![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sporadic CJD |
CSF analysis of protein 14.3.3 and RTQuIC |
|
|
|
Hippel-Lindau syndrome |
Retinal angioma CNS haemangioblastoma Phaechromocytoma Renal cell carcinoma |
|
|
|
Fabry disease |
Pain - extremeties + GI tract Kidney - failure Heart - many ways Skin - angiokeratoma in lower body Eye - whorl-like cornea CNS - early stroke |
|
|
|
Myotonic dystrophy |
Cataracts (blue dot) Early balding Hypersomnia Conduction problem Insulin resistance |
|
|
|
Hashimoto's encephalopathy |
Ataxia Dementia Myoclonic jerk when startled Non-specific EEG |
|
|
|
BIH/IIH |
Diagnosis: Lumbar puncture opening pressure >25 Treatment: acetazolamide, bariatric surgery for weight loss |
|
|
|
Diabetic amyotrophy |
Proximal weakness Minimal sensory loss |
|
|
|
Alcoholic and unresponsive |
CT head - rule out subdural haematoma |
|
|
|
Refsum disease |
Autosomal recessive Raised phytanic acid Night blindness (retinitis pigmentosa) Shortening of fourth toe (epiphyseal dysplasia) |
|
|
|
EEG findings |
HSV encephalitis - frontotemporal slowing with periodic sharp wave complexes |
|
|
|
Circle of Willis and vascultare |
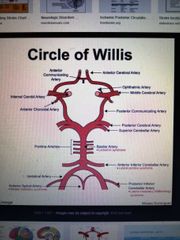
Anterior circulation - MCA, ACA, anterior choroidal artery Posterior circulation - vertebral artery, basilar artery, PCA |

|
|
|
MS drugs MOA |
Fingolimod - modulates S1P receptor to prevent lymphocyte migration across BBB
Glatiramer - mimics myelin peptide, competes with myelin antigen for their presentation to T cells
Ocrelizumab - B-cell cytotoxic
Alemtuzumab - T-cell cytotoxic
Beta-interferons - increases anti-inflammatory agents, reduces number of inflammatory cells crossing BBB Teriflunomide - active metabolite of leflunomide, inhibits pyrimidine synthesis |
|
|
|
Periodic paralysis |

|
|
|
|
Paraganglioma |
Pulsatile tinnitus X, XI, XII nerve lesions |
|
|
|
Cerebral sinus thrombosis |
Headache Seizure Raised ICP Septic cause: otitis media, meningitis, facial cellulitis Non-septic cause: pregnancy, thrombophilia, Behcet's
Absent delta sign (filling defect)
Treat with SC LMWH |
|
|
|
Parkinson's medication |

|
|
|
|
Brachial neuritis |
Assumed immune mediated Post-vaccination or illness Short spell of shoulder pain that resolves Followed by progressive weakness and wasting |
|
|
|
McArdle's disease |
Muscle pain with exercise Dark urine (rhabdo) Second wind phenomenon |
|
|
|
Botulism |
Descending paralysis starting with eye and bulbar muscles |
|
|
|
Neuroleptic malignant like syndrome |
Sudden withdrawal of levodopa in PD Mildly raised creatinine |
|
|
|
Paroxysmal hemicrania |
Same symptoms as cluster headache but shorter (eg 2-25min) and more frequent attacks (50 attacks a day) and more common in females Treatment: indometacin |
|
|
|
Rare forms of encephalitis |
Bickerstaff (?autoimmune) - ataxia + ophthalmoplegia (just like Miller fisher) - drowsiness/hyperreflexia
Limbic - cognitive decline + seizure - temporal lobe - autoimmune/paraneoplastic - treat with IVIg
Anti-NMDA Rasmussen (paeds) ADEM (paeds) SSPE - caused by measles, always fatal |
|
|
|
Stroke distribution |

|
|
|
|
Kearns-Sayre syndrome (mitochondrial disease) |
Ophthalmoplegia Ptosis Night blindness (retinitis pigmentosa) Cerebellar syndrome Sensorineural hearing loss |
|
|
|
Young patients with stroke |
ECHO - atrial septal aneurysm Contrast ECHO (bubble test) - PFO |
|
|
|
IBM Vs paraneoplastic myopathy Vs polymyositis Vs alcohol related myopathy Vs MND |

|
|
|
|
Paraganglioma of the head and neck |
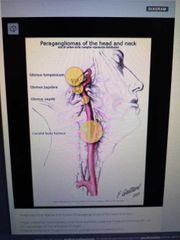
|
|
|
|
Tropical spastic paraparesis |
Afrocaribbean HTLV-1 associated myelopathy No cure |
|
|
|
Homocystinuria |
Marfan-like Malar rash Livedo reticularis VTE Lens dislocation (downward and inward) Treat: B6(pyridoxine) |
|
|
|
Neurosarcoidosis |
Bilateral facial palsy Optic nerve dysfunction Papilloedema Palate dysfunction Meningitis Myelopathy (spinal cord) |
|
|
|
Oculomasticarory myorhythmia |
Pathognomonic for Whipple's disease |
|
|
|
Tolosa-Hunt syndrome |
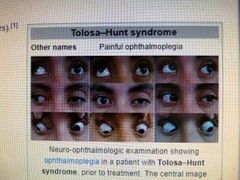
Caused by inflammation in cavernous sinus and superior orbital fissure Unilateral headache Painful ophthalmoplegia |
|
|
|
Myotomes |

|
|
|
|
Dermatomes |

|
|
|
|
Anterior circulation stroke |

Lacunar syndrome (most are caused by infarct of MCA branches) |

Right MCA infarct involving inferior parietal lobe |
|
|
Hemiballismus |

|
|
|
|
Posterior cerebral artery stroke - P1 syndrome |
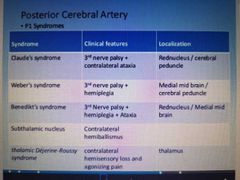
|
|
|
|
Posterior cerebral artery stroke - P2 syndromes |

|
|
|
|
Cerebellar stroke syndromes |
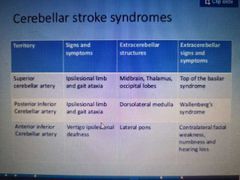
PICA - lateral medullary/wallenberg's syndrome AICA - lateral pontine syndrome |
|

