![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where are the Parathyroid Glands normally located?
|
Posterior surface of the Thyroid
|
|
|
What is the embryological origin of the Parathyroid glands?
|
Inferior parathyroids = 3rd Pharyngeal Pouch
Superior = 4th Pharyngeal Pouch |
|
|
Normal Parathyroid
-cuboidal Chief Cells = synthesize & secrete PTH |
What is seen here?
|
|
|
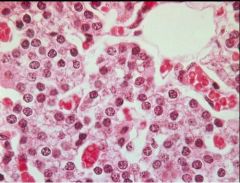
Waterclear cells of Parathyroid
-form of Chief Cell with more abundant, clear PTH secretions in their cytoplasm |
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Oxyphil Cells of Parathyroid
-contain numberous, red-staining Mitochondria -late stage chief cells = no longer secrete PTH |
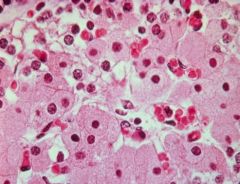
What is seen here?
|
|
|
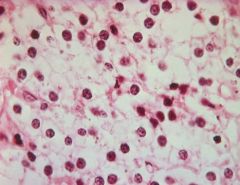
Waterclear cells of Parathyroid
-form of Chief Cell with more abundant, clear PTH secretions in their cytoplasm |
What is seen here?
|
|
|
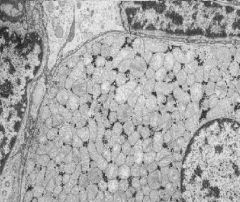
Oxyphil cell = stuffed with Mitochondria
|
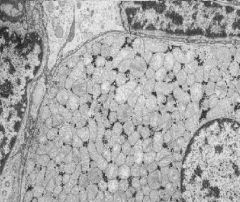
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Normal adult Parathyroid gland
-interspersed fat cells that increase with relative age -presence of fat cells helps differentiate from Hyperplastic Parathyroids |
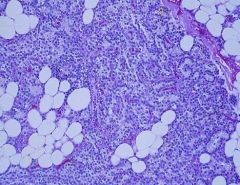
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Describe the structure of PTH
|
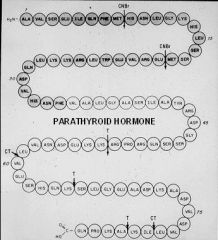
84 amino acids in length
-only first 34 are needed for function |
|
|
What are the 3 main functions of PTH?
|
1. Mobilize Calcium from Bone by stimulating Osteoclastic resorption
2. Promote renal excretion of Phosphate by decreasing tubular reabsorption of PO4 3. Stimulate 1,25-OH2D3 synthesis by the kidney, thus promoting Ca+ absorption from the gut |
|
|
What cells produce Calcitonin?
|
Parafollicular Cells ("light cells") in the Thyroid gland
|
|
|
What are the functions of Calcitonin?
|
1. Inhibits Osteoclastic resorption of bone
2. Reduced calcium release from bone leads to: -lower serum Ca++ -compensatory increase in PTH secretion |
|
|
What stimulates the release of Calcitonin?
|
elevated free serum Calcium
|
|
|
Thyroid tumor that arises from Parafollicular C cells & secretes Calcitonin
|
Medullary Carcinoma
|
|
|
Medullary Carcinoma of the Thyroid
-causing tracheal compression Calcitonin |
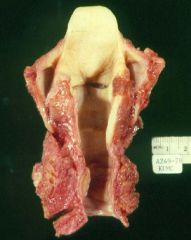
What is seen here? What does it secrete?
|
|
|
Medullary Carcinoma of the Thyroid
-nests of polygonal cells in an Amyloid stroma -Parafollicular cell nests are encircled by dense fibrous tissue -Upper right = psammoma bodies = focal calcifications |
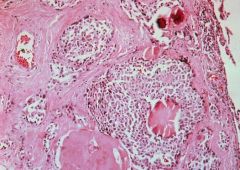
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What is Medullary Carcinoma associated with?
|
MEN II
-Medullary CA of thyroid -Pheochromocytoma -Parathyroid Hyperplasia or Adenoma |
|
|
List the sequence of metabolic events initiated by increased PTH
|
1. Ca+ is mobilized from bone by Osteoclasts
2. Serum Ca++ rises 3. Urine Ca+ rises 4. Urine PO4 increased by decreased resorption 5. Serum PO4 decreases due to renal loss 6. Serum Alkaline Phosphatase rises (PTH stimulates Osteoblasts) |
|
|
Resorption of Distal Phalanges
-due to Hyperparathyroidism |
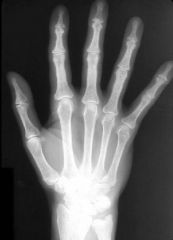
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Bone resorption in Hyperparathyroidism = Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
-Upper left = multinucleated Osteoclasts are digging a resorption pit -Lower right = Osteoblasts are adding new bone |
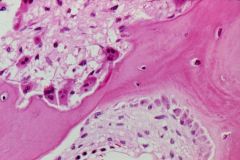
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
-due to Primary Hyperparathyroidism -cystic changes in the bone due to osteoclastic resorption |
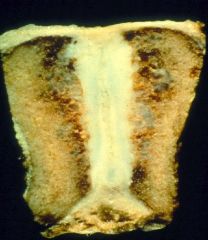
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Liquified focus fo bone resorption in Hyperparathyroidism
|
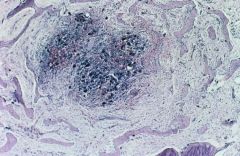
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
"Brown tumor" = fibrous replacement of resorbed bone leading to formation of non-neoplastic tumor-like masses -center = clusters of osteoclasts -Right = brownish deposits of Hemosiderin |
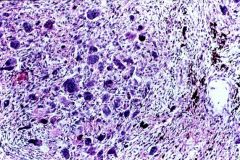
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Metastatic calcification of the kidney due to Hyperparathyroidism
-blue staining, rounded deposits of Calcium Phosphate -brown deposits of Hemosiderin |
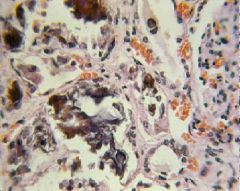
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What are the 3 most common causes of Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
|
1. Parathyroid Adenoma = 81%
2. Parathyroid Hyperplasia = 15% 3. Parathyroid Carcinoma = 6% |
|
|
What are the lab findings associated with Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
|
1. increased PTH
2. increased Ca+ = hypercalcemia + hypercalciuria 3. decreased serum Phosphorus 4. increased serum Alkaline Phosphatase |
|
|
Parathyroid Adenoma
|
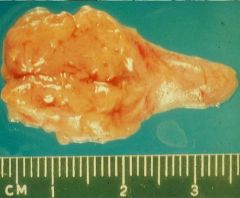
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Oxyphil cell Parathyroid Adenoma
-normal rim of parathyroid tissue containing fat cells is visible |
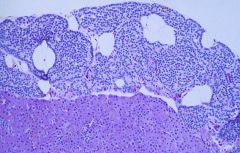
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Chief Cell Adenoma
-absence of fat cells within adenoma |
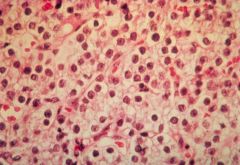
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Primary Parathyroid Hyperplasia
|
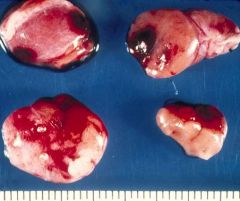
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Waterclear cell Parathyroid Hyperplasia
|
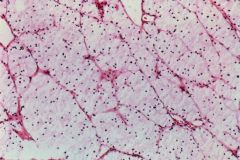
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What are the most common clinical causes of Hypercalcemia?
|

-
|
|
|
Microscopic changes in the Bone Marrow due to Malignant Lymphoma
-Malignant Lymphoblasts secrete PTH-like hormone (PTHrP) that signals Osteoclasts to resorb bone |
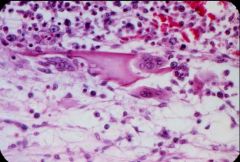
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What are the most common neoplasms that produce PTHrP & cause Hypercalcemia
|
1. Lung CA = 25%
2. Breast CA = 20% 3. Squamous CA of Head, Neck, Esophagus, Cervix = 19% 4. Malignant Lymphoma = 14% 5. Renal Cell CA = 8% |
|
|
Describe the metabolic process of Vitamin D
|
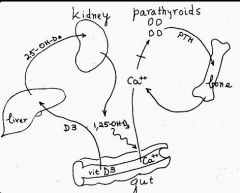
-
|
|
|
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
-diffusely enlarge & hyperplastic parathyroids |
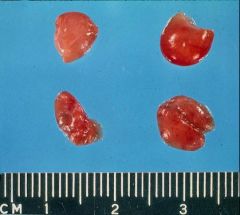
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Diffuse Chief Cell Hyperplasia due to Sedoncary Hyperparathyroidism
|
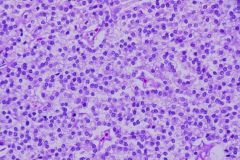
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Osteoclasts resorbing bone in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
|
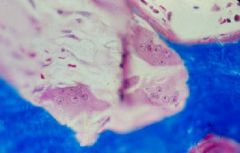
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Define Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
What is the most common cause? |
Compensatory Parathyroid Hyperplasia in response to decreased concentration of serum Ca+
Chronic Renal Failure = kidney doesn't convert Vitamin D into its active form -> 1, 25-(OH)2D3 |
|
|
What are the most common causes of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism?
|
1. Chronic renal failure = conversion of Vitamin D to its optimal active form is impeded -> decreased intestinal absorption of Ca+
2. Vitamin D deficiency 3. Malabsorption |
|
|
What are the causes of Hypoparathyroidism?
|
1. accidental surgical excision (usually during Thyroid surgery)
2. developmental absence of Parathyroids 3. Absence of Thymus & Parathyroids = DiGeorge Syndrome 4. Autoimmune hypoparathyroidism 5. Pseudohypoparathyroidism |
|
|
What are the clinical features of Hypoparathyroidism?
|
1. Hypocalcemia
2. Neuromuscular excitability & tetany -Chvostek's sign = tap facial nerve -> contraction of facial muscles -Trousseau's sign = occlusion of brachial artery with BP cuff -> carpal spasm 3. Psychiatric disturbances 4. Cardiac conduction defects 5. Cataracts develop due to calcifications of the lenses |
|
|
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
-PTH receptors in Bone & Kidney are insensitive to PTH |
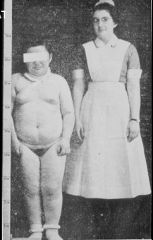
What is the cause of Short stature, short neck, & short fingers in this boy?
|

