![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mucocele
|

Rupture of salivary gland duct due to local trauma, NEVER on upper lip, mucin-filled cyst-like (not a true cyst) cavity, granulation tissue and foamy histiocytes present
|
|
|
Ranula
|
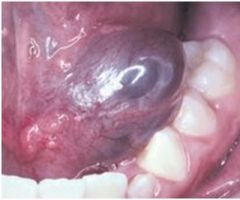
Mucocele (blue, dome shaped swelling) on the floor of the mouth, spilled mucin from sublingual gland, granulation tissue and foamy histocytes, tx: remove roof of lesion for small lesions, remove entire gland for larger lesions
|
|
|
Salivary Duct Cyst
|
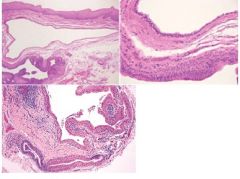
True cyst adjacent to gland duct, arises from salivary gland tissue, “Mucous Retention Cyst”, develops from ductal obstructions, lined by thin cuboidal epithelium, excretory gland duct lined by columnar epithelium, major and minor salivary glands
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis
|
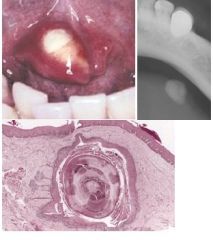
Calcified structures that develop within the salivary duct system, most often submandibular gland duct, radiopaque masses, possible pain or swelling, concentric laminations around amorphous debris, squamous metaplasa of duct, tx: “milk” stone out of duct with massage or sialagogues (drugs)
|
|
|
Sialadenitis
|
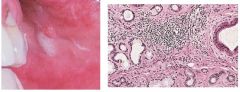
Inflammation of salivary gland due to bacteria (s. aureus), viral (mumps), sialolithiasis, congential strictures or adjacent tumor; purulent exudates, chronic sclerosing sialadentitis: chronic inflammatory infiltrate with associated acinar atrophy and ductal dilation and fibrosis; acute tx: antibiotics and rehydration
|
|
|
Sialadenosis
|
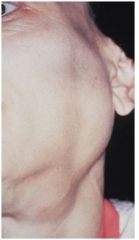
Non-inflammatory, salivary gland enlargement, parotid gland most common, systemic issue -> dysregulation of autonomic control of salivary acini-> hypertrophy of acinar cells, excessive accumulation of secretory granules
|
|
|
Sialorrhea
|
Excessive salivation due to apthous ulcers or ill-fitting dentures, Water Brash (episodic hypersecretion of saliva), Drooling in mentally retarded
|
|
|
Xerostomia
|
Subjective dry mouth, usually due to medications in older people, saliva is ropey, thick or foamy, prone to dental caries and candidiasis, dorsal tongue is fissured and filiform papillae are atrophied
|
|
|
Sjogren Syndrome
|
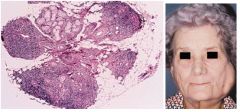
Chronic systemic autoimmune involving salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction, Sicca Syndrome (dry mouth and eyes), primary=sicca alone, secondary=sicca+another AI dz; Elevated IgG, RF, Anti-SS-A and B, antinuclear Abs; females >> males; confirm w/ shirmer test; lymphocytic infiltration of salivary glands, destruction of acinar cells, presence of FOCAL chronic inflammatory aggregates (more foci = more accurate diagnosis of SS)
|
|
|
Benign Lymphoepithelial Lesion
|
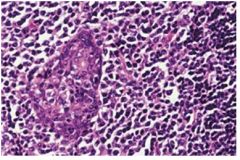
associated w/ Mikulicz disease, autoimmune disease, BILATERAL salivary and lacrimal enlargmenet, lymphocytic infiltration of the parotid gland with associated epimyoepithelial island
|
|
|
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
|
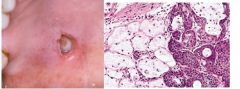
Local inflammatory destruction of salivary glands, mimics malignant process, PALATAL salivary glands most common (hard>soft), H: necrotic mucous acini and adjacent ductal squamous metaplasia, ulceration in later stages, no tx necessary but biopsy to rule out malignancy
|
|
|
Pleomorphic Adenoma
|
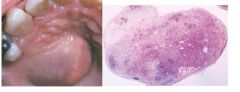
MOST COMMON salivary gland tumor, Mixture of ductal and myoepithelial elements, parotid gland superficial lobe most common, palate>upper lip>buccal mucosa, H: well-circumscribed, encapsulated, benign tumor with variable microscopic pattern, mix of epith and myoepith present w/ mesenchyme-like background, fat or osteoid can be present, rare malignant transormation
|
|
|
Oncocytosis
|
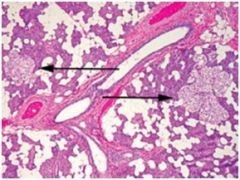
Transformation of ductal and acinar cells to ONCOCYTES, proliferation and accumulation of oncocytes in salivary glands, H: focal nodular collections of oncocytes, polyhedral, w/ lots of granular eosinophilic cytoplasm (result of proliferation of mitochondria); no tx necessary
|
|
|
Oncocytoma
|
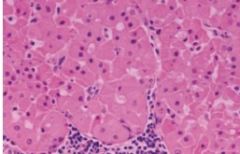
a type of Monomorphic Adenoma, benign salivary gland tumor composed of large epithelial cells (oncocytes), cells have swollen granular cytoplasm, well-circumscribed tumor made of SHEETS of polyhedral cells, abundant granular, eosinophilic cytoplasm (mitochondria)
|
|
|
Warthin’s Tumor (Papillary Cystadenoma Lymphomatosum)
|
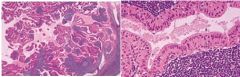
Benign monomorphic adenoma tumor, parotid gland only near mandibular angle, associated with smoking, bilateral (but not at same time), caused by heterotropic salivary tissue w/in parotid lymph nodes; 2 layers: inner luminal layer with tall columnar cells, palasading, centrally placed nuclei, second layer of cuboidal or polygonal cells with more vesicular nuclei, epith has papillary infoldings that protrude into cystic spaces
|
|
|
Canalicular Adenoma
|
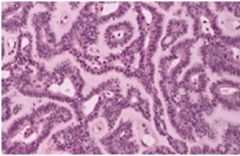
Monomorphic Adenoma, always in minor salivary glands, upper lip, H: uniform single layer of columnar or cuboidal cells forming canal-like ductal structures with deeply basophilic nuclei
|
|
|
Basal Cell Adenoma
|
Monomorphic Adenoma, Benign, unlike canalicular adenoma usu. affects parotid gland, H: encapsulated or well-circumscribed, cords of basaloid cells arranged in a trabecular pattern
|
|
|
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
|
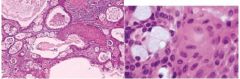
most common salivary gland malignancy, wide age range, parotid gland, blue-pigmented mass, H: mixture of mucus-producing cells and squamous (epidermoid )cells, intermediate cells (progenitor cells), low grade: cyst formation w/ lots of mucous cells; high grade tumor: solid islands of squamous and intermediate cells w/ pleomorphism and mitotic activity
|
|
|
Intraosseous Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
|
Malignant, salivary gland tumor within the jaw, most common intrabony salivary tumor, associated with impacted teeth or dentigerous (odontogenic) cysts
|
|
|
Acinic Cell Adenocarcinoma
|
Malignant, serous acinar differentiation, good prognosis
|
|
|
Malignant Mixed Tumors
|
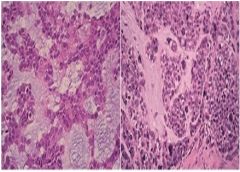
Malignant counterpart to benign mixed tumor or pleomorphic adenoma, most common: “carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma” (Epithelial cells of benign pleomorphic adenoma -> malignant), H: areas of malignant degeneration of epithelial cells w/in tumor, cellular pleomorphism (pleomorphic nuclei) and abnormal mitotic activity
|
|
|
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
|
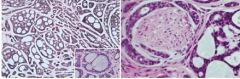
common salivary malignancy, dull ache -> incr intensity, mixture of myoepithelial cells and ductal cells; Three histo patterns: Cribriform, tubular, solid; PERINEURAL INVASION (not pathognomonic) ie pain due to cells around nerve bundle, bad prognosis over time
|
|
|
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma
|
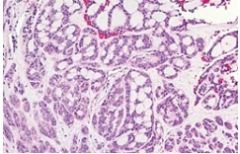
common malignancy, always minor salivary glands, H: Cribriform pattern mimics adenoid cystic carcinoma, perineural invasion common also mimics ACC, unlike ACC good prognosis
|

