![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autonomic vs somatic NS |
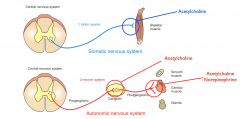
Somatic only one neuron, ANS 2 neurons Both use acetylcholine, ANS also NE after postganglionic cell
|
|
|
Preganglionic neurotransmitter in ANS |
Acetylcholine |
|
|
Postganglionic neurotransmitter in ANS |
Acetylcholine and norepinephrine |
|
|
Compare and contrast autonomic and somatic nervous system |
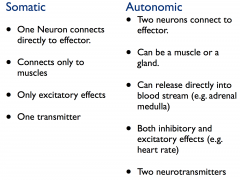
|
|
|
Is the preganglionic fibre longer in the sympathetic nervous system or parasympathetic nervous system? |
Parasympathetic
|
|
|
Postganglionic fiber is longer in the |
Sympathetic NS |
|
|
Name three major differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic NS |
1. Sympathetic have short preganglionic fibres and longer postganglionic fibers. Parasympathetic are the opposite. 2. Parasympathetic has some nerves from the brain (CN III, VII, IX, and X) and then sacral spine (S2-S4), sympathetic entirely contained in spinal cord 3. Parasympathetic has ACh at both pre and postganglionic synapses, sympathetic has NE at postganglionic synapse
|
|
|
Muscarinic receptors |
ACh receptors found after postganglionic Metabotropic (slow) Inhibitory and excitatory depending on subtype (M1-5) Target tissues: Bronchoconstriction (M3), decrease HR (M2) Atropine will inhibit |
|
|
Nicotinic receptors |
ACh receptors Excitatory and fast Postganglionic (sympa and parasympa) |
|
|
Name the three NE receptors |
Alpha - excitatory (except in gut) Beta 1 - inhibitory Beta 2 - Inhibitory |
|
|
Describe the ANS responses in the lung |

|
|
|
What brain region exhibits a lot of control over ANS? |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
What is the main neural controller of the gut? |
Myenteric plexus Can function independently |
|
|
Describe autonomic nervous system control of enteric nervous system |
PNS generally stimulatory, increases secretions, motility and blood flow (rest and digest). SNS inhibitory reducing secretions and decreasing motility and blood flow |

