![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sebhorrheic Keratosis
|
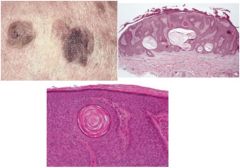
Benign proliferation of epidermal basal cells, NOT oral, dermatosis papulos nigra (suborrheic keratosis in blacks), acanthosis, pseudocysts (keratin-filled invaginations), upward proliferation
|
|
|
Ephelis (Freckle)
|
Hyperpigmented macule of the skin, SSE with abundant melanin production in basal layer (same # of melanocytes), no elongation of rete ridges, NEVER elevated, sun-exposure effect
|
|
|
Actinic Lentigo (Liver Spots, Age Spots)
|
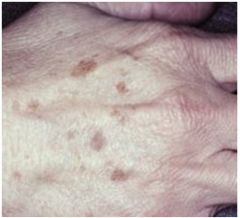
Due to sun-exposure, but doesn’t change color intensity (unlike ephelis), NOT oral, well-demarcated, but irregular borders, increased melanin, no malignancy
|
|
|
Lentigo Simplex
|
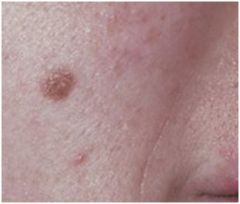
Benign cutaneous melanocytic hyperplasia w/in basal layer, no color change with sun, darker than ephelis, basal keratinocytes, melanin incontinence, multiple lesions associated w/ peutz jeghers syndrome
|
|
|
Peutz-Jegher’s Syndrome
|
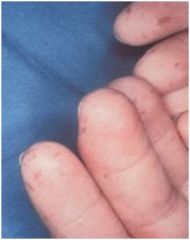
Freckle-like lesions of hands, perioral skin and oral mucosa (buccal and labial mucosa) most affected, multiple circumscribed macules covered w/ intact mucosa, intestinal polyposis, Circumoral lentigines, GI adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Addison’s Disease
|
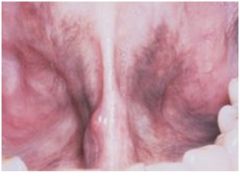
Adrenal cortical insufficiency, diffuse hypermelanosis, multiple dark macules covered by intact mucosa, mral lesions are first indication of disease, “bronzing of the skin”
|
|
|
Melasma (mask of pregnancy)
|
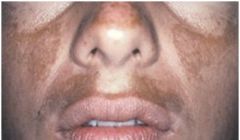
Bilateral hyperpigmentation of sun-exposed skin of face and neck, associated with pregnancy, increased melanin deposition, wood lamp for melanin visualization (epidermal pigment is enhanced, dermal pigment is not), tx: sunscreens w/ zinc oxide or titanium dioxide
|
|
|
Oral Melanotic Macule
|
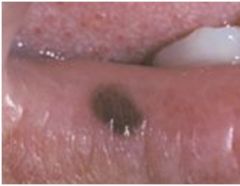
NOT associated w/ sun-exposure, flat, brown mucosal discoloration, lower lip macule less than 5mm, increase in melanin and melanocytes, melanin incontinence
|
|
|
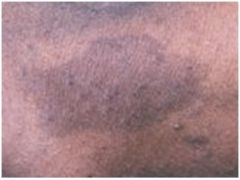
Oral Melanoacanthoma
|
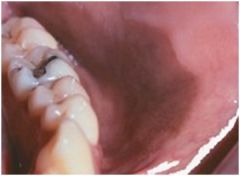
almost exclusively African Americans, dramatic enlargement within months, smooth darkly pigmented macule of buccal mucosa
|
|
|
Café-au-lait Spot
|
Flat, brown macules, >1.5cm in diameter, present in 1/10 ppl, 6+ spots present =neurofibromatosis, similar lesions seen in Albright Syndrome
|
|
|
Acquired Melanocytic Nevi
|
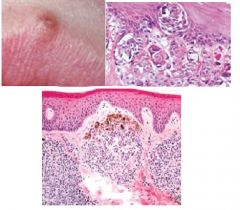
benign localized proliferation of neural crest derived cells, most common tumor, hard palate, over years produces slightly elevated soft papule, melanocytic nevus cell nests in basal layer and lamina propria, regress in midlife, can resemble melanoma -> biopsy
|
|
|
Congenital Melanocytic Nevi
|
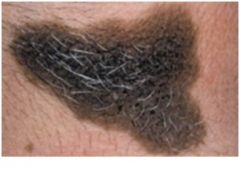
larger than acquired form, hypertrichosis (excess hair), "bathing trunk" or "garment nevus" or "giant hairy nevus", infiltration of cells between collagen bundles, 3-15% undergo malignant transformation into melanoma
|
|
|
Halo Nevus
|
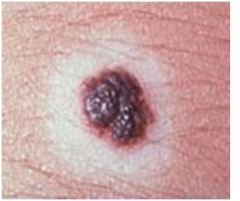
Melanocytic nevus with a pale HYPOpigmented border, autoimmune attack on melanocytes, affects trunk on 10-20 yr olds, often regress
|
|
|
Blue Nevus
|
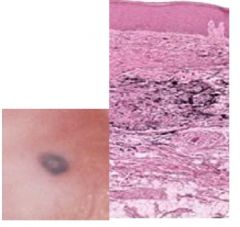
Tyndall effect causes blue color, lesion on palatal mucosa, melanin particles in spindle-shaped melanocytes deep to epith in lamina propria, compound nevus, looks like melanoma -> biopsy
|
|
|
Melanoma
|
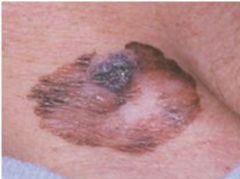
Malignant neoplasm of melanocytic origin, UV radiation, acute sun damage, BRAF gene mutations, ABCDE clinical diagnosis (asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter >6mm, evolving), invasion depth correlated w/ prognosis, Clark system and Breslow classification (more accurate) used to measure depth, BANS (back, posterior arm, neck, scalp)=worst prognosis
|
|
|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma
|
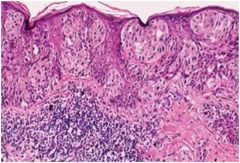
Most common, nodular, deeply pigmented exophytic lesion, spread of atypical melanocytes ALONG basilar portion of epidermis, invasion into higher epithelium, Pagetoid pattern, lateral spread
|
|
|
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
|
From Lentigo meligna or Hitchinson’s Freckle (precursor lesions), Sun-exposure, fair-skined older ppl, melanoma in situ in a radial growth phase
|
|
|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
|
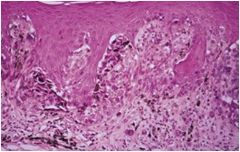
African Americans, Oral melanoma (poor prognosis), also palms, soles and under nails, atypical melanocytes IN the basal portion of epithelium, invasion into the superficial lamina dura, dendritic processes
|
|
|
Vitiligo
|
Autoimmune, onset after stress, sun-exposure or injury, NO melanocytes present in involved skin, thyroid dz is common in these pts
|
|
|
Pityriasis (Tinea) Versicolor
|
can be HYPO or HYPERpigmented, caused by a fungus, more obvious when patient is tan, “spaghetti and meatballs” (spores w/ short mycelium) seen with KOH stain
|

