![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
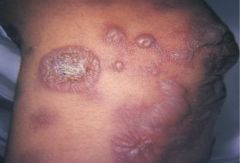
Bulla * A circumscribed, elevated lesion that is more than 5 mm in diameter * Usually contains serous fluid, and looks like a blister * This photograph is of bullae associated with erythema multiforme |
|
|
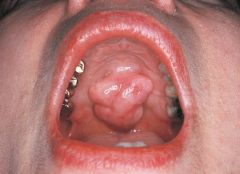
Lobule * A segment or lobe that is part of a whole * These lobes sometimes appear fused together * This photograph is of lobulated torus palatinus |
|
|
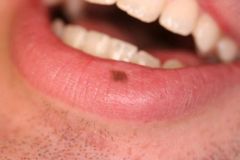
Macule * An area that is usually distinguished by a color different from that of the surrounding tissue * It is flat and does not protrude above the surface of the normal tissue * A freckle is an example of a macule |
|
|
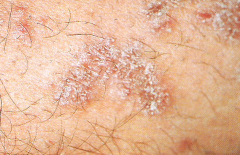
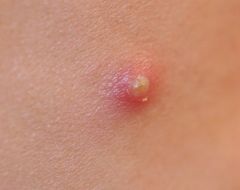
Papule * A small, circumscribed lesion usually less than 1 cm in diameter * It is elevated or protrudes above the surface of normal surounding tissue |
|
|
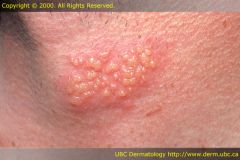
Pustule * Variously sized circumscribed elevations containing pus
|
|
|
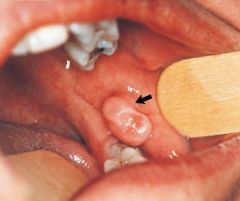
Vesicle * A small, elevated lesion less than 1 cm in diameter that contains serous fluid |
|
|
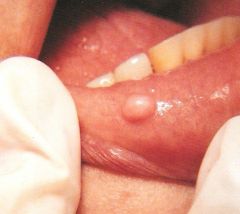
Pedunculated * Attached by a stemlike or stalklike base similar to that of a mushroom |
|
|
Sessile * Describing the base of a lesion that is flat or broad instead of stemlike |
|
|
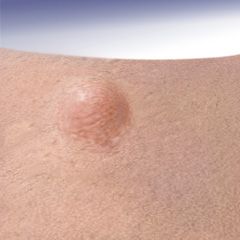
Nodule * A palpable solid lesion up to 1 cm in diameter found in soft tissue * Can occur above, level with, or beneath the skin surface |
|
|
Palpation * The evaluation of a lesion by feeling it with the fingers to determine the texture of the area * Descriptive terms for palpation are soft, firm, semifirm, and fluid filled * These terms also describe the consistency of a lesion |
|
|
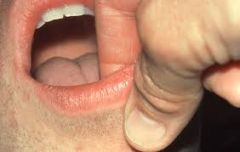
An abnormal redness of the mucosa or gingiva |
Erythema |
|
|
Paleness of the skin or mucosal tissues |
Pallor |
|
|
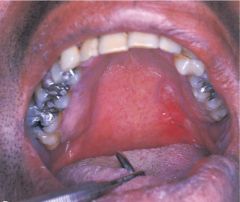
Erythroplakia * A clinical term used to describe an oral lesion that appears as a smooth red patch or granular red and velvety patch * Less common than leukoplakia * 90% of erythroplakias demonstrate epithelial dysplasia or squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
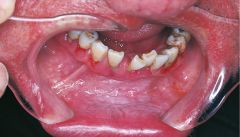
Leukoplakia * A clinical term for a white, plaquelike lesion on the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or diagnosed as a specific disease * This photograph is of leukoplakia associated with chewing tobacco |
|
|
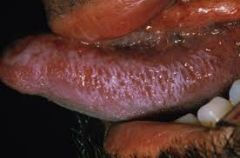
Corrugated * Wrinkled |
|
|
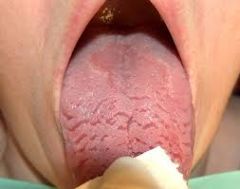
Fissured * A cleft or groove, normal or otherwise, showing prominent depth * This photograph is a fissured tongue |
|
|
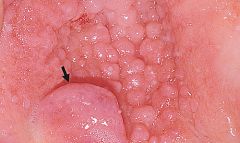
Papillary * Resembling small, nipple-shaped projections or elevations found in clusters |
|
|
Coalescence * The process by which parts of a whole join together, or fuse, to make one |
|
|
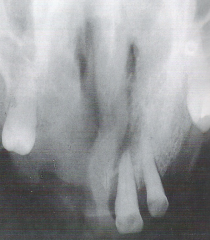
Diffuse * Describes a lesion with borders that are not well defined, making it impossible to detect the exact parameters of the lesion * Can make treatment more difficult and, depending on the biopsy results, more radical |
|
|
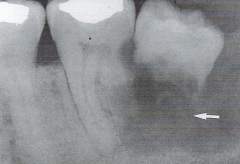
Mulitilocular MACHO- Myxoma- Ameloblastoma- Central giant cell granuloma- Hemangioma- Odontogenic keratocyst * Describes a lesion that extends beyond the confines of one distinct area * Defined as many lobes or parts that are somewhat fused together * A multilocular radiolucency is sometimes described as resembling soap bubbles * This photograph is of odontogenic keratocyst |
|
|
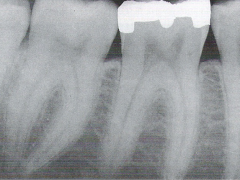
Radioucent * Describes the black or dark areas on a radiograph * Radiant energy can pass through these structures * Less dense tissue, such as pulp, is seen as a radiolucent structure |
|
|
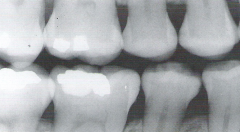
Radiopaque * Describes the light or white area on a radiograph that results from the inability of radiant energy to pass through the structure * The more dense the structure, the more light or white it appears on the radiograph |
|
|
Radiolucent and Radiopaque * A mixture of light and dark areas within a lesion * Denotes a stage in lesion development |
|
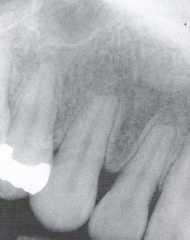
|
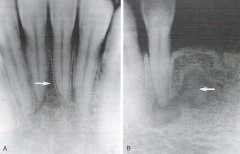
Root Resorption * Radiographically, the apex of the tooth appears shortened or blunted and irregularly shaped * Occurs as a response to stimuli, which can include a cyst, tumor, or trauma |
|
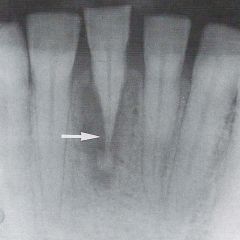
|
External Root Resorption * Arises from tissue outside the tooth, such as the periodontal ligament |
|
|
Internal Root Resorption * Triggered by pulpal tissue reaction from within the tooth * The pulpal area can be seen as a diffuse radiolucency beyond the confines of the normal pulp area |
|
|
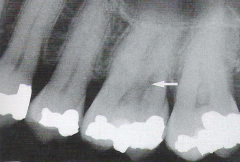
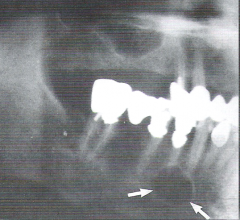
Scalloping Around the Root * A radiolucent lesion that appears to extend up the periodontal ligament and between the root |
|
|
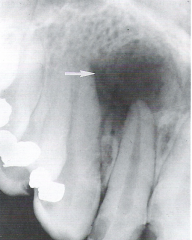
Unilocular * Having one compartment or unit that is well defined or outlined as in a simple radicular cyst |
|
|
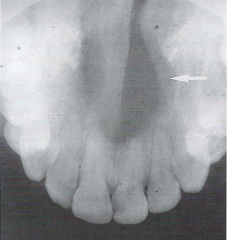
Well Circumscribed * Used to describe a lesion with borders that are specifically defined and in which one can clearly see the exact margins and extent |
|
|
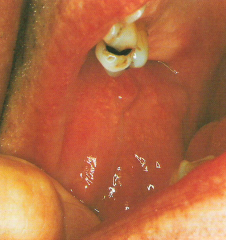
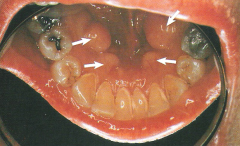
Fordyce Granules
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
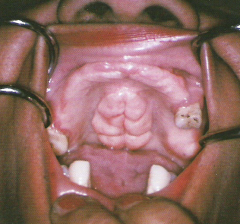
Torus Palatinus
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
Mandibular Tori
Clinical Diagnosis
|
|
|
Melanin Pigmentation
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
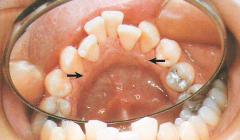
Retrocuspid Papillae
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
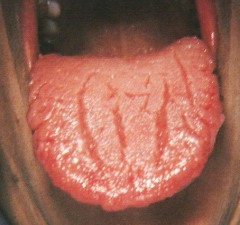
Fissured Tongue
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
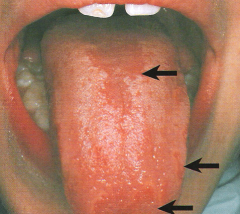
Median Rhomboid Glossitis and Geographic Tongue
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
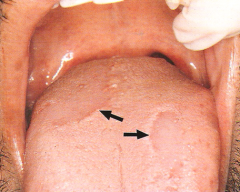
Geographic Tongue
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
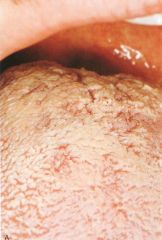
White Hairy Tongue
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
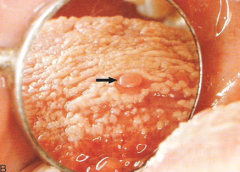
Circumvallate Papilla
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
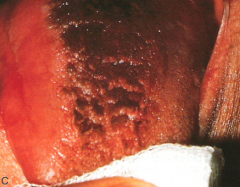
Black Hairy Tongue
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
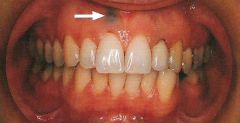
Amalgam Tattoo (Focal Argyrosis)
Clinical Diagnosis |
|
|
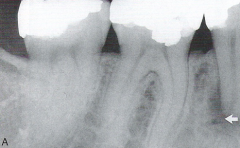
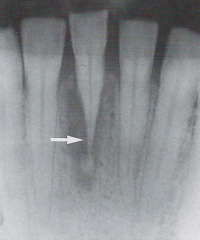
Periapical Pathosis
Radiographic Diagnosis |
|
|
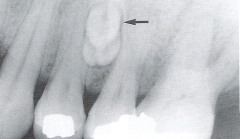
External Resorption
Radiographic Diagnosis |
|
|
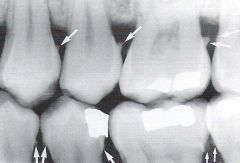
Heavy Interproximal Calculus
Radiographic Diagnosis |
|
|
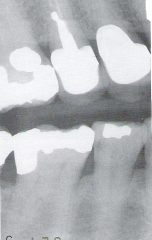
Caries
Radiographic Diagnosis |
|
|
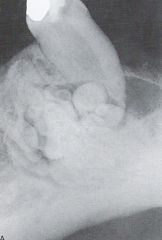
Compound Odontoma *Easily Diagnosed from Radiograph Alone*
Radiographic Diagnosis: Pathology
|
|
|
Compound Odontoma * Easily Diagnosed from the Radiograph Alone*
Radiographic Diagnosis: Pathology |
|
|
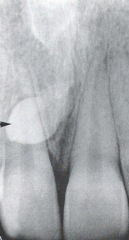
Mesiodens / Supernumerary Tooth
Radiographic Diagnosis: Abnormality |
|
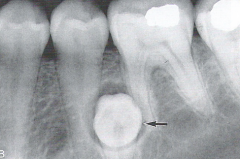
|
Supernumerary Tooth (Dentigerous Cyst)
Radiographic Diagnosis: Abnormality |
|
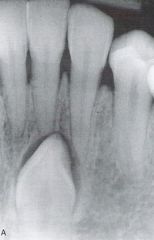
|
Impacted Mandibular Cuspid
Radiographic Diagnosis: Abnormality |
|
|
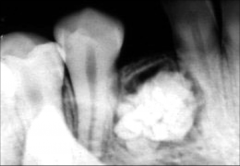
Complex Odontoma *Not Diagnosed from the Radiograph Alone*
Radiographic Diagnosis: Pathology |
|

|
Impacted Maxillary Cuspid
Radiographic Diagnosis: Abnormality |
|
|
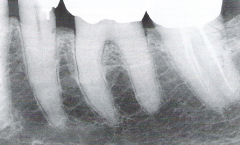
Calcified Pulp
Radiographic Diagnosis |
|
|
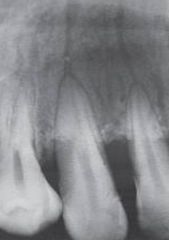
Nutrient Canals
Radiographic Diagnosis: Normal Anatomic Landmark |
|
|
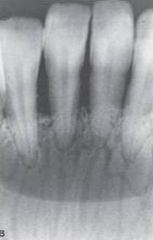
Nutrient Canals
Radiographic Diagnosis: Normal Anatomic Landmark |
|
|
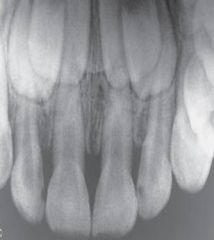
Mixed Dentition
Radiographic Diagnosis: Normal Anatomic Landmark |
|
|
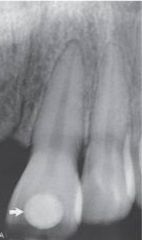
Cubic Zirconia
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
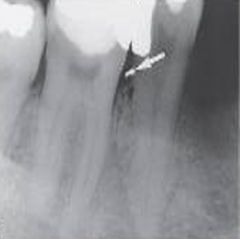
Amalgam Fragment
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
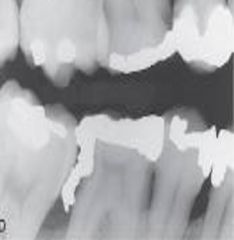
Overhang
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
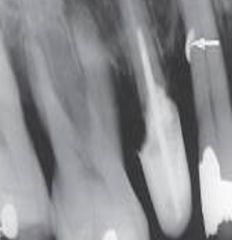
Broken Instrument
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
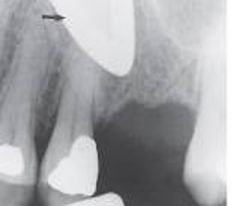
Eyeglass Frames
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
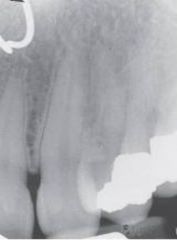
Piercing
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
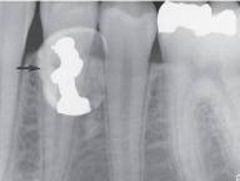
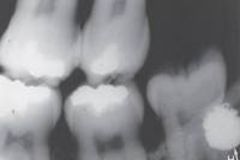
Retained Deciduous Tooth with an Amalgam Restoration
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
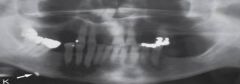
Shotgun Pellet
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
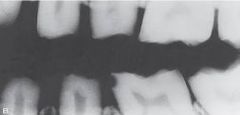
Shrapnel
Radiographic Diagnosis: Unusual Findings |
|
|
Amelogenesis Imperfecta *Radiographic Aspect*
Historical Diagnosis: Family History |
|
|
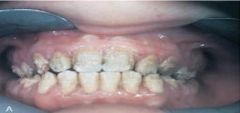
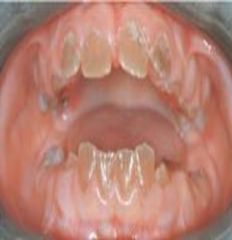
Amelogenesis Imperfecta *Clinical Appearance*
Historical Diagnosis: Family History |
|
|
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta *Clinical Appearance*
Historical Diagnosis: Family History |
|
|
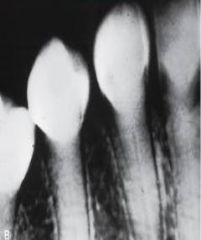
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta *Radiographic Appearance*
Historical Diagnosis: Family History |
|
|
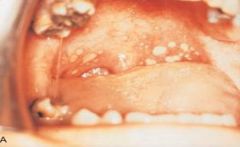
Ulcerative Colitis
Historical Diagnosis: Medical or Dental Status |
|
|
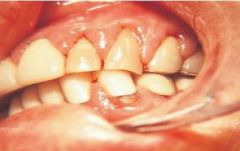
Gingival Enlargement *Patient is Taking a Calcium Channel Blocker*
Historical Diagnosis: Medical or Dental Status |
|
|
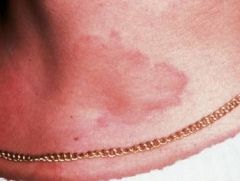
Hives/Urticaria from an Allergic Reaction
Historical Diagnosis: Medical or Dental Status |
|
|
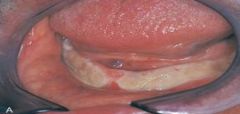
Skin Graft: White Patient *The same anomaly can look different with different pigmentation*
Historical Diagnosis: Medical or Dental Status |
|
|
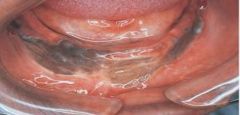
Skin Graft: Black Patient *The same anomaly can look different with different pigmentation*
Historical Diagnosis: Medical or Dental Status |
|
|
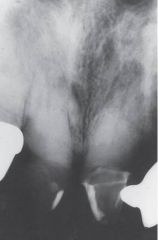
Paget Disease "Cotton-Wool Effect"
*Elevated Serum Alkaline Phosphatase Level*
Laboratory Diagnosis |
|
|
Blood Chemistries, Urinalysis, and Cultures |
Laboratory Diagnosis |
|
|
* Often the main component of the definitive diagnosis
* Adequate tissue sample is necessary |
Microscopic Diagnosis |
|
|
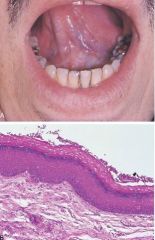
White Lesion * A white lesion cannot be diagnosed on the basis of clinical appearance alone * The microscopic appearance can vary from a thickening of the epithelium to epithelial dysplasia, which can be premalignant
Microscopic Diagnosis
|
|
|
Diagnosis is made using the information gained during the surgical procedure. |
Surgical Diagnosis |
|
|
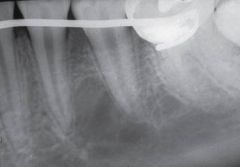
Traumatic Bone Cyst * May appear as a radiolucency that scallops around the roots * When the lesion is opened surgically, an empty void is found
Surgical Diagnosis |
|
|
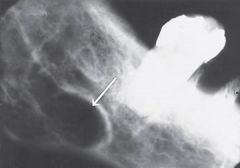
Static Bone Cyst * Surgical examination of the well-circumscribed, radiolucent area reveals salivary gland tissue entrapped during development
Surgical Diagnosis
|
|
|
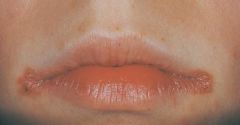
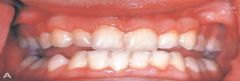
Angular Cheilitis * May be associated with a deficiency of B-complex vitamins * Most commonly a fungal condition and responds to topical application of an antifungal cream or ointment such as Nystatin
Therapeutic Diagnosis |
|
|
Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (NUG) *Responds to Hydrogen Peroxide*
Therapeutic Diagnosis |
|
|
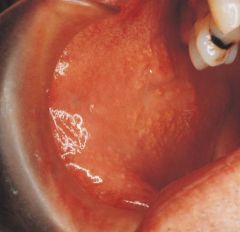
Fordyce Granules *No Treatment* * Clusters of ectopic sebaceous glands * Appear as yellow lobules in clusters * Commonly observed on vermillion border of lips and buccal mucosa
Variant of Normal |
|
|
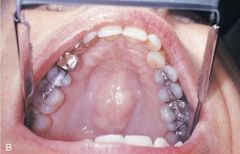
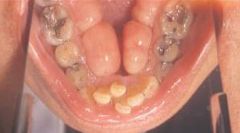
Torus Palatinus *No Treatment Unless they Interfere with Speech, Swallowing, or a Prosthetic Appliance* * An exophytic growth of normal compact bone * Observed clinically in the midline of the hard palate * Inherited, gradual formation * Occurs more commonly in women * May take on various shapes and sizes, may be lobulated, and is covered by normal soft tissue
Variant of Normal
|
|
|
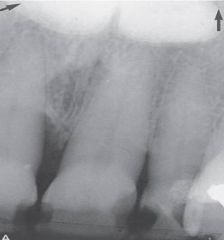
Torus Palatinus: Radiographic Appearance |
|
|
Mandibular Tori *No Treatment Unless Bothersome or in the Way* * Outgrowths of dense bone found on the lingual aspect of the mandible in the area of the premolars above the mylohoid ridge * Usually bilateral * Often lobulated or nodular * Can appear fused together * Have no predilection for either sex
Variant of Normal |
|
|
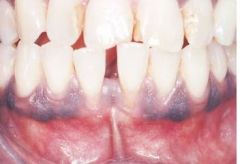
Melanin Pigmentation * The pigment that gives color to skin, eyes, hair, mucosa, and gingiva * Most commonly observed in dark-skinned individuals
Variant of Normal |
|
|
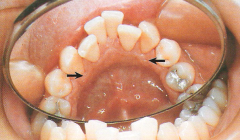
Retrocuspid Papilla * A sessile nodule on the gingival margin of the lingual aspect of the mandibular cuspids
Variant of Normal
|
|
|
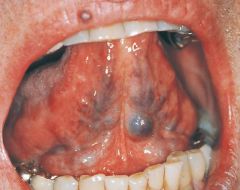
Lingual Varicosities * Clinical appearance: red-to-purple enlarged vessels or clusters * Usually observed on the ventral and lateral surfaces of the tongue * Most commonly observed in individuals older than 60 years of age
Variant of Normal |
|
|
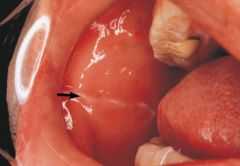
Linea Alba * A "white line" that extends anteroposteriorly on the buccal mucosa along the occlusal plane * May be bilateral * May be more prominent in patients who have a clenching or bruxing habit
Variant of Normal |
|
|
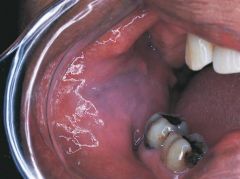
Leukoedema *No Treatment* * A generalized opalescence on the buccal mucosa * Most commonly observed in black adults * If the mucosa is stretched, the opalescence becomes less prominent
Variant of Normal |
|
|
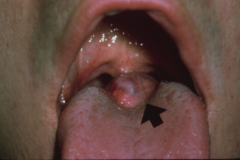
Lingual Thyroid Nodule *Treatment includes evaluation to determine whether the thyroid gland is present in its normal location* * Undescended, trapped remnants of thyroid tissue * Clinical Appearance: A mass in the midline of the dorsal surface of the tongue posterior to the circumvallate papillae in the are of the foramen cecum; usually has a sessile base and is 2 to 3 cm in width * Predilection in females; linked to hormonal changes
Benign Conditions of Unknown Cause |
|
|
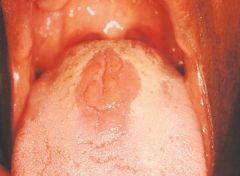
Median Rhomboid Glossitis *No Treatment Necessary, but Antifungal Treatment may be Used* * Clinical Appearance: Flat or slightly raised oval or rectangular erythematous area in center of tongue * May be associated with a chronic infection with Candida albicans
Benign Condition of Unknown Cause |
|
|
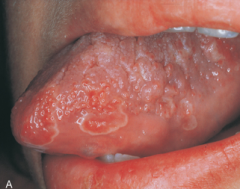
Geographic Tongue *No Treatment Usually*
Clinical Appearance: * Eryhematous patches surrounded by a white or yellow border* Diffuse areas devoid of filiform papillae * Distinct presence of fungiform papillae * There appear to be remission and changes in the depapillated areas * Genetic factors may play a role in presence * May be exacerbated by stress * Ocasionally, the patient may complain of a burning discomfort * No treatment usually indicated
Benign Condition of Unknown Cause |
|
|
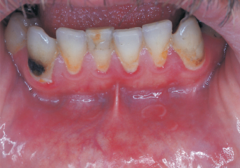
Ectopic Geographic Tongue * Term used to describe geographic tongue found on mucosal surfaces other than tongue
Benign Conditions of Unknown Cause |
|
|
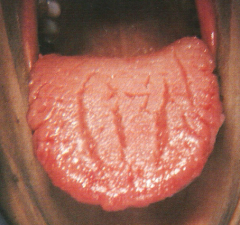
Fissured Tongue *No Treatment Necessary* * Clinical Appearance: The dorsal surface of the tongue appears to have deep fissures or grooves * Cause: Unknown. Probably involves genetic factors. Seen in about 5% of the population * Home Care: Direct the patient to brush the tongue gently with a toothbrush to remove debris
Benign Conditions of Unknown Cause |
|
|
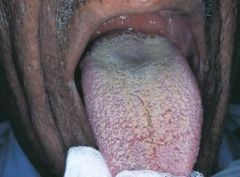
White Hairy Tongue * Clinical Appearance: Elongated filiform papillae are white * Result of either an increase in keratin production or a decrease in normal desquamation * Home Care: Direct the patient to brush the tongue gently with a toothbrush to remove debris
Benign Conditions of Unknown Cause |
|
|
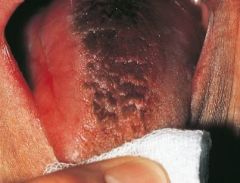
Black Hairy Tongue * Clinical Appearance: Papillae are brown-to-black because of chromogenic bacteria * Contributing Factors: Tobacco, foods, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, and chemical rinses * Home Care: Direct the patient to brush the tongue gently with a toothbrush to remove debris
Benign Condition of Unknown Cause |

