![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Spironolactone is effective in the treatment of hypertension because it blocks
beta-adrenergic receptors. B.Ca2+ channels. C.aldosterone effects on the kidney. D.cortisol effects on the kidney. E.alpha-adrenergc receptors. |
Aldosterone effects on the kidney
|
|
|
Angiotensin receptor-1 (AR1) antagonists are primarily used for
A. acute coronary thrombosis with pulmonary edema. B. combination with ACE inhibitors. C. hepatic cirrhosis with ascites. D. hypertension. E. patients with increased aldosterone secretion |
Hypertension
|
|
|
Angiotensin receptor-1 (AR1) antagonists differ from angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in that AR1 antagonists cause
A. cough and angioedema in some patients. B. greater decreases in tissue levels of angiotensin II. C. more secretion of renin. D. more stimulation of aldosterone secretion. E. superior antihypertensive responses in some patients |
Superior antihypertensive responses in some patients
|
|
|
Nearly two-thirds of filtered sodium is reabsorbed in which segment of the nephron?
A. Collecting ducts B. Distal convoluted tubules C. Proximal renal tubules D. Thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle E. Thin descending limb of the loop of Henle |
Proximal Renal tubules
|
|
|
Which portion of the nephron utilizes the greatest amounts of ATP?
A. Collecting ducts B. Distal convoluted tubules C. Proximal renal tubules D. Thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle E. Thin descending limb of the loop of Henle |
Thick Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs is LEAST effective when used alone for prolonged treatment of patients with edema?
A. Amiloride B. Ethacrynic acid C. Furosemide D. Hydrochlorothiazide E. Mannitol |
Amiloride
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs is used to treat hypocalcemic states?
A. Acetazolamide B. Amiloride C. Captopril D. Furosemide E. Hydrochlorothiazide |
Hydrochlorothiazide
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs has an antihypertensive effect at low doses and an antidiuretic effect at high doses?
A. Bumetanide B. Hydrochlorothiazide C. Lisinopril D. Losartan E. Spironolactone |
Hydrochlorothiazide
|
|
|
Furosemide can produce all of the following effects EXCEPT
A. acute renal failure. B. enhanced renin secretion. C. hypokalemia. D. metabolic alkalosis. E. toxicity similar to that of sulfonamides. |
Enhanced renin secretion
|
|
|
All of the following diuretics act at the lumenal side of renal tubules EXCEPT
A. bumetanide. B. ethacrynic acid. C. hydrochlorothiazide. D. spironolactone. E. triamterene. |
Spironolactone
|
|
|
Spironolactone is effective in the treatment of hypertension because it
a) behaves as a beta-adrenergic antagonist (beta blocker) b) blocks Ca++ channels c) blocks aldosterone effects on the kidney d) blocks acetylcholine binding |
blocks aldosterone effects on the kidney
|
|
|
Which of the following combinations of diuretic drugs is LEAST effective?
a) Bumetanide and hydrochlorothiazide b) Furosemide and triamterene c) Hydrochlorothiazide and amiloride d) Spironolactone and triamterene e) Spironolactone and furosemide |
Spironolactone and Triamferene
|
|
|
Furosemide can produce all of the following effects EXCEPT
a) hypokalemia b) acute renal failure c) toxicity similar to that of sulfonamides d) enhanced renin secretion e) metabolic alkalosis |
Enhanced renin secretion
|
|
|
All of the following diuretics act at the lumenal side of renal tubules EXCEPT
a) hydrochlorothiazide b) triamterene c) ethacrynic acid d) bumetanide e) spironolactone |
Spironolactone
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs has an antihypertensive effect at low doses and an antidiuretic effect at high doses?
a) Bumetanide b) Lisinopril c) Spironolactone d) Hydrochlorothiazide e) Losartan |
Hydrochlorothiazide
|
|
|
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors are used clinically for all of the following indications EXCEPT
a) treatment of cardiac systolic dysfunction b) therapy of normal-renin associated hypertension c) management of hypokalemia d) treatment of acute coronary thrombosis and pylmonary edema e) prevention of cardiac remodeling in hypertensive states |
Management of hypokalemia
|
|
|
What does angiotensin do to blood vessels?
|
Vasoconstriction
|
|
|
ACE inhibitors such as Captopril are effective in the treatment of congestive heart failure because they are
a) afterload reducing agents b) preload reducing agents c) direct vasoconstrictors d) direct vasodilators e) effective in increasing sodium and water retention |
Afterload reducing agents
|
|
|
What does kidney dysfunction have a major impact on?
|
Drug clearance
Drug T 1/2 Adverse effects - the longer you have the drug or metabolite around, the higher the chance there is for an adverse effect, either from the drug or the metabolite. |
|
|
What are the risk factors for CKD?
|
1. Diabetes mellitus
2. Hypertension 3. Cardivascular disease 4. Family Hx of ESRD 5. In US prevalence of CKD in people >65 w/o hypertension and diabetes is 11% (apparently, just through surviving) |
|
|
What is the strongest independent predictor of progression of CKD?
|

Albumin to Creatinine ratio
|
|
|
Does GFR stabilize after declining below 50% of normal?
|

It doesn't stabilize at some lower level. It just keeps going down. This is the problem
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for progression of CKD?
|

1. Proteinuria
2. Diabetes Mellitus 3. Smoking 4. High dietary protein consumption 5. Obesity 6. Blacks have Increased risk 7. Women have increased risk 8. Cardiovascular Disease |
|
|
What are the complications of CKD?
|

1. Anemia
2. Osteodystophy 3. Cardiovascular problems 4. Operations - even minor |
|
|
What are people most likely to die from if they have CKD?
|

Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
|
What clears ACE inhibitors?
|

Kidney
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of ACE inhibitors?
|

1. Teratogenic
2. Hypotension 3. Cough 4. Hyperkalemia 5. Abnormal taste |
|
|
What are the drug interactions associated with ACE inhibitors?
|

1. Lithium increases (easy to get lithium toxicity)
2. NSAIDs (reduce ACE inhibitor levels) 3. K+ Supplements (Increased hyperkalemia) |
|
|
How is Lithium associated with ACE inhibitors?
|

Lithium, is used to treat mania or depression and is increased by ACE inhibitors. Lithium toxicity is a risk.
|
|
|
What is the interaction between ACE inhibitors and NSAIDs?
|

If NSAIDs are taken chronically, it may reduce ACE inhibitor levels
|
|
|
What is the interaction between K+ and ACE inhibitors?
|

ACE inhibitors can create hyperkalemia, so don't take K+ supplements
|
|
|
How do you know if something is an Angiotensin Receptor Antagonist?
|
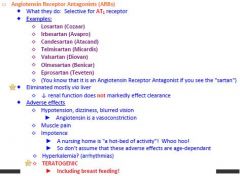
Angiotensin Receptor Antagonist is you see SARTAN
|
|
|
What eliminates Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists?
|
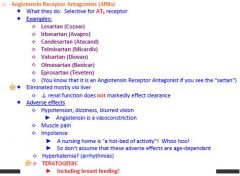
Liver, so decreased renal function does not affect clearance
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects caused by Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists?
|
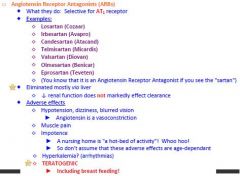
1. Teratogenic -including breast feeding
2. Impotence 3. Muscle pain 4. Hypotension, dizziness, blurred vision 5. HYPERKALEMIA |
|
|
What are the drug interactions associated with Angiotensin Receptor Inhibitors?
|

1. Lithium
2. NSAIDs 3. K+ sparing diuretics 4. K+ supplements 5. Fluconazole 6. Rifampin |
|
|
What problem occurs in patients taking Fluconazole and Angiotensin Receptor Inhibitors?
|

Decreases fluconazole's metabolism to an active metabolite
|
|
|
What drug interactions occur between Angiotensin Receptor Inhibitors and Rifampin and Erythromycin?
|

Increases the metabolism
|
|
|
What are the Contraindications in CKD?
|

1. General Anesthetics
2. Midazolam 3. NSAIDs 4. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 5. Analgesics |
|
|
Why don't we use General Anesthetics in CKD?
|

May increase K+ levels resulting in increased risk of cardiovascular incident
|
|
|
Why do we want to avoid Midazolam in patients with CKD?
|

Causes Prolonged Sedation
|
|
|
Which analgesics are okay to use in CKD?
|

Morphine
Tramadol |
|
|
In patients who have CKD what is the best choice of analgesia for perioperative?
|

Morphine or Fentanyl
|
|
|
In patients who have CKD what is the best choice of analgesia for postoperative?
|

Tramadol or Codeine
|

