![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
271 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of the respiratory system |
Exchange of gases Regulation of pH Trap and expel pathogens and irritants Vocalization |
|
|
How does vocalization of the respiratory system work |
You forced air through the vocal cords to talk |
|
|
Ventilation |
Physical act of moving air or breathing |
|
|
Respiration |
Gas exchange |
|
|
External respiration |
Happens in the lungs |
|
|
Internal respiration |
Happens at the tissues |
|
|
Structure of the upper respiratory tract includes |
Nose, pharynx, larynx |
|
|
Characteristics of the upper respiratory tract |
Warms and moistens the air and is mucus lined |
|
|
Structure of the lower respiratory tract |
Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli Cartilage and smooth muscle |
|
|
Characteristics of the lower respiratory tract |
Single layer of epithelium with elastic fibers Secrete surfactant and have macrophage |
|
|
Surfactant |
Oily substance that helps keep air sacs open |
|
|
What do we breathe in and out |
O2 in CO2 out |
|
|
Diaphragm |
Dome-like structure that pulls on lungs |
|
|
Pleura |
Double layered Sac that covers each lung and contains a thin layer of fluid between layers |
|
|
Muscles involved in inhalation |
Diaphragm, scalenes, and external intercostals contract |
|
|
Muscles involved in exhalation |
Diaphragm, scalenes, and external intercostals to relax |
|
|
how much blood per minute do the lungs receive |
Same amount as the rest of the body |
|
|
The right ventricle to the pulmonary artery is under what kind of pressure |
Very low |
|
|
Long has a tendency to what while thorax has a tendency to what |
Collapse while thorax expands |
|
|
Intrapleural pressure |
Helps keep the lung expanded |
|
|
Ventilation in the lungs |
Is inhalation muscles contract it pulls on the parietal pleura, section of fluid and intrapleural space pulls on visceral pleura pulling on the lungs to expand them Expansion of the lungs causes drop in pressure within lung and air Flows In - pressure gradient Expiration in reverse - muscles relax shrinking thoracic volume creating increase pressure on gases and lungs forcing the air out |
|
|
Compliance |
Ability of the lungs to stretch |
|
|
Elasticity |
Ability of the lungs recoil after stretching |
|
|
Bronchoconstriction |
Constriction of smooth muscles within respiratory tract |
|
|
Bronchodilation |
Relaxation of smooth muscle |
|
|
Respiratory distress syndrome |
When babies are born too early and long stick together and are very hard to expand |
|
|
Tidal volume |
Volume of air in resting exhalation or inhalation |
|
|
Average tidal volume |
500 ml |
|
|
Inspiratory Reserve volume |
Amount of air taken in after normal inhalation |
|
|
Expiratory Reserve volume |
Amount of air breathed out after normal exhalation |
|
|
Vital capacity |
The maximum amount of air that you can voluntarily move in or out of the lung |
|
|
How to figure out vital capacity |
IRV + Erv + TV |
|
|
Average vital capacity for men and women |
Men 4800 women 3100 |
|
|
Residual volume |
The amount of air that cannot be forced out of the lungs |
|
|
Dead Space |
Air that never reaches the alveoli Last air in first air out |
|
|
Partial pressure |
The pressure exerted by a single gas within a mixture of gases in a closed system |
|
|
Under Pressure gases will |
Dissolve into liquid |
|
|
Hemoglobin |
Oxygen-carrying molecule in red blood cell |
|
|
Hemoglobin will never reach 100% saturation we can only carry a about |
97% |
|
|
What affects O2 binding |
PH and temperature |
|
|
One red blood cell carries how many O2 |
4 |
|
|
Four main gases in our atmosphere |
Nitrogen - PN 2 Oxygen- 02 Carbon - PCO2 Water - H2O |
|
|
Oxygen exchange from alveoli to blood |
Po2 of alveoli is 100 mmhg Po2 of pulmonary blood flow is 40 mm HG 02 flows down pressure gradient from alveoli into blood O2 carried in Blood by binding to hemoglobin |
|
|
Oxygen exchange from blood to tissues |
At arterial end of capillary the po2 of blood is 100 mmhg Po2 of tissues is always lower 40 mm HG 02 flows down pressure gradient from the blood into tissues Po2 of venous blood flow back to lungs is 40 mm HG |
|
|
Carbon dioxide exchange from tissues to blood |
Pco2 is a byproduct of metabolism so it is high and cells and tissues Pco2 of tissues is 46 mm HG well of blood at capillary is 40 mmhg Carried by Blood h3o see leaves red blood cell while hemoglobin binds to H+ |
|
|
Gas exchange picture |
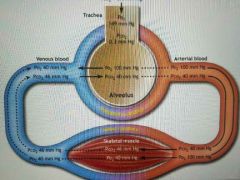
|
|
|
Three ways carbon dioxide can be carried by Blood |
Bound to hemoglobin - 23% Dissolved into plasma - 7% Converted into bicarbonate - vast majority |
|
|
Equation of how it's bound into bicarbonate |
CO2 + H2O⬅➡ H2CO3⬅➡ H+ + HCO3 |
|
|
Bicarbonate picture |
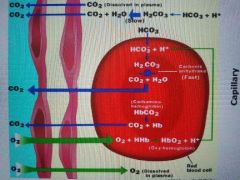
|
|
|
Hyundai Accent exchange from blood to alveoli |
Blood arrives at the lungs - alveolar pco2 is 40 mmhg so netflow is out of lungs into atmosphere Hco3 moves back into RBC and forms h2co which is converted to CO2 + H2O both diffuse out of blood into alveoli |
|
|
Medulla oblongata in regulation of ventilation |
Causes contraction of diaphragm and intercostal |
|
|
Breathe in for how long breathe out for how long |
In 2 seconds out for 3 |
|
|
Peripheral chemoreceptors |
Carotid and aortic bodies |
|
|
What do peripheral chemoreceptors do |
Sense changes in oxygen, pH, and pco2 Increase ventilation |
|
|
What stimulates peripheral chemoreceptors |
Pathological conditions |
|
|
Central chemoreceptors are found |
In the CNS |
|
|
What do central chemoreceptors do |
Detect pH changes in the CSF Increase ventilation |
|
|
What does blood-brain barrier block |
Hydrogen ions from entering the brain but not CO2 |
|
|
What happens if blood flow drops to area of lung |
Capillary clothes off and blood shunted to another area of the lung |
|
|
If po2 in alveoli drops |
Arterioles and capillaries constrict |
|
|
If po2 in alveoli increases |
Arterioles and capillaries dilate |
|
|
Carbon monoxide binds tighter to |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
Where do we have to keep our pH at |
Between 7.38-7.42 |
|
|
Acidosis |
Too much hydrogen ions |
|
|
Where do most H+ is come from |
Aerobic respiration |
|
|
What is the byproduct of aerobic respiration |
CO2 |
|
|
CO2 + H2O⬅➡ H+ + hco3⬅➡ H2 CO3 |
Makes acid |
|
|
Buffer |
Combines with H+ to increase pH |
|
|
The more hydrogen |
The more acidic we are |
|
|
the less hydrogen |
The more basic we are |
|
|
Increased ventilation can reduce |
Acidity |
|
|
Kidneys excrete what into urine and what is reabsorbed into blood |
H+ into urine and hco3 is reabsorbed into blood to buffer more H+ |
|
|
Respiratory acidosis |
You are in an acidic State due to some sort of respiratory issue |
|
|
Formula for being in respiratory acidosis |
CO2 + H2O⬅➡ H2 CO3⬅➡⬆H+ +HCO3 |
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis |
Two basic getting rid of too much CO2 caused by hysterically hyperventilating |
|
|
Metabolic acidosis |
When you become acidic due to metabolic reasons, the reactions push from right to left |
|
|
Metabolic alkalosis |
When you are too basic and don't have enough hydrogens Dehydration |
|
|
Increased ventilation makes you |
Acidic |
|
|
Decreased ventilation makes you |
Basic |
|
|
Kidneys |
Next |
|
|
Function of the kidney |
Regulate blood volume Ion balance Regulate PH Excretion of waste Produce two hormones |
|
|
Ion balance |
Regulate vitamin levels |
|
|
Regulate PH |
Kidney will secrete hydrogen ions into urine depending on the acidity level |
|
|
Excretion of waste |
Urea and uric acid |
|
|
Production of two hormones |
EPO or erythropoietin Renin |
|
|
EPO |
Increases RBC production, testosterone encourages this |
|
|
Nephron |
Functional unit of kidney, where urine is produced |
|
|
Each kidney has how many nephrons |
About a million |
|
|
Peritubular capillaries |
Job is to pull good stuff back into the blood |
|
|
Micturition |
Physical act of urinating |
|
|
Internal and external sphincter muscles are what kind |
Smooth external skeletal |
|
|
There are stretch receptors in the wall of the bladder that will |
Send impulses that activate parasympathetic nervous system to interact smooth muscles in the bladder wall |
|
|
How much urine does it take to stimulate the urge to urinate |
About 200 to 400 ml |
|
|
What are the pressures for filtration |
Blood pressure within the glomerulus early because inside is 55, the outside is 30, 25 trying to come in and 7 trying to go out |
|
|
Filtrate contest similar to plasma except |
No large proteins, cells or platelets |
|
|
Glomerulus filtrate rate |
Amount of fluid that filters into Bowman's capsule per unit of time |
|
|
Average GFR |
180 liters a day |
|
|
Proximal tubular reabsorption process |
Hydrostatic pressure in the peritubular capillary is 10 mm HG Na + flows down concentrate gradient from inside tubule Lumen to inside tubular wall cell via carrier protein Glucose flows down concentration gradient into interstitial fluid across cell membrane via carrier molecule Na + / k+ pump sends and a back out of cell 65 to 75% of filtrate reabsorbed into to proximal tubule Small proteins leave Lumen into tubule via endocytosis into cell of wall and degraded |
|
|
Proximal tubular wall is how thick |
Single cell thick |
|
|
Saturation |
Too much glucose to bind to receptors or co-transporter |
|
|
Sodium glucose co-transporter |
Only the amount that are able to bind can and the rest go to the urine |
|
|
Secretion |
Opposite of reabsorption from blood to tubule |
|
|
Integration the cell has carriers that recognize |
Foreign substances |
|
|
Loop of henle is responsible for |
Excreting NaCl to set up hypertonic environment for reabsorption of water into Vasa recta |
|
|
In loop of henle |
Concentrated urine is created because water is pulled from it |
|
|
ADH |
Antidiuretic hormone |
|
|
What does the ADH do |
Friends to cells of the collecting duct causing water channels to insert into the cell membrane of cells in the wall, water then leaves collecting duct and is reabsorbed into capillaries |
|
|
Where is ADH secreted from |
Posterior pituitary |
|
|
Clearance |
The kidneys ability to remove a substance from filtrate |
|
|
Provides an indication of the kidneys ability to |
handle substance |
|
|
If less substance is in urine than filtrate |
Net reabsorption |
|
|
If more of substance is in urine than filtrate |
Net secretion |
|
|
If the same amount of substance in urine than filtrate |
No net reabsorption or secretion |
|
|
Osmolarity |
Concentration of solutes per liter of fluid |
|
|
Water consumption must equal |
Water excretion |
|
|
Excessive urination can |
Decrease blood volume and blood pressure |
|
|
Excessive sweating can |
Increase tissue osmolarity |
|
|
Aldosterone |
Comes from adrenal cortex |
|
|
Where NA+ Is, |
Water will follow |
|
|
Excessive salt results in |
Excessive water in blood plasma, which increases blood pressure |
|
|
Excess salt without drinking water results in |
High osmolarity causing cells to shrink |
|
|
Aldersterone results in NA+ what and K what and where |
Na reabsorption and K loss at distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts |
|
|
Aldersterone results in NA+ what and K what and where |
Na reabsorption and K loss at distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts |
|
|
Aldersterone acts to open |
Na+ channels allowing na+ to enter tubular wall cell and then be pumped back out by Na+/K+ pump and flow into blood |
|
|
Steps of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway |
Low blood pressure stimulates in afferent arteriole Cells in afferent arteriole entering nephron secrete renin Renin converts angiotensinogen (plasma protein) to angiotensin 1 In blood, angiotensin 1 converted to angiotensin 2
|
|
|
Angiotensin 2 causes: |
Release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex Release of ADH Stimulates thirst Vasoconstriction Increase cardiac output |
|
|
A c e inhibitors |
Medication for high blood pressure which inhibits anything after the renin conversion to Angiosten one not happen |
|
|
Atrial natriuretic peptide |
From atria to heart, stimulated by high blood pressure, which then results in NA+ and water excretion |
|
|
What is ANP stimulated by |
Stretch in atria |
|
|
Acid-base regulation at kidney |
Hco3 usually reabsorbed and H+ secreted |
|
|
Digestion |
Next |
|
|
Digestion |
Breakdown of food into molecular component parts to be absorbed into bloodstream |
|
|
Absorption |
Component parts enter bloodstream We could absorb peptides amino acids and fatty acids |
|
|
Motility |
Propelling food through the system churning mixing and moving along |
|
|
Secretion |
Fluid and enzymes secreted by organs or accessory organs to aid in digestion |
|
|
Examples of accessory organs |
Salivary Stomach Pancreas Liver |
|
|
Examples of accessory organs |
Salivary Stomach Pancreas Liver |
|
|
Three major types of motility |
Migrating Motor complex Peristaltic contractions Segmentation |
|
|
Migrating Motor complex |
Series of contraction throughout digestive organs, occurs between meals |
|
|
How long does migrating Motor complex take |
About 90 minutes to complete |
|
|
Peristaltic contractions |
Progressive waves of contractions for propelling food along, occurs during and following meals |
|
|
Segmentation |
Random contractions for mixing, occurs and small intestine due to presence of food |
|
|
Saliva |
Moistens food for swallowing |
|
|
Bolus |
Slimy ball of food that occurs after chewing |
|
|
Amylase |
Begins carbohydrate digestion |
|
|
Lipase |
Begins digestion of fats |
|
|
When is lipase active |
Not until the stomach |
|
|
Lysosome and immunoglobulins |
Weak antimicrobial that is found in sweat and saliva |
|
|
Mastication |
Fancy word for chewing |
|
|
Esophagus roll in digestion |
Deglutition Mucus added to the bolus Peristaltic contractions move food to the stomach |
|
|
Deglutition |
Swallow |
|
|
Stomach structure |
Has a fundus body and pylorus Rugae |
|
|
In between rugae |
Gastric glands |
|
|
Goblet cells |
Secrete mucus and bicarbonate |
|
|
Parietal cells |
Secrete HCL Secretes intrinsic factor A little deeper from goblet Denatures proteins and destroys pathogens |
|
|
What does hydrochloric acid do to proteins |
Denature them, unfolds them |
|
|
What does intrinsic factor do |
Absorbs vitamin B12 |
|
|
Chief cells |
Secrete pepsinogen and protease |
|
|
Pepsinogen is converted to |
Pepsin |
|
|
Protease |
Enzymes that breaks protein up |
|
|
G cells |
Secrete gastrin into blood Controls motility and gastric juice secretions |
|
|
Chyme |
Soupy mixture of food and fluids |
|
|
How much chyme will enter the small intestines at a time |
Two tablespoons |
|
|
How much is absorbed in the stomach |
Very little |
|
|
Main job of the stomach |
To start digestion of proteins and fats |
|
|
What are the two things that can be absorbed in the stomach |
Aspirin and alcohol |
|
|
The what is helicobacter pylori |
Something that causes stomach ulcers |
|
|
Cephalic phase of gastric regulation |
Peristaltic contractions in gastric juice secretion begin when we see smell or think of food |
|
|
Gastric phase of gastric regulation |
The release of gastric juices in response to distension of stomach and protein in stomach |
|
|
Intestinal phase of gastric regulation |
Inhibition of gastric activity when chyme enters the small intestine, it slows gastric emptying |
|
|
What happens when too much food is released into the intestines |
A hormonal signal is sent to the stomach telling it to slow down otherwise it won't get digested |
|
|
Job of the pancreas |
To secrete juices into the intestines to help us Digest |
|
|
What stimulates pancreas to secrete juices |
Cck |
|
|
Bicarbonate |
Neutralizes acid in chyme |
|
|
Trypsin |
Activates pancreatic enzymes |
|
|
Two types of protease s |
Endopeptidases and exopeptidases |
|
|
Endopeptidases |
Breaks the backbone of carbon nitrogen Bond C-c-n-c-c-n |
|
|
Exopeptidases |
Removes amino acids from the backbone C-c-n-c-c-n |
|
|
Lipase |
Digest lipids |
|
|
What can we digest into the intestines |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
Bile and bile salts |
Synthesized by the liver and stored and gallbladder Secreted for digestion and absorption of lipids |
|
|
Bile salts do what |
Emulsify fats into tiny droplets so that lipases can get digested |
|
|
If you cannot secrete bile what happens |
Fats cannot get digested and bilirubin cannot be released as well |
|
|
Bile release is stimulated by |
Cck and secretin |
|
|
Liver functions |
Stores glucose as glycogen Detoxifies drugs alcohol and hormones Secretes bilirubin into small intestine for excretion from body |
|
|
Where are plasma proteins made |
Liver |
|
|
Where does everything we eat go first |
To the liver |
|
|
Bile is made up of |
Water, cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile salts |
|
|
90% of digestion and absorption happens where |
Small intestine |
|
|
Microvilli are also called |
Brush border |
|
|
What does the brush border contain and do |
It contains lipase, protease, and amylase It finishes digestion that the mouth, stomach, and pancreas couldn't do |
|
|
Once digested from brush border where does it go |
Into the blood |
|
|
Plicae |
Gives more surface area and intestines some more food touches mucus for digestion |
|
|
Secretin and cck |
Both inhibit acid production Secreted into the bloodstream in response to chime Stimulates pancreas and liver to release juices |
|
|
Brush border enzymes and glucose galactose |
Disaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides Glucose galactose enter cell via na+ glucose co carrier carried out by facilitated diffusion than simple diffusion into capillary |
|
|
Brush border enzymes and fructose |
Enter cell by facilitated diffusion, out the same way simple diffusion into capillary |
|
|
We are all born with normal what |
Lactase enzymes |
|
|
Brush border enzymes and proteins |
Die and tripeptides can enter the cell with an H + Co carrier and exit the cell in the same manner Amino acids removed and enter cells via na Co carrier and exit with the same mechanism Small peptides enter via endocytosis and exit by exocytosis |
|
|
Brush border enzymes and lipids |
Biocell emulsifies lipids lipase begins digestion and form micelle and enter cell directly Recent the sized into triglycerides by smooth ER and packaged into chylomicrons by Golgi and sent to lymph Eventually enters the blood In the blood chylomicron with triglyceride broken apart again so cell can utilize fatty acids and glycerol |
|
|
The large intestine can't |
Digest or absorb |
|
|
Haustra |
Bulging pockets contractions Propel feces |
|
|
Mass movement |
Waiver of forward contraction three to four times a day |
|
|
Concentrates waste by |
Absorbing most of the remaining water and electrolytes |
|
|
Reproduction |
Next |
|
|
Gametes |
Haploid Eggs and sperm |
|
|
Haploid |
Half the number of chromosomes |
|
|
Zygote |
Fertilized egg or diploid |
|
|
Autosomal chromosome |
Gene's for bodily jobs Chromosome 23 is gender |
|
|
Mitosis review |
Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
Meiosis review |
IPMATPMAT The second m is where the sisters finally split |
|
|
During fetal development the hormone get stuck at |
Prophase 1 until puberty |
|
|
Presence or absence of Y chromosome |
Determines male or female |
|
|
Gender determination depends on |
Presence or absence of sry gene Produces testis determining Factor protein |
|
|
Where does gamete production begin |
In utero |
|
|
Testes means |
Witness |
|
|
Seminiferous tubules |
Site of spermatogenisis |
|
|
How many tubules inside each teste |
200-300 |
|
|
Sertoli cells |
Surround developing sperm to nourish and protect |
|
|
Sperm mature from... |
Outer edge of tubule to lumen Grow tails, lose cytoplasm, and concentrate mitochondria in midpiece |
|
|
Leydig cells |
Located outside of tubules Secrete testosterone |
|
|
Hormones |
GnRH FSH LH Sertoli cells. Leydig cells Androgen bind. prot. Testosterone Spermatocyte |
|
|
Epididymis |
Coiled tubules sitting next to the testi Sperm travel here to be stored and further mature Learn to swim here |
|
|
Vas Deferens |
Carries sperm from epididymis to urethra, and unites with the prostate gland, carrying sperm out the penis Sperm is stored here |
|
|
Vasectomy |
Vas deferens snipped and tied in scrotum |
|
|
Men mature how much sperm per day |
Millions |
|
|
If a man has less than 50 million sperm |
He has fertility problems |
|
|
Accessory glands |
Add fluid to sperm |
|
|
Prostate |
Adds fluid sugar, and nutrients to seman Enzymes to liquify seman Contains the bicarbonate |
|
|
Seminal vesicles |
Adds fluid, fructose, and vitamin C to the semen Has an enzyme that coagulates the semen giving it the opportunity to go through the cervix by holding it in place |
|
|
How long does seman stay coagulated |
20 minutes |
|
|
Bulbourethral glands |
Add fluid to the semen Mucus and bicarbonate |
|
|
How much of semen is fluid and how much is sperm |
95% fluid 5% sperm
|
|
|
How many sperm per ejaculation |
300 to 500 million |
|
|
Ovary |
Site of oogenisis |
|
|
Oogenisis |
Development of eggs |
|
|
How many eggs are women born with |
2 million |
|
|
How many eggs actually mature |
400 |
|
|
Follicular phase of the menstrual cycle |
Fluid-filled sac containing the egg GnRH stimulates FSH which stimulates several follicles to grow LH stimulates estrogen production from follicle preparing lining of the uterus As estrogen increases FSH and LH decrease slightly very high levels of estrogen now enhance GnRH - FSH / LH LH surge causes ovulation |
|
|
Ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle |
Ovulation - release of egg from follicle 16 to 24 hours after LH surge ovulation happens Egg caught by fimbriae in oviduct Cilia beat toward uterus moving egg along |
|
|
What is the egg covered in while moving toward the uterus |
Zona pellucida Or glycoprotein coat |
|
|
Luteal phase of the menstrual cycle |
Corpus luteum - remnants of burst follicle Produces progesterone and estrogen this lasts 12 days while progesterone and estrogen decline Continue to thicken lining of uterus inhibin and estrogen inhibits GnRH Two days later blood vessels and uterus contract killing cells - menstration |
|
|
Oral contraceptives contain |
Progesterone and estrogen that they can cervical music and inhibit GnRH |
|
|
Upon ejaculation, smooth muscles in the vas Deferens and accessory glands contract |
Combining sperm with fluid |
|
|
How long does it take to semen that is deposited at the cervix to reach the oviduct |
About 30 minutes |
|
|
How long can semen live in the cervix |
3 to 7 days |
|
|
Capacitation |
Final step of maturation of the sperm Removal of glycoprotein from Outer membrane of sperm head |
|
|
You cannot fertilize an egg until |
Sperm is capacitated |
|
|
How long does it take sperm to be capacitated |
7 hours |
|
|
How long does the egg live |
12 to 48 hours |
|
|
Where does most fertilization take place |
In the distal oviduct |
|
|
Of the 300 million sperm deposited how many actually make it to the egg |
A few hundred because some will get lost |
|
|
What happens when the sperm reaches the egg |
They really sends items from acrosome to dissolve layers around it |
|
|
When one sperm reaches the egg cell membrane it does what |
Binds to sperm binding receptor in fuses with membrane allowing nucleus to enter egg |
|
|
Binding of one sperm causes what |
Reaction in the egg membrane so no other sperm can bind - shuts off receptors |
|
|
What part of the sperm enters the egg |
Only the nucleus |
|
|
After fertilized egg does what |
Continuous meiosis and begins mitosis Travels down to uterus which takes about 4 days |
|
|
Blastocyst |
Hollow ball of cells begins implantation into thick lining and gross finger-like extensions into lining very close to maternal blood supply |
|
|
When does implantation occur |
7 to 10 days after fertilization |
|
|
Cells that will become the placenta produce |
Human chorionic gonadotropin or HCG |
|
|
HCG does what |
Ends up in Mom's bloodstream and secreted in urine Pregnancy test detects this Maintains corpus luteum Stimulates testosterone in male fetus |
|
|
How long does HCG maintain corpus luteum |
About 7 weeks |
|
|
Placenta will begin to secrete what |
Estrogen |
|
|
How long from conception will labor begin |
38 weeks |
|
|
How is labor thought to be induced |
Buy oxytocin released from baby and mother or drop in progesterone |
|
|
What happens during labor |
Baby drops lower into pelvis pushing on cervix Relaxin from ovaries and placenta soften cervix Cervical stretch from weight of baby induces oxytocin released from mother causes uterine contractions |
|
|
What kind of feedback is cervical stretching |
Positive |
|
|
Three stages of birth |
Labor - dilation and effacing Pushing and delivery Expulsion of placenta |
|
|
Prolactin |
Milk production |
|
|
Oxytocin |
Milk let down |
|
|
Menopause |
Cessation of menses Ovaries quit responding to FSH and LH |
|
|
Average age of menopause |
51 to 52 |

