![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the NDM? |
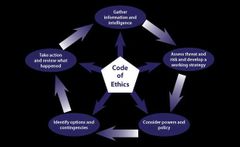
|
|
|
What is coopers colour code? |

|
|
|
Name 7 pre incident indicators. |
1-Unnatural hindering of your moments ie blocking a door. 2-Sudden change of status of subjects near to yourself ie predator crawling. 3-A verbal exchange with yourself initiated by a stranger. 4-Subjects hiding hands causing unnatural walking posters. 5-Vehicles stopping sponsored or slightly to the front or rear. 6-A second pass by a vehicle or subject. 7-Undue attention towards yourself. |
|
|
9 causes of aggression |
1-Peronslaity 2- Frustration 3-Environmental stress 4-Mental illness 5-Territory 6-Responses to threat 7-Disease or injury 8-Alcohol and drugs 9-Conditions learnt |
|
|
How far is close intimate in proximity? |
Body line 6 inch |
|
|
How far is Intimate proximity? |
Body line 18inch |
|
|
How far is personal proximity? |
18inchs to 14ft |
|
|
How far is public proximity? |
14+ft |
|
|
7 warning signs for conflict |
1-Behaviour may stop/start abruptly 2-Direct prolonged eye contact 3-Facial colour darkens 4-Standing tall/Head back 5-Large movements 6-Ground kicking 7-Breathing rate accelerates |
|
|
What are the 10 danger signs of conflict? |
1-Fists clench and unclench2-Facial colour may become paler3-Lips tighten over teeth4Head drops to protect throat5-Eyebrows droop to protect eyes6-Hands rise above the waist7-Shoulders tense8-Stance moves from square to sideways9-Stare is now at intended target10-Lowering of body to launch forward |
|
|
Profile subject behavior patterns steps 1 to 6. |
1) Compliance 2) Verbal Resistance and gestures 3) Passive resistance 4) Active resistance 5) Aggressive resistance (attack) 6) Serious and aggravated |
|
|
What are 3 priorities with an aggressor? (In order of importance) |
1) Maximise safety to the public. 2) Minimise the injury to the officer. 3) Minimise the injury to the subject. |
|
|
4 advantages of the chemical cocktail. |
1) Additional strength. 2) Increased pain threshold. 3) Increased awareness. 4) Detailed focus on immediate threat. |
|
|
What are the 5 disadvantages |
1) General muscle tightening 2) Time distortion 3) Tunnel vision 4) Auditory exclusion 5) Sequence of events jumbled |
|
|
Impact factors in conflict. |
1) Size, Age, Strength and Gender. 2) Skill Level 3) Weapons 4) Environment 5) Alcohol/Drugs 6) Perceived danger 7) Number of people/aggressors 8) Exhaustion or injury |
|
|
How can a PC defend themselves legally. |
-Self defence common law "the right of the person to protect themselves" "In defence of others" force "is reasonable to repel and attack" and "circumstance may justify a preemptive strike." "You may use force as is reasonable and necessary to advert the danger" -Section 3 criminal law act " A person may use such force as is reasonable in the circumstances in the prevention of crime, or in effecting or assisting in the lawful arrest of offenders or suspected offenders or of persons unlawfully at large" -Section 117 of PACE: allows officees where necessary to use force. |
|
|
What are Articles 2, 3 and 8 on the humam rights act? |
-Art 2 Right to life -Art 3 Prohibition of tortureArt 8 Right to respect for private and family life. |
|
|
The 5 step model for resistance appeal. |
1) Simple Appeal 2) Reasonable Appeal 3) Personal Appeal 4) Final Appeal 5) Action |
|
|
What are the components of communication? |

|
|
|
What is priority order for injuries? |
1st major bleeds 2nd airways 3rd breathing 4th circulation |
|
|
What is a primary survey DR CABC |
1. Danger 2. Responsiveness 3. Cat bleed 4. Airway open 5. Breathing 6. Circulation |
|
|
AVPU |
Alert Voice Pain Unresponsive |
|
|
What is ABCDE of cuffing? |
Apply cuffs Be sure to ask for tightness Check tightness Double lock Evidence
|
|
|
What is the reactionary gap? |
6ft to 10ft (2m) |
|
|
What is contact and cover |
Contact comes into contact with the individual Cover ensures the safety of the contact officer |
|
|
Causes of positional asphyxiation |
Laying prone Sitting and then head drops between knees Windpipe/ diaphragm is restricted |
|
|
Signs of positional asphyxiation. |
Person stops struggling/fighting Face is discolored/blue/gurgling/gasping. Panicking Tells you they cannot breath Suddenly becomes quiet and tranquil |
|
|
Identify options and contingencies: |
1. Presence (Visible) 2. Communications 3. Primary control (1st level of physical defense) 3. Secondary Control Skills (pava) 4. Defensive or offensive skills 5. Potentially lethal deadly force |

