![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which term describes a disorder present at and existing from the time of birth?
|
Congenital
|
|
|
Which term describes partial anodontia or the lack of one or more teeth?
|
Hypodontia
|
|
|
Which epithelial lined tract is a developmental anomaly located in the corners of the mouth?
|
Commissural lip pit
|
|
|
The formation of dentin is called?
|
dentinogenesis
|
|
|
The first branchial arch divides into two maxillary processes and the?
|
mandibular process
|
|
|
The body of the tongue develops from the?
|
first branchial arch
|
|
|
Which term defines the joining of two adjacent teeth by cementum only?
|
Concrescence
|
|
|
Odontogenesis (tooth development) in the human embryo occurs at?
|
5 weeks
|
|
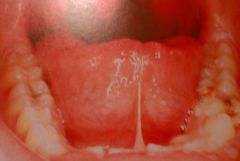
This patient exhibits an extensive adhesion of the tongue to the floor of the mouth caused by the short lingual frenum. You suspect?
|
Ankyloglossia
|
|
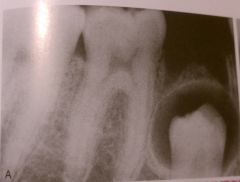
This unilocular radiolucency around the crown of an unerupted second premolar is most likely a?
|
Dentigerous Cyst
|
|
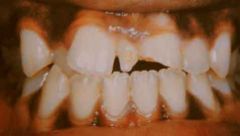
The supernumerary tooth in this illustration is called?
|
Mesiodens
|
|
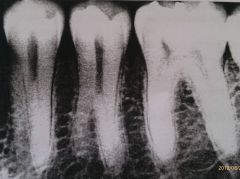
The development anomaly seen in this radiograph is?
|
Supernumerary roots on the premolars.
|
|
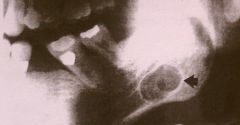
The pseudocyst seen in this radiograph is surrounded by salivary gland tissue. It is a/an:
|
Stafne bone cyst
|
|
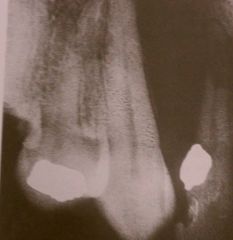
The pear-shaped radiolucency observed in this radiograph is most likely a:
|
Globulomaxillary cyst
|
|
|
This patient exhibits an extensive adhesion of the tongue to the floor of the mouth caused by the short lingual frenum. You suspect:
|
Ankyloglossia
|
|
|
Clinically the lingual thyroid nodule appears as a smooth nodular mass:
|
At the base of the dorsal tongue posterior to the circumvallate papillae.
|
|
|
The most common cyst observed in the oral cavity is caused by pulpal inflammation and is called a
|
Radicular cyst
|
|
|
This cyst is characterized by its unique histologic appearance and its frequent recurrence rate.
|
Odontogenic keratocyst
|
|
|
The lateral periodontal cyst occurs most often on the lateral aspect of a tooth root, which is usually the:
|
Mandibular cuspid / premolars
|
|
|
Radiographically this radiolucent cyst is often heart shaped that is caused by the anatomic Y shape of the area:
|
Nasopalatine canal cyst
|
|
|
This cyst has a strong predilection for females?
|
Nasolabial Cyst
|
|
|
Which one of the following is not true about the thyroglossal tract cyst?
a. It is found in individuals younger than 20 years. b. There is no sex predilection. c. Clinically it is located below the hyoid bone. d. Conservative nonsurgical treatment is sufficient. |
Conservative nonsurgical treatment is sufficient.
|
|
|
Which one of the following is not considered a pseudocyst?
a. Thyroglossal tract cyst b. Static bone cyst c. Simple bone cyst d. Aneurysmal bone cyst |
Thyroglossal tract cyst
|
|
|
This pseudocyst is filled with salivary gland tissue that may be an extension of the sublingual gland.
|
Static bone cyst
|
|
|
Total hypodontia is often associated with a hereditary disturbance called?
|
Ectodermal dysplasia
|
|
|
The most common supernumerary tooth is called?
|
Mesiodens
|
|
|
Nonerupted supernumerary teeth should be extracted because of the following risk:
|
Cysts around the crowns
|
|
|
For which condition would pulp vitality be nonvital?
|
Radicular Cyst
|
|
|
Dens in dente is a developmental anomaly often seen with?
|
A periapical lesion
|
|
|
Which tooth is most commonly affected by dens in dente?
|
Maxillary Lateral
|
|
|
Another name for dens invaginatus is?
|
Dens in dente
|
|
|
Enamel hypoplasia is the result of a disturbance of or damage to ameloblasts during enamel matrix formation. Which one of the following would not be a factor?
|
Genetics
|
|
|
Pitting is the most common type of enamel hypoplasia seen in patients who have which condition during tooth development?
|
Febrile illness
|
|
|
Ingesting water with four times the amount of flouride causes?
|
Brown to black staining
|
|
|
Which one of the following defines a disturbance of the maturation of the enamel matrix?
|
Enamel hypocalcification
|
|
|
Regional odontodysplasia is:
|
A decrease in radiodensity seen on one or more unerupted teeth in a quadrant.
|
|
|
Impacted teeth cannot erupt because of:
|
Physical obstruction
|
|
|
Regional odontodysplasia is also referred to as:
|
Ghost Teeth
|
|
|
Multiple supernumerary teeth may be a component of which of the following?
|
Cleidocranial dysplasia
|

