![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Most common viral enterocolitis in a) infants b) adults c) 2nd most common in kids |
a) Rotavirus b) Norwalk c) Adenovirus |
|
|
Painful Bloody low volume diarrhea mainly in distal colon Person-to-person transmission Lactose (-), non-motile |
Sheigella
*Invasive - invade and destroys mucosal cells |
|
|
Painful bloody low volume diarrhea Superficial ulcer and villous blunting Animal Contact Comma/S-shaped |
Campylobacter
*Invasive *sequlae of arthritis and guillian barre |
|
|
Painful bloody low volume diarrhea linear ulcers in Ileum/Colon Poultry contact Motile, lactose (-) |
Salmonella
*Invasive *Temp/Pulse dissociation and rose-colored spots |
|
|
Painful bloody low volume diarrhea LAD and necrotizing granulomas Daycare breakouts |
Y. entercolitica
*Invasive *Pseudoappendicitis |
|
|
Rice-Water Diarrhea 12-24 hrs after exposure person-to-person or infected seafood Coma-shaped |
V. cholerae
*Toxogenic - toxin increases cAMP to open Cl- channels |
|
|
Watery Diarrhea 12-24 hrs after exposure Meat/fish contact |
Clostridium perfringins
*Toxogenic *Skin infection = gas gangrene |
|
|
Diarrhea w/ hrs of ingestion of contaminated food |
Staph aureus (Gm +)
*Preformed toxin that is heat stabile (not destroyed by cooking!) |
|
|
Flaccid paralysis is baby w/in hrs of eating contaminated honey or canned food. Quickly progresses to respiratory distress |
C. botulinum (Gm +)
*Preformed heat-labile toxin that inhibits Ach release at NMJ |
|
|
Shiga-like toxin producing Gm (-) bacteria that can lead to HUS after ingestion of contaminated beef.
|
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7
*ABX counterindicated! |
|
|
Name the E. coli strain in each of the following: 1) cholera-like diarrhea (rice-watery) common in travelers 2) Shigella-like diarrhea (painful, blood) 3) watery & Common in kids, adheres to mucosa surface and flattens villi to prevent absorption
|
1) Enterotoxogenic E coli (ETEC)
2) Enteroinvasive E coli (EIEC)
3) Enteropathogenic E coli (EPEC) |
|
|
Roundworm transmitted by fecal-oral that transiently travels to lungs and back to GI to lay eggs visible to feces |
Ascaris Lumbricoides
*Trx w/ Me/Albendazole |
|
|
Parasite transmitted by skin penetration in soil. Causes peptic-ulcer like disease (N/V, diarrhea, epigastric pain) |
Strongyloids stercoralis
*Trx w/ Me/Albendazole |
|
|
Pinworm transmitted fecal-orally. Cause noctural anal pruritis ddxed w/ "scotch-tape" test |
Enterobius vermicularis
*Trx w/ Me/Albendazole |
|
|
Whipworm infection that causes bloody diarrhea and rectal prolapse |
Trichuris
*Trx w/ Me/Albendazole |
|
|
Fluke transmitted by snails that penetrate skin. Form granulomas in liver & Spleen and can lead to SCC in bladder |
Schistosoma (S. haematobium = bladder CA)
*Trx w/ praziquantal |
|
|
Amebia that causes dysentary diarrhea (low vol bloody painful) w/ RUQ pain and Flask-shaped ulcers |
Entamoeba histolytica
*trx w/ metro |
|
|
Fatty, greasy, foul-smelling diarrhea after drinking river water |
Giardia Lamblia
*trx w/ metro |
|
|
Watery diarrhea in AIDS pts that stain w/ acid-fast stain |
Cryptosporidium
*trx w/ nitazoxanide |
|
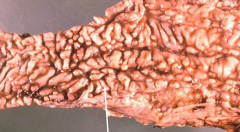
|
Crohns Disease (IBD)
*Skip lesions w/ cobblestoning (shown here) due to deep fissure leisons *can effect anywhere in GI tract (except the rectum) and thus may cause malabsorption |
|
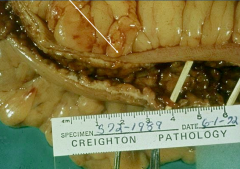
|
Crohns Disease (IBD)
*creeping fat and stricture that narrows lumen |
|
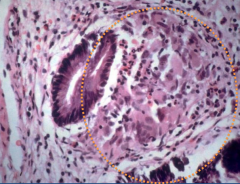
|
Crohns Disease (IBD)
*granuloma (in context of symp of IBD) = DDX of crohns! |
|
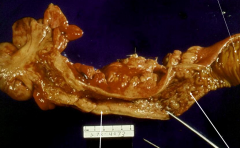
|
Crohns Disease (IBD)
*Stricture - causes "string sign on x-ray" *Strictures and Fistula = severe disease that recquires trx w/ TNF-alpha blockers (infliximab) |
|
|
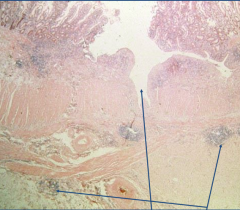
Crohns Disease (IBD)
*transmural ulcer w/ inflammation extending in serosa - depth of ulcer predisposes to fistula |
|
|
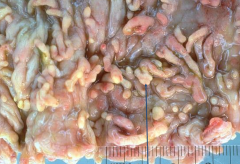
Ulcerative Collitis (IBD)
*pseudopolyp = regenerative islands of mucosa and granulation tissue |
|
|
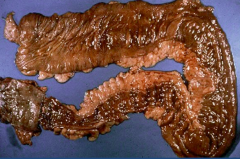
Ulcerative Collitis (IBD)
*Colon involvement always effecting rectum *Continuous lesions *Haustra may be lost causing "lead-pipe" on x-ray and toxic megacolon |
|
|
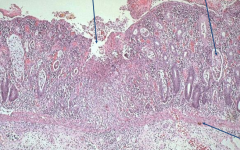
Ulcerative Collitis (IBD)
*Superficial (mucosa & sub-mucosa only) broad-based ulcers *crypt abscesses filled w/ debris and neutros |
|
|
What is the trx for mild-mod IBD? |
Steroid to induce remission (but only once or twice due to increased risk of infection) followed by Mesalamine/Suflasalazine to maintain remission
*UC is curative w/ collectomy but should be reserved for severe |
|
|
What other P-ANCA + disorder is associated Ulcerative Collitis (IBD)? |
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis |
|
|
Pt complains of diarrhea that has blood/mucus mixed in and often wakes him up at night w/ the urge to defecate. Stool sample is + for Fecal Calprotectin |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Colon (inidicated by bloody/mucus diarrhea)
Calprotectin = neutro marker sensitive for intestinal inflammation |
|
|
Name 4 d/o's commonly associate w/ both UC and CD. |
*Ankylosing spondylitis *Uvuitis *Erythema nodosum *Pyoderma gangrenosum |
|
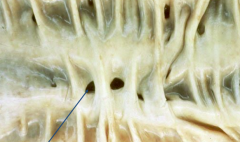
|
Diverticulosis
*False diverticulum (mucosa & submucosa) due to increased luminal pressure (due to low fiber) *most in Sigmoid *can cause hematochezia *can rupture to cause peritonitis or fistula (often w/ bladder to cause penumaturia) |

