![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gene |
A length of DNA that codes for a single polypeptide or protein. |
|
|
Locus |
The position of a gene on a chromosome |
|
|
Allele |
The different forms a gene can exist in, different alleles of a gene can have slightly different nucleotide sequences but they still occupy the same position (locus). |
|
|
Genotype |
Refers to the alleles of a gene possessed by an individual, the different alleles can be represented by letters. |
|
|
Homozygous |
When two allele copies are identical in an individual, the different alleles can be represented by letters. |
|
|
Heterozygous |
When the two allele copies are different in an individual |
|
|
Phenotype |
An observable characteristics of an organism, affected by their phenotype. Phenotype = Genotype + Environment. |
|
|
Dominant Alleles |
They are always expressed in the phenotype |
|
|
Recessive Alleles |
They are only expressed in the phenotype if no dominant allele is present. |
|
|
Codominance |
Sometimes both alleles can be expressed in the phenotype at the same time, this is when an individual is heterozygous and they express both alleles as a result. |
|
|
F1 Generation |
When a homozygous dominat individual is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual the offspring are called the F1 Generation, they are all heterozygous. |
|
|
F2 |
If two individuals from the F1 Generation are crossed, the offspring they produce are called the F2 Generation. |
|
|
Sex Linkage |
Some Genes are found on a region of a sex chromosome that is not present on the other sex chromosome. As the inheritance of these genes is dependent on the sex of the individuals they are called sex-linked genes. |
|
|
Autosomal Linkage |
This occurs on the autosomes (any chromosome that isn't a sex chromosome), two or more genes on the same chromosome do not assort independently during meiosis therefore making them linked. |
|
|
Crossing Over |
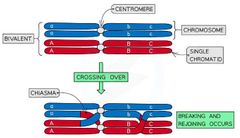
The process by which non-sister chromatids exchange alleles. This occurs during Meiosis I where homologous chromosomes are in very close proximity and non-sister chromatids can cross over and get entangled. |
|
|
Independent Assortment |
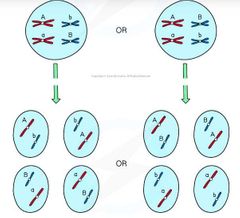
The production of different combinations of alleles in daughter cells due to the random alignment of homologous pairs along the equator during metaphase I. |
|
|
Mutations |
Genetic Variation can be caused by mutations, as mutations can result in the generation of new alleles which may be advantageous, disadvantageous or have no effect. |
|
|
Monohybrid Inheritance |
This looks at how the alleles for a single gene are passed on from one generation to the next. |
|
|
Monohybrid Crosses |
They look at how the alleles of one gene transfers across generations |
|
|
Dihybrid Crosses |
They look at how the alleles of two genes transfer across generations |
|
|
Epistasis |
When two genes on different chromosomes affect the same feature e.g One gene can affect the expression of another gene. |
|
|
Chi-Squared Test |
Determines whether there is a significant difference between the observed and expected results in an experiment.If the chi-squared value represents a larger probability than the critical probability then it can be stated that the differences between the expected and observed results are significant and not due to chance. The null hypothesis can be rejected. |
|
|
Calculating Chi-Squared |
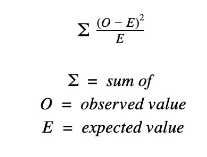
|
|
|
Continuous Variation |
The difference between individuals of a species where the differences are quantitative (Measurable) |
|
|
Discontinuous Variation |
The differences between individuals of a species where the differences are qualitative (Categoric) |
|
|
Bottleneck Effect |
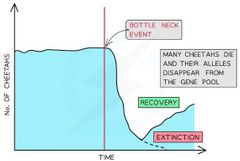
|
|
|
Genetic Isolation |
When two populations of the same species become reprouductively isolated from each other. |
|
|
Speciation |
The formation of new species from pre-existing species over time, as a result of changes to gene pools from generation to generation |
|
|
Allopatric Speciation |
Occurs as a result of geographical isolation, when species become seperated by barriers e.g body of water. |
|
|
Sympatric Speciation |
This takes place with no geographical barrier, a group of the same species could be living in the same place but in order for speciation to take place there must exist two populations within that group and no gene flow occurs between them. Something then happens that splits the two populations e.g Ecological and Behavioural seperation. |
|
|
Ecological Seperation |
Populations are seperated because they live in different environments within the same area e.g soil pH differs. |
|
|
Behavioural Seperation |
Populations are seperated because they have different behaviours e.g feeding, communication. |
|
|
Artifical Selection (Selective Breeding) |
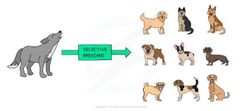
The process by which humans choose organisms with desirable traits and selectively breed them together to enhance the expression of these traits over time and over many generations. |
|
|
Ethical issues associated with Artifical Selection/ Selective Breeding |
Inbreeding, Reduction in gene pool, Inheritance of harmful genetic defects, Vulnerable to disease. |

