![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nuclear membrane |
Surrounds the nucleus and is porous. It allows certain materials to pass in and out of the nucleus |
|
|
DNA |
Deoxyribonucleic acid Combined with protein, they make up chromosomes. DNA looks like a twisted ladder and provided the instructions for all cellular activities and structures |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Inside the nucleus Creates ribosomes, which then leave and go to the cytoplasm |
|
|
Centrioles |
Made of microtubules. Found in most animal cells. They allow movement of the organelles and support for the cell |
|
|
Nucleotide |
Composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base |
|
|
Nitrogenous bases |
Adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine. A pairs with T G pairs with C Form the rungs on the DNA ladder. |
|
|
Amino Acids |
The small building blocks that make up a protein. Each "three-letter word" of the nitrogenous bases codes for a different amino acid. |
|
|
Gene |
A short section of the DNA that contains the instructions to make a specific protein. |
|
|
Genome |
All of an organisms genes. |
|
|
Traits |
Variations in characteristics caused by different genes. |
|
|
Cell cycle |
Sequence of events in order from one cell division to another. |
|
|
Interphase |
Growing and working, copies organelles, replicates chromosomes to form sister chromatids |
|
|
Sister chromatids |
The chromosome and its copy which carry identical instructions for the functions of a cell. |
|
|
Parent cell |
The original cell that divides into two |
|
|
Daughter cells |
The parent cell after division |
|
|
Mitosis |
Contains prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Divided the cytoplasm in half Pinching in animal cells Vesicles form the cell plate in plants |
|
|
Prophase |
Chromatids thicken and become joined. Nucleolus disappears and the nuclear membrane breaks down. Centrioles start to form spindles |
|
|
Spindle |
Moves the chromatids during cell division |
|
|
Metaphase |
Sister chromatids attach to the spindle fibres. The chromatids line up across the middle of the cell. |
|
|
Anaphase |
Sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibres and move towards opposite poles of the cell |
|
|
Telophase |
Nuclear membranes form, the spindle disappears, chromosomes lengthen and thin, nucleoli reappear. |
|
|
Mutation |
A change in the DNA can be neutral Harmful Beneficial |
|
|
Cancer |
Cells divide rapidly and uncontrollably. Form tumours. Use more nutrients than normal cells. Enlarged nuclei Can be benign or malignant |
|
|
Benign tumours |
Stay in one place and do not interfere with the functioning of the surrounding tissue and organs |
|
|
Malignant tumours |
Invade surrounding tissues and interfere with their functions. |
|
|
Metastasis |
The spread of cancer cells always from their original location. (Malignant tumours do this). |
|
|
Carcinogen |
A substance that can cause cancer. Asbestos Some pesticides Radiation Chemicals in tobacco |
|
|
The functions of cell division |
Growth Repair Reproduction |
|
|
Transcription |
mRNA is formed at the DNA In the nucleus |
|
|
Translation |
When the tRNA uses the mRNA to bring the proper amino acids and form proteins in the rRNA |
|
|
Why don't cells simply increase size to grow? |
Volume increases faster than surface area so the cell cannot function efficiently. |
|
|
Name the two main categories of cells. |
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic. |
|
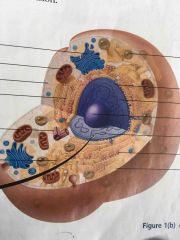
Label |
Golgi apparatus Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Rough ER centriole Smooth ER Lysosomes Nuclear membrane Nucleus Nucleolus Chromosome Ribosome Cell membrane |
|
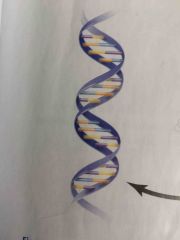
What is this? |
DNA |
|

Label |
Yellow-nitrogenous base Green- sugar molecule Purple- phosphate molecule Entirety- nucleotide |
|
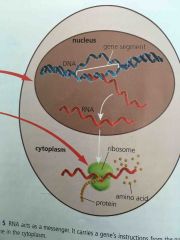
Describe. |
The DNA is unzipped to form mRNA which leaves the nucleus and goes out into the cytoplasm to find a ribosome. Once it finds a ribosome, tRNA will bring the |
|
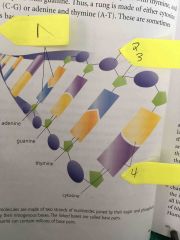
Label the yellow |
1- nitrogenous bases 2- phosphate molecule 3- sugar molecule 4- nitrogenous bases |
|
|
What is the human genome? |
The human genome is all of the genes in a human. It is contained in the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus of almost every cell in the body. |
|
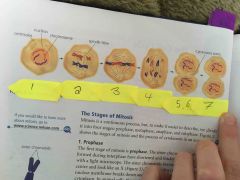
Label the yellow |
1- interphase 2- prophase 3- metaphase 4- anaphase 5- telophase 6- cytokinesis starts 7- cytokinesis ends |

