![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gene for marfan
|
Fibrillin
|
|
|
Gene for OI
|
collagen
|
|
|
Locus heterogeneity
|
Mutations @ diff loci but still produce the same phenotype Ex: OI - chrom 17 (colA1 gene), or chrom 7 (colA2 gene) |
|
|
Auto Rec & Locus Hetero in Congen Deafness
|
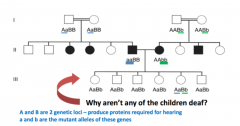
Scenario: Couple A = AaBB (a = mutant allele) --> through auto rec recurrence, 50% are affected (homos) Couple B - AABb (b = mutant allele) --> through auto rec recurrence, 50% are affected (homos) One affected from couple A (aaBB), and one affected from couple B (AAbb) get married.
|
|
|
Compound Heterozygote
|
Showing phenotype bc you inherited mutant gene from both parents Even though mutant gene are different alleles for each parent |
|
|
Germline mosacism
|
also called GONADAL mosacism mutation is present in proportion of germline cells Presence of 2 affected kids = germline mosacism |
|
|
mitochondrial inheritance
|
all offspring of affected female = AFFECTED
|
|
|
variable expression in mito disorders
|
heteroplasmy -- depends on number of mito w mutant gene
mito dna segregates passively during division --> unequal distribution of mutant/non-mutant mito dna leads to heteroplasmy and variable expression |
|
|
List of mito diseases
|
1. Leber hereditary optic neuropathy = progressive blindness around 20-30 yrs 2. MELAS = mito enceph, lactic acidosis, Stroke-like episodes 3. MERRF = myoclonic epilepsy w ragged red fibers (muscle) |
|
|
Disorders w non-Mendelian/Unexpected Inheritance Patterns
|
1. Digenic disorders = retinitis pigmentosa 2. imprinting = prader willi and angelman syndromes (both are parent of origin effect) 3. triplet repeat disorders = huntington (autodom), myotonic (autodom) and fragile x (x-linked) |
|
|
Digenic disorders
|
mutations in 2 genes = additive and required to produce disorder Think of retinitis pigmentosa = mutations in 2 independent loci (ROM1 & peripherin) - both need to be deleted in order for the disease to occur |
|
|
Imprinting (parent of origin effects)
|
some genes only active when transmitted --> methylation of specific loci (epigenetic change) & silencing the gene
|
|
|
Prader Willi Syndrome
|
- caused by a) microdeletion of paternal chromosome 15 (70% of thetime), or by maternal uniparental disomy of chrom 15 - Mental/developmental delays - Underdeveloped genitals |
|
|
Anticipation
|
Earlier age w each generation of pedigree --> the greater the # of repeats, the earlier the age of onset and the more severe --> huntington is more severe if from father |

