![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
"__________ located in tissue signal tissue damage or trauma" |
Pain Receptors (nociceptors) |
|
|
Pain stimulus converted into a nerve signal that travels along peripheral nerves to the ________ (head) or _______ (body). |
Brainstem, Spinal Cord |
|
|
Processing occurs in _______ first and then the _______ where it reaches conscious perception. |
Thalamus, Cortex |
|
|
What is the order that function is lost due to Local Anesthetic? -Touch -Motor Control -Temperature/Pain -Proprioception (joint position) |
1) Temperature/Pain [small fibres] 2) Touch [medium fibres] 3) Proprioception (joint position) [large fibres] 4) Motor Control [large fibres] |
|
|
Large diameter ___ fibres transfer information to the brain very quickly because they are thickly covered by an insulator called myelin. |
A (fibres) |
|
|
What functions are transferred via Large A fibres (A-alpha, A-beta)? |
Sense muscle position, reflex activity, touch and pressure |
|
|
The smallest A fibres (A-delta) conduct nerve impulses more slowly because they are _______? |
Thinly Myelinated |
|
|
What functions are transferred via small A fibres (A-delta)? |
Pain & Temperature |
|
|
Smaller, ____ fibres lack myelin and conduct nerve impulses extremely slowly. |
C |
|
|
What functions are transferred via C fibres ? |
Pain & Temperature |
|
|
What is the structural difference between A fibres and C fibres? |
A fibres have Myelin, while C fibres lack Myelin. |
|
|
Large fibres conduct impulses quickly because they have large _______ distances (gaps) |
Intra-Nodal |
|
|
Nerves conduct information to the brain from tissues through the generation of _______ _______? |
Action Potentials |
|
|
Action potentials are propagated along the nerve as a result of a: A) Passive process which allows current to flow from down the axon B) Active process involving the opening of potassium & chloride channels C) Active process involving the opening of sodium & potassium channels D) A combination of a) and c) |
Answer: D |
|
|
How do impulses travel along the nerve from the tissues to the brain? |
Electrical impulses are generated at the terminals and travel up the nerve fibre through the opening of sodium channels in the axon membrane. |
|
|
To block electrical conduction in nerve fibres, several ______ need to be affected ? |
Nodes
[note: this is why it takes a longer time to inhibit motor function ] |
|
|
What are two example of Sodium Channel Blockers ? |
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Saxitoxin (STX) |
|
|
Which Sodium Channel Blocker is found in puffer fish testes and fugu? |
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) |
|
|
Which Sodium Channel Blocker is found in dinoflagellates and filter feeding shellfish (clams, mussels etc.) ? |
Saxitoxin (STX) |
|
|
How long does it take the body to remove the sodium channel blockers ? |
About an hour |
|
|
TTX and STX bind to a specific receptor on the ________ of the sodium channel to prevent sodium influx. |
Outside |
|
|
General chemical structure of Amide? |

|
|
|
General chemical structure of Ester? |
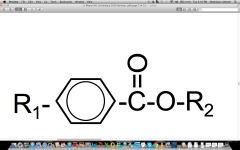
|
|
|
Why do local anesthetics need to have a lipophilic group ? (usually an aromatic group) |
To pass through the membrane bilayer, in order to block the sodium channel from the INSIDE. |
|
|
What causes the stinging sensation when you are injected with a local anesthetic? |
Due to the low pH of the drug kept in and when it is buffered |
|
|
How do you think it was determined that amides and esters LA work from inside the axon? |
A quaternary amine (which normally cannot pass due its positive charge) will work if injected directly into an axon but not when outside the axon. |
|
|
What is "Redistribution"? |
Body's blood stream tries to take compounds found locally and redistribute them throughout the body. |
|
|
How are esters and amides broken down? |
Esters – broken down by plasma esterases
Amides – broken down in liver by N-dealkylation and hydrolysis. |
|
|
"High concentrations (mM) of local anesthetics are used to achieve a block."
True or False? |
True: Increases the driving force to cross the axon membrane. |
|
|
"Hydrophobicity decreases potency of Local Anesthetics"
True or False? |
False: Hydrophobicty Increases ability of drug to cross the axon membrane. |
|
|
"Rate of metabolism is unimportant to the duration of a local anesthetic block. "
True or False? |
True: Rate of Redistribution determines block length. (Toxicity is affected by the Rate of Metabolism) |
|
|
" Lowering the pH can increase block efficacy and duration of local anesthetics"
True or False? |
False: Decreases the amount of uncharged drug, which decreases the amount passing into the axon, as well as increase the Redistribution rate (which would decrease duration). |
|
|
"Co-injected vasoconstrictors (e.g. epinephrine) can lengthen block duration. "
True or False? |
True: Delays the Redistribution rate, because the blood flow is much slower. |
|
|
What are the various routes of administration of local anesthetics? |
-Topical/ Surface -Infiltration (directly into affected tissue) -Nerve Block (near but NOT into the nerve) -Spinal (Subarachnoid or Intrathecal Injection) -Epidural (Into the fat surrounding the nerve) |
|
|
Which is faster to onset time, Spinal Anesthesia or Epidural Injection? |
Spinal is faster (5-10 mins), Epidural has more barriers to diffusion. |
|
|
What are the symptoms of central nervous system toxicity? |
Initial nervousness, dizziness, blurred vision and tremors (or lip tingling) Later drowsiness, convulsions, unconsciousness and respiratory arrest
|
|
|
What causes central nervous system toxicity? |
Direct effect of local anesthetics on neuronal sodium channels. |
|
|
What are the symptoms of cardiotoxicity? |
Hypotension, cardiovascular collapse, bradycardia and cardiac arrest. |
|
|
What causes cardiotoxicity? |
Direct effect of local anesthetics on cardiac and arteriolar sodium channels. [Indirect effect due to sympathetic blockade (spinal/epidural) and central nervous system] |
|
|
Which Local Anesthetics are administered topically? |
Benzocaine (skin/mucous membranes) Lidocaine Bupivacaine
|
|
|
Which Local Anesthetics are administered via infiltration? |
Procaine (dental) Lidocaine Bupivacine |
|
|
What are the routes of administration for Procaine? |
Infiltration (dental) |
|
|
What are the routes of administration for Benzocaine? |
Topical (skin/mucous membranes) |
|
|
What are the routes of administration for Lidocaine? |
All routes: topical, infiltration, epidural, caudal, spinal |
|
|
What are the routes of administration for Bupivacaine? |
All routes: topical, infiltration, epidural, caudal, spinal |

