![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
134 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atoms exist as independent particles in nature.
TRUE or FALSE? |
FALSE.
rarely exist |
|
|
What is a chemical bond?
|
A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together.
|
|
|
Why are most atoms chemically bonded to each other?
|
Because as independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy.
|
|
|
Most atoms are ______ stable themselves than when combined.
MORE or LESS? |
less
|
|
|
By bonding with each other atoms ______ in potential energy.
INCREASE or DECREASE? |
decrease
|
|
|
Nature favors arrangements in which potential energy is ________.
MINIMIZED OR MAXIMIZED. |
minimized
|
|
|
What happens to atoms' valence electrons when they bond?
|
They're redistributed in ways that make the atoms more stable.
|
|
|
The way in which the electrons are redistributed determines what?
|
The type of bonding.
|
|
|
What is ionic bonding?
|
Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between cations and anions.
|
|
|
Covalent bonding results from the sharing of electron pairs between how many atoms?
|
Two.
|
|
|
In a ______________ bond, the shared electrons are "owned" equally by two bonded atoms.
|
purely covalent
|
|
|
In _____ bonding, many atoms transfer electrons the resulting positive and negative ions combine due to to mutual electrical attraction.
|
ionic
|
|
|
In _________ bonding, atoms share shared electron pairs to form independent molecules.
|
covalent
|
|
|
Bonding between atoms of ________ elements is rarely purely ionic or covalent.
DIFFERENT or THE SAME? |
different
|
|
|
___________ is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons.
|
Electronegativity
|
|
|
To the degree of which bonding between atoms of two elements is ionic or covalent can be estimated how?
|
By calculating the difference in the elements' electronegatives.
|
|
|
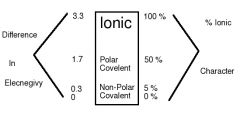
The electronegativity difference between F and Cs is 4.0 - 0.7 = 3.3, so it is classified as ______.
|
ionic
|
|
|
Know this!
|
|
|
Atoms with high electronegativity gain ________ causing the atoms to become anions.
|
valence electrons
|
|
|
Atoms with low electronegativity _____ valence electrons causing the atoms to be _____.
|
lose, cations
|
|
|
Bonding between atoms with an electronegativity difference of ______ or an ionic characters of __% or less are typically covalent.
|
1.7 or lower, 50
|
|
|
Bonding between 2 atoms of the same element is completely ________. (H)
|
covalent
|
|
|
The H-H bond is what kinda of bond?
|
Non-polar covalent.
|
|
|
How does H exists?
|
As pairs of atoms held together by covalent bonds.
|
|
|
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
|
A covalent bond in which the bonding electrons are shared equally by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balance distribution of electrical charge.
|
|
|
Bonds having _-_ % ionic character corresponding to electronegativity differences of roughly _-_ are non-polar covalent bonds.
|
0, 5, 0, 0.3
|
|
|
In bonds with significantly different electronegatives, the electrons are _____ attracted the more electronegative atom in polar bonds.
|
more
|
|
|
Polar bonds have an uneven distribution of ______.
|
charge
|
|
|
Polar bonds have __-__ % ionic character, corresponding to electronegative differences of __ -__.
|
5, 50, 0.3, 1.7
|
|
|
What is a polar covalent bond?
|
A covalent bond in which the bonded atoms have an unequal attraction for the shared electrons.
|
|
|
When is a covalent bond formed?
|
When atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
|
|
|
When do non-polar covalent bonds form?
|
When atoms share one or more pairs of electrons relatively equally.
|
|
|
When is an ionic bond formed?
|
Between a negative ion (anion) and positive ion (cation).
|
|
|
What is a molecule?
|
A neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bond.
|
|
|
A single molecule of a ________ is an individual unit capable of existing on its own.
|
chemical compound
|
|
|
A chemical compound whose smallest units are molecules is what kind of compound?
|
Molecular.
|
|
|
The composition of a compound is given how?
|
By it's chemical formula.
|
|
|
_______________ indicates the relative numbers of atoms of each kind in a chemical compound by using atomic symbols and numerical subscripts
|
Chemical formula
|
|
|
What is the chemical formula of a molecule referred to as?
|
A molecular formula.
|
|
|
_______ formula shows that the types and numbers of atoms combine in a single molecule of a molecular compound.
MOLECULAR, COVALENT, IONIC, or CHEMICAL? |
Molecular
|
|
|
What does H20 actually say?
|
A single water molecule consists of one oxygen atom joined by seperate covalent bonds to 2 hydrogen atoms.
|
|
|
How many atoms are in a diatomic molecule?
|
2.
|
|
|
The composition of a compound is given by it's _______ formula.
|
chemical
|
|
|
Covalent bonds ___ stay bonded as long as their potential energy remains close to the minimum.
DO or DON'T? |
do
|
|
|
What is bond length?
|
The average of the distribution between 2 bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy between them.
|
|
|
How many atoms are in a diatomic molecule?
|
Two, dummy.
|
|
|
As atoms near each other, their ______ particles begin to intereact.
CHARGED or UNCHARGED? |
uncharged
|
|
|
Attraction between particles decreases in potential energy of the atoms while repulsion _______.
|
increases
|
|
|
The relative strength of attraction and repulsion between charged particles depends on what?
|
The distance between the two atoms.
|
|
|
In forming a covalent bond, H atoms ________ energy as they change from isolated individual atoms to parts of a molecule.
GIVE OFF or RELEASE? |
release
|
|
|
What is the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms called?
|
Bond energy.
|
|
|
All individual __ atoms contain a single, unpaired electron in a 1s atomic orbital.
|
H
|
|
|
Noble-gases exist ________ly in nature.
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT? |
independent
|
|
|
State the octet rule.
|
Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons has an octet of electrons in it's highest occupied energy level.
|
|
|
Some exceptions to octet rule please?
|
B, H, Be, S, Xe, & P.
|
|
|
Some elements can be surrounded by more than 8 electrons when they combine with what kind of elements? (F)
|
Electronegative
|
|
|
What is a method of electron configuration in which only the valence electrons of an atom of a particular element are shown indicated by dots placed around the elements symbol?
|
Electron-dot notation
|
|
|
..
: F : . |
Florine's electron dot notation?
|
|
|
How can you determine how many valence electrons are in an element?
|
By adding the subscripts in it's noble gas notation.
|
|
|
H = ?
2 |
H : H
|
|
|
An unshared pair is a pair of electrons not involved in what?
|
Bonding exclusively to one atom.
|
|
|
What are Lewis structures?
|
Formations in which atomic symbols represent nuclei and inner shell electrons.
|
|
|
A ______ bond is a covalent bond in which 1 pairs of electrons are shared between 2 atoms.
SINGLE or DOUBLE? |
single
|
|
|
A ______ bond is a covalent bond in which 2 pairs of electrons are shared between 2 atoms.
SINGLE or DOUBLE? |
double
|
|
|
All 4 electrons in a double bond belong to what?
|
Both atoms.
|
|
|
A ______ bond is a covalent bond in which 3 pairs of electrons are shared between 2 atoms.
TRIPLE or DOUBLE? |
triple
|
|
|
What kind of bonds are referred to as multiple bonds?
|
Triple and Double bonds.
|
|
|
Double bonds have _______ bond energies and are generally ______ than single bonds.
|
greater, shorter
|
|
|
When does the need for multiple bonds become obvious?
|
If there aren't enough valence electrons to complete octets by adding unshared pairs.
|
|
|
What does resonance refer to?
|
Bonding in molecules or ions that can't be correctly represented by a Lewis structure. (Hybrids)
|
|
|
To indicate resonance, a double headed arrow is placed _______ a molecule's resonance structures.
|
between
|
|
|
Na+ has a charge of _.
|
1+
|
|
|
There is an electrical force of attraction between ________ charged ions.
|
oppositely
|
|
|
Most ionic compounds exist as what?
|
Crystalline solids.
|
|
|
What is a crystal of any ionic compound?
|
A 3-D network of positive and negative ions mutually attracted to each other.
|
|
|
What is the simplest collection of atoms from which an ionic compound can be established?
|
A formula unit.
|
|
|
One formula unit of NaCl is one sodium _____ plus one chloride ______.
|
cation, anion
|
|
|
Nature favors arrangements in which potential energy is ________.
MINIMIZED or MAXIMIZED? |
minimized
|
|
|
In an ionic crystal, ions ________ their potential energy by combing in a crystal lattice.
MINIMIZE or MAXIMIZE? |
minimize
|
|
|
How do chemists compare bond strengths in ionic compounds?
|
They compare the amount of energy released when separated ions in a gas come together to form a crystalline solid.
|
|
|
What is lattice energy?
|
The energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gases.
|
|
|
What do negative values of lattice energy indicate?
|
That energy is released when the crystalline is formed.
|
|
|
What is the force that holds ionic compounds together?
|
A very strong overall attraction between positive and negative charges.
|
|
|
The forces of attraction between molecules are much ______ than the forces among formula units in ionic bonding.
STRONGER or WEAKER? |
stronger
|
|
|
What does the melting/boiling point and hardness of a compound depend on?
|
How strongly its basic units are attracted to each other
|
|
|
Ionic compounds generally have ________ melting/boiling points than molecular compounds.
INCREASING or DECREASING? |
increasing
|
|
|
Are ionic compounds hard and brittle?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
Why are ionic compounds hard and brittle?
|
Because in an ionic crystal, even a slight shift of one row of ions relative to another causes a large buildup of repulsive forces. These forces make it difficult for layer to move relative to another causing ionic compounds to be hard. If one layer is moved however, the repulsive forces make the layers part completely, causing them to be brittle.
|
|
|
Many _____ compounds dissolve in water.
|
ionic
|
|
|
What happens when ionic compounds dissolve in water?
|
Their ions separate from each other and become surrounded by water molecules.
|
|
|
The attraction between positive and negative ions in a crystalline ionic compound cause layers of ions to ______ motion.
RESIST or ATTRACT? |
resist
|
|
|
The attraction between positive and negative ions in a crystalline ionic compound cause layers of ions to resist motion. As a result of this, what happens?
|
The crystal shatters! :-(
|
|
|
A charged group of covalently bonded atoms is what?
|
Polyatomic.
|
|
|
_________ ions combine with ions of ______ charges to form ionic compounds.
|
Polyatomic, opposing
|
|
|
[NH4]+ shows what?
|
That the group as a whole has a charge of 1+ and the 7 protons of N plus the 4 of H show a total charge of 11+.
|
|
|
Within a metal, the vacant orbitals in the atom's energy level _ overlap.
S, P, D, or F? |
s
|
|
|
Within a metal, the vacant orbitals in the atom's energy level s overlap. What does this allow?
|
The outer electrons of the atoms to roam freely throughout the entire metal.
|
|
|
_________ electrons don't belong to any one atom but instead move freely about the metal's network of empty atomic orbitals.
|
Delocalized
|
|
|
What is metallic bonding?
|
The chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons.
|
|
|
What accounts for the high electrical and thermal conduct characteristics of all metals?
|
The freedom of electrons to move in a network of metal atoms.
|
|
|
Can metals absorb a wide range of frequencies?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
Metals can absorb a wide range of frequencies. What does this absorption of light contribute to?
|
The excitation of metal atoms' electrons to higher energy levels. However they then fall soon after, emitting light. This light creates the metallic appearence of metals.
|
|
|
What is malleability?
|
The ability of a substance to be hammered or beaten into thin sheets.
|
|
|
What is ductility?
|
The ability of a substance to be drawn, pulled, or extruded through a small opening to produce a wire.
|
|
|
How is malleability and ductility possible?
|
Because metallic bonding is the same in all directions throughout the solid
|
|
|
Metallic bond strength varies with the _______ charge of the metal atoms and the number of electrons in the metal's electron sea.
|
nuclear
|
|
|
What is the enthalpy of vaporization?
|
The amount of energy absorbed by as heat when a specified amount of a substance vaporizes at constant pressure.
|
|
|
What is molecular polarity?
|
An uneven distribution of molecular charge.
|
|
|
How many atoms are in a linear molecule?
|
2.
|
|
|
VSEPR stands for...?
|
"Valence-Shell, Electron-Pair, Repulsion".
|
|
|
What does VSEPR state?
|
That repulsion between the sets of valence-level electrons surrounding an atom causes these sets to be oriented as far as possible.
|
|
|
VSEPR says that shared electron pairs will be... what?
|
As far away from each other as possible.
|
|
|
Ammonia (NH3) and Water (H2O) are molecules in which the central atom has neither shared and unshared electron pairs.
TRUE or FALSE? |
False. BOTH.
|
|
|
How many unshared pairs does a water molecule have?
|
2.
|
|
|
How are double and triple bonds treated in VSEPR theory?
|
The same as single bonds.
|
|
|
List some things about Linear structures.
|
- 2 atoms bonded to central atom.
- 0 lone pairs. - AB2 kinda molecules. - BeF2 is an example. |
|
|
List some things about Tetrahedral structures.
|
- 4 atoms bonded to central atom.
- 0 lone pairs. - AB4 kinda molecules. - CH4 is an example. |
|
|
List some things about Trigonal-Planar structures.
|
- 3 atoms bonded to central atom.
- 0 lone pairs. - AB3 kinda molecules. - BF3 is an example. |
|
|
VSEPR theory _______ reveal the relationship between a molecule's geometry and the orbitals occupied by it's bonding electrons.
|
doesn't
|
|
|
Water molecules are _______.
|
bent
|
|
|
What does hybridization explain?
|
How the orbitals of an atom become rearranged when the atom forms covalent bonds.
|
|
|
What is hybridization?
|
The mixing of 2 or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new hybrid atomic orbitals of equal energies.
|
|
|
Methane (CH4) has what kind of geometry?
|
Tetrahedral.
|
|
|
What are hybrid orbitals?
|
Orbitals of equal energy produced by the combination of 2 or more orbitals of the same atom.
|
|
|
What are intermolecular forces?
|
The forces of attraction between molecules.
|
|
|
The strongest intermolecular forces exist between _____ molecules.
|
polar
|
|
|
Why do polar molecules act as tiny dipoles?
|
Because of their uneven charge distribution.
|
|
|
How is a dipole created?
|
By equal but opposite charges that are separated by a short distance.
|
|
|
Draw a dipoleish thing.
|
---+--->
H - Cl |
|
|
What are the forces of attraction between polar molecules are known as?
|
Dipole-dipole forces.
|
|
|
Why do some hydrogen-containing compounds have unusually high boiling points?
|
Because of the presence of a particularly strong type of dipole-dipole force.
|
|
|
What is hydrogen bonding?
|
The intermolecular force in which a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom is attracted to an unshared pair of electrons of an electronegative atom in a nearby molecule.
|
|
|
What are London dispersion forces?
|
The intermolecular attractions resulting from the constant motion of electrons and the creation of instantaneous dipoles.
|
|
|
-
|
-
|

