![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an aneuploidy? |
Condition of having an abnormal number of chromosomes |
|
|
Aortic atresia means? |
Abnormality in which there’s a small or absent opening between the left ventricle and aorta. |
|
|
What’s the bat wing appearance? |
Fetal unilateral Pleural effusion |
|
|
What’s atrioventricular defect? |
Abnormal development of the central portion of the heart; AKA endocardial cushion defect. |
|
|
What is Bochdalek hernia? |
Herniation of abdominal contents into the chest cavity because there is an Opening in the left posterolateral portion of diaphragm |
|
|
What is chordae tendineae? |
Tendons in the heart that attach to mitral valve to left ventricle and tricuspid valve to right ventricle to their respective papillary muscle |
|
|
What is chordae tendineae? |
Tendons in the heart that attach to mitral valve to left ventricle and tricuspid valve to right ventricle to their respective papillary muscle |
|
|
What’s coarctation of the aorta? |
Narrowing of the aortic arch |
|
|
What is CCAM? |
Mass consisting of abnormal bronchial and lung tissue that develops within the fetal chest. |
|
|
What is CCAM? |
Mass consisting of abnormal bronchial and lung tissue that develops within the fetal chest. |
|
|
What is diaphragmatic hernia? |
Herniation of the abdominal contents into the chest cavity through a defect in the diaphragm |
|
|
This is a genetic disorder that has an absent thymus or hypoplastic thymus, ultimately leads to impairment of the immune system and susceptibility to infection, cognitive disorders, congenital heart defects, palate defect, hormonal abnormalities. |
DiGeorge syndrome |
|
|
What are the fetal shunts? |
3; Ductus arteriosus, ductus venosus, foramen ovale |
|
|
What are the fetal shunts? |
3; Ductus arteriosus, ductus venosus, foramen ovale |
|
|
What is Ebstein anomaly? |
Malposition of the tricuspid valve that causes multiple heart defects. |
|
|
What are the fetal shunts? |
3; Ductus arteriosus, ductus venosus, foramen ovale |
|
|
What is Ebstein anomaly? |
Malposition of the tricuspid valve that causes multiple heart defects. |
|
|
What is ectopic cordis? |
Condition in which the heart is located either partially or completely outside the fetal chest. |
|
|
What’s another name for atrioventricular defect? |
Endocardial cushion defect |
|
|
What is eventration of the diaphragm? |
Lack of the muscle in the dome of the diaphragm. |
|
|
What is foramen of Moragni? |
An opening located right anteromedially within the diaphragm |
|
|
Systemic disorder that leads to the development of tumors within various organs. |
Tuberous sclerosis |
|
|
Systemic disorder that leads to the development of tumors within various organs. |
Tuberous sclerosis |
|
|
Ventricular septal defect means? |
Opening within the septum that separates the right ventricle and left ventricle |
|
|
Systemic disorder that leads to the development of tumors within various organs. |
Tuberous sclerosis |
|
|
Ventricular septal defect means? |
Opening within the septum that separates the right ventricle and left ventricle |
|
|
What’s hypoplastic left heart syndrome? |
Small or absent left ventricle due to (incomplete development) |
|
|
Systemic disorder that leads to the development of tumors within various organs. |
Tuberous sclerosis |
|
|
Ventricular septal defect means? |
Opening within the septum that separates the right ventricle and left ventricle |
|
|
What’s hypoplastic left heart syndrome? |
Small or absent left ventricle due to (incomplete development) |
|
|
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome means? |
Small or absent right ventricle due to incomplete development |
|
|
What is lecithin to sphingomyelin ratio? |
A test of the amniotic fluid that predicts fetal lung maturity. |
|
|
What are papillary muscle? |
Paired muscles in both sides of the heart that hold in place either mitral or tricuspid valves. |
|
|
What’s pentalogy of Cantrell? |
It’s group of disorders: omphalocele, ectopic cordis, cleft sternum, anterior diaphragmatic defect, pericardial defects. |
|
|
Pleural effusion is? |
Abnormal fluid accumulation in pleural space. |
|
|
What is pulmonary sequestration? |
Separate mass of non functioning lung tissue with its own blood supply. |
|
|
What is pulmonary sequestration? |
Separate mass of non functioning lung tissue with its own blood supply. |
|
|
What’s pulmonary stenosis? |
Narrowing of pulmonary valve |
|
|
What is pulmonary sequestration? |
Separate mass of non functioning lung tissue with its own blood supply. |
|
|
What’s pulmonary stenosis? |
Narrowing of pulmonary valve |
|
|
What’s tetralogy of fallot? |
Group of abnormalities consisting of overriding aortic root, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy. |
|
|
What is pulmonary sequestration? |
Separate mass of non functioning lung tissue with its own blood supply. |
|
|
What’s pulmonary stenosis? |
Narrowing of pulmonary valve |
|
|
What’s tetralogy of fallot? |
Group of abnormalities consisting of overriding aortic root, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy. |
|
|
What’s transposition of greater vessels? |
The left ventricle is going to PA. Right ventricle to aorta. |
|
|
What’s tricuspid regurgitation? |
Leakage of the blood back through the tricuspid valve |
|
|
Monosomy X is called? |
Turner syndrome |
|
|
The chamber closest to the fetal spine is? |
Left atrium |
|
|
What chamber sends blood to flow through ductus arteriosus and into descending aorta? |
Right ventricle |
|
|
For the outflow tracts, normal positioning of the pulmonary artery is? |
Anterior to the aorta and should be visualized crossing over it. |
|
|
Right ventricle can send blood to? |
Through Ductus arteriosus and into descending aorta. |
|
|
Explain fetal circulation? |
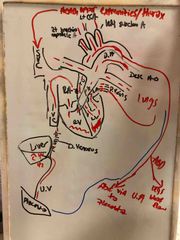
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the most anterior positioned chamber of the heart? What is the most posterior chamber of the heart? |
Anterior- right ventricle Posterior- left atrium (anterior to the spine) |
|
|
What is the leading cause of cardiac death in neonatal period. When found in females, what should be suspected? |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome; suspect turners syndrome. Also connection to Trisomy 18. |
|
|
What is the leading cause of cardiac death in neonatal period. When found in females, what should be suspected? |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome; suspect turners syndrome. Also connection to Trisomy 18. |
|
|
Sono finding in utero, aortic atresia. Aortic stenosis, coarctation of the aorta , no communication visualize between the left atrium and left ventricle. Absent or small left ventricle. |
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
|
|
What is the leading cause of cardiac death in neonatal period. When found in females, what should be suspected? |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome; suspect turners syndrome. Also connection to Trisomy 18. |
|
|
Sono finding in utero, aortic atresia. Aortic stenosis, coarctation of the aorta , no communication visualize between the left atrium and left ventricle. Absent or small left ventricle. |
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
|
|
This finding is seen in four chamber view. Stenosis of tricuspid valve, pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary atresia, enlarged left Ventricle but small /absent right ventricle. Fetal Hydrops. Suspect? |
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome |
|
|
What is the leading cause of cardiac death in neonatal period. When found in females, what should be suspected? |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome; suspect turners syndrome. Also connection to Trisomy 18. |
|
|
Sono finding in utero, aortic atresia. Aortic stenosis, coarctation of the aorta , no communication visualize between the left atrium and left ventricle. Absent or small left ventricle. |
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
|
|
This finding is seen in four chamber view. Stenosis of tricuspid valve, pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary atresia, enlarged left Ventricle but small /absent right ventricle. Fetal Hydrops. Suspect? |
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome |
|
|
What’s the most common form of cardiac defect? |
Ventricular septal defect |
|
|
What is the leading cause of cardiac death in neonatal period. When found in females, what should be suspected? |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome; suspect turners syndrome. Also connection to Trisomy 18. |
|
|
Sono finding in utero, aortic atresia. Aortic stenosis, coarctation of the aorta , no communication visualize between the left atrium and left ventricle. Absent or small left ventricle. |
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
|
|
This finding is seen in four chamber view. Stenosis of tricuspid valve, pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary atresia, enlarged left Ventricle but small /absent right ventricle. Fetal Hydrops. Suspect? |
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome |
|
|
What’s the most common form of cardiac defect? |
Ventricular septal defect |
|
|
Ventricular septal defect can be isolated, but if not what is it associated with? |
Tetralogy of fallot |
|
|
AVSD are commonly associated with? |
Trisomy 18, trisomy 21, aneuploidy |
|
|
Atrioventricular defects are? |
Absence atrial and ventricular septum. |
|
|
What anomaly is associated with tricuspid regurgitation? |
Ebstein anomaly (atrialized right ventricle), transposition of greater vessels, tetralogy of fallot, ASD, coarctation of the aorta. Prognosis poor. |
|
|
For coarctation of the aorta, most common location is? |
Left subclavian artery and ductus arteriosis. |
|
|
Finding; right ventricular enlargement. Pulmonary artery enlargement. Narrowing of aortic arch. |
Coarctation of the aorta |
|
|
Finding: overriding aortic root, subaortic VSD, pulmonary stenosis, (right ventricular hypertrophy manifests after birth). |
Tetralogy of fallot |
|
|
Echogenic intracranial focus is associated with? |
Trisomy 21 |
|
|
Most common fetal cardiac tumor? |
Rhabdomyoma |
|
|
This tumor is located in the myocardium of the heart and associated with tuberous sclerosis. |
Rhabdomyoma |
|
|
What is pentalogy of Cantrell? |
Combination of ectopic cordis and omphalocele. |
|
|
What is the most common lesion that occupies the chest, resulting pulmonary hypoplasia. Common finding? |
Diaphragmatic hernia. Oligohydramnios. Assoc with bilateral renal agenesis and abnormal facial features: potter syndrome. |
|
|
CCAM is? Most are Unilateral or bilateral? |
Mass consisting of abnormal bronchial and lung tissue. Mass is solid and cystic. However it can appear echogenic. Similar to pulmonary sequestration. Unilateral |
|
|
What’s pulmonary sequestration? |
Aka bronchopulmonary sequestration. Separate mass of non functioning lung tissue with its own blood supply. Echogenic triangular shaped mass. (Left side of chest)can resolve like CAM however it can also leave to developing fetal Hydrops. |
|
|
Finding includes anechoic stomach bubble adjacent to the four chamber heart view. Malposition of the heart. Other abdominal organs, liver pancreas, spleen may be located along the chest. |
Diaphragmatic hernia |
|
|
All of the following are sonographic sign of Ebstein anomaly except: A. Enlarged right atrium B. Malpositioned tricuspid valve C. Narrowing of aortic arch D. Fetal Hydrops. |
C. Narrowing of aortic arch |
|
|
All of the following are sonographic features of pentalogy of Cantrell except? A. Omphalocele B. gastroschisis C. Cleft sternum D. Diaphragmatic defect |
D. Diaphragmatic defect |
|
|
Which of the following is considered to be the most common cardiac defect? |
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |

