the mutualistic relationship between algae and corals.
|
Corals in tropics are colorful because of symbiotic relationship between the coral and algae.
Coral provide protection and carbon dioxide to algae and algae provide food. Recently the coral are losing their color and turning white. This is due to global warming. The association between the two is breaking and death of coral results. This is an example of abiotic factor that causes a change in ecological niche. |
|
|
How do the four types of Biodiversity sampling work?
1. Canopy fogging: 2. Quadrat sampling: 3. Transect sampling: 4. Netting: |
1. Canopy fogging- effectively collects information about biodiversity of insects. Low doses of insectecide are sprayed into the top of the trees, and insects fall and are collected on a large screen shaped like a funnel.
2. Quadrat sampling- a square area is marked using a pre-made square of plastic, or stakes and string. Quadrats can range in size from 1m2 to 20 m2, depending on the type of habitat. Different species and their numbers are counted. Counting is repeated many times throughout the habitat to get an accurate representation. Transect Sampling: -done using a transect line -transect line is usually rope or measuring tape thats been marked at intervals ex. every metre -at each interval the type and number of species along the line are recorded Netting: -mesh nets used to capture birds and bats, and fish/ other organisms -birds, bats, fish, and others are identified, blood may be taken for genetic analysis, measure, and may be tagged. -theyre often released |
|
|
What is biodiversity?
|
the amount and variety of life forms including species found within a specific region, as well as all the numbers and types of species within and beyond the region
|
|
|
what is the influence of forests on climate?
|
When large forested areas are cleared, the local annual precipitation drops and climates become hotter and drier, and csn lead to the desertification of an area
-on hot days, water escapes from the stomata of trees and adds water vapour to the atmosphere -this helps to reduce temperatures and form rain clouds -more than half the moisture above tropical forests comes from the trees |
|
|
what is the effect of logging to ecosystems?
|
-logging effects climate, causes erosion in wetlands, destroyes habitats for many species
|
|
|
What are the 6 services ecosystems provide?
|
1. provides food and clean water
2. cycles nutrients 3. converts atmospheric carbon to biomass (which influences climate and weather 4. pollination of crops and natural vegetation 5. balance of processes like growth and decomposition 6. provides beauty and spirituality |
|
|
How are ecological footprints measured?
|
-measures the impact one person or a population of people make on the environment
-based on the amount of energy you use, waste you produce, and land you use |
|
|
how can we lower our ecological footprints?
|
1. walk/bike instead of driving
2. carpool 3. lower your thermostat 4. turn off lights/unplug things when not in use 5. hang laundry out to dry instead of using drier 6. use energy efficient lights 7. use a renewable energy source for energy 8. compost and recycle 9. collect and reuse rain water 10. grow your own vegetables and fruits and spices! |
|
|
Explain symbiosis and one example where this relationship is affected
|
-Symbiosis is the interaction between members of two different species that live together in close association, two examples are mutualism and parasitism.
-Coral in Canada’s oceans have a mutualistic relationship with algae -Algae offer coral(the host) up to 90% of their energy requirements -Coral offer algae protection, nutrients, constant supply of carbion dioxide for photosynthesis -When ocean temperatures increase by 2º C for more than 6 weeks then algae leave their host, and the coral turn white, because the algae provided the colour. |
|
|
Is there just one factor regulates population size?
|
No. There are many abiotic and biotic factors which affect population size.
|
|
|
Explain adaptations of pitcher plant and the reasons for.
|
Pitcher plants live in bogs, which have very little nutrients in their soil, such as nitrogen. They have adapted to get their nutrients by being carnivorous, and feeding on insects. Pitcher plants engulf their prey inside a hollow basin filled with water and digestive juices.
|
|
|
Identify ecological niches of an organism from readings.
|
The brown bat’s ecological niche includes abiotic elements, such as the time of night it flies, the temperatures in which it can stand, the space it uses for roosting and hibernation. The biotic elements of its niche include its competitors (the common night hawk), its prey (insects), and its predators.
|
|
|
Explain the effects of humans on carrying capacity with specific examples
|
As populations increase, urban sprawl tends to occur expanding farther away from city cores. It reduces carrying capacity by destroying habitats and polluting more from the people who live in the new developments. Humans become more dependent on automobiles, we decrease our amounts of farmlands since roads are built, and reduction of carrying capacity.
|
|
|
How do biotic and abiotic factors act as limiting factors?
|
They act as limiting factors by the fluctuation of their availability, for example when a biotic factor like competition increases, there will not be as many sources for both species. Also, if an abiotic factor like water decreases, a species will not have enough of that resource to survive.
|
|
|
What are conditions that influence exponential population growth?
|
Extensive resources, lack of predators, increased amounts of prey, protection by law, influence exponential growth.
|
|
|
A _________ is an area of land over which the run-off drains into a body of water.
|
Watershed
|
|
|
__________ is the measure of the amount of energy or biomass transferred from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level.
a ______ is a catagory of organisms gain their energy. |
trophic efficiency, trophic level
|
|
|
_________ is the total mass of living organisms in an ecosystem.
____________ is the process in which an organism ingests materials, especially toxins, at a faster rate that it eliminates them. _____________ is a process in which the concentration of ingested toxins increases as it moves from one trophic level to the next |
biomass, bioaccumulation, biomagnification.
|
|
|
Explain with examples dependence on multiple ecosystems
|
-predators may follow their prey to a new ecosystem
-temperatures may become too warm or cold, forcing an organism to migrate |

