![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
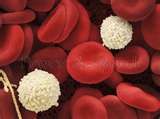
Leukocytes
|
Leukocytes
White blood cells (WBC) FUNCTION: (1) Primary infection-fighting blood cells |
|
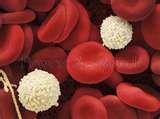
Erythrocytes
|
Erythrocytes
Red Blood cells (RBC) FUNCTION: (1) Blood cells involved in the TRANSPORT of oxygen and CO2 |
|
|
Platelets
|
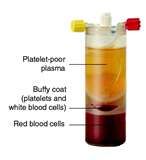
Platelets
Formed elements in the blood which develop when megakaryocytes disintegrate. FUNCTION: (1) Platelets are involved in hemostasis and bloodclotting |
|
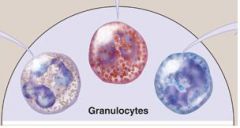
Granulocytes
|
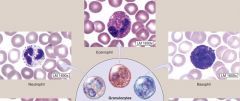
Granulocytes-
A mature leukocyte that contains multi-lobed & VERY VISIBLE cytoplasmic GRANULES *which are colored by specific types of dyes e.g Wright Stain EXAMPLES: (N-E-B) (1) Neutrophils (2) Eosinophils (3) Basophils |
|
|
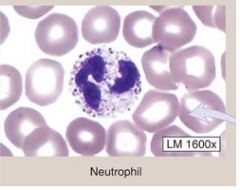
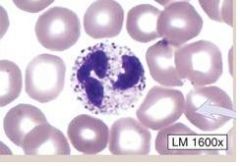
Neutrophils-
(1) comprise 60-70% of all leukocytes (2) Contain LILAC GRANULES (retains neutral stains) (3) Has MULTI-LOBED NUCLEUS (4) Usually elevated during BACTERIAL infections FUNCTION: (1) active PHAGOCYTIC cell in bacterial infection |
|
|
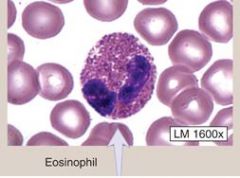
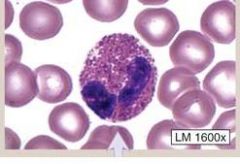
Eosinophils
(1) Comprise 2-4% of all leukocytes (2) Have BI-LOBED NUCLEUS (3) Their granules stain ORANGE/RED (4) Usually elevated during PARASITIC infections & ALLERGIC REACTIONS FUNCTION: ? |
|
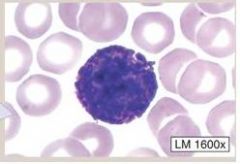
Basophils
|
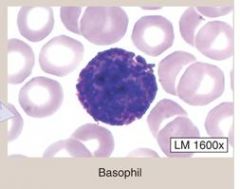
Basophils-
(1) Comprise 0.5-1.0% of leukocytes (2) BI-LOBED/S-SHAPED nucleus (3) Their granules stain DARK BLUE FUNCTION: (1) Release HEPARIN, HISTAMINE and other chemicals to induce allergic responses (2) enhance INFLAMMATORY response (3) Binds to IgE |
|
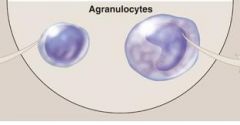
|
Agranulocytes-
(1) One form of a leukocyte (2) contains a SINGLE, ROUND, DENTED/non-lobed nuclei (3) LACKS visible cytoplasmic GRANULES CATEGORIES: (1) Monocytes (2) Lymphocytes |
|
|
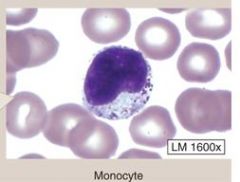
Monocytes-
(1) These are LARGE leukocytes (2) DENTED/BEAN Shaped |
|
|
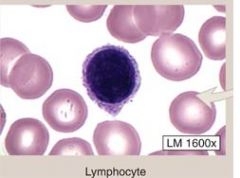
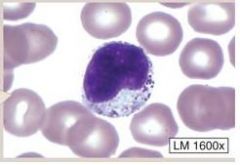
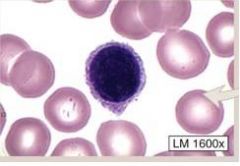
Lymphocytes-
(1) SMALLER leukocytes (2) Relatively LARGE, ROUND nucleus (3) very LITTLE cytoplasm (4) 2nd most common form of WBC CATEGORIES: (1) B cells (specific immunity) (2) T cells (specific immunity) (3) NK cells (non-specific immunity) |
|
|
Non-Specific Mechanism
|
Non-Specific Mechanism
(1) The 1st LINE OF DEFENSE (2) enables the body to defend against ANY microbe INCLUDES: (1) physical barriers (skin, mucous membranes) (2) chemical factors (gastric juice, lysozyme in tears). (3) antimicrobial substances (complement & interferons) (4) phagocytic cells (neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes & macrophages) (5) NK cells |
|
|
Specific Mechanism
|
Specific Mechanism-
(1) may be triggered by a microbe FUNCTION: (1) aids in the DESTRUCTION of SPECIFIC MICROBES (2) B & T lymphocytes involved TYPES: (1) Humoral immunity (2) Cell-mediated immunity |
|
|
Humoral Immunity
|
Humoral Immunity-
(1) SPECIFIC IMMUNITY (2) B-lymphocytes are stimulated to mature into antibody-producing PLASMA cells MAIN FUNCTION: (1) The antibodies RECOGNIZE & REACT with SPECIFIC ANTIGENS on the surface of the microbe in a highly SELECTIVE fashion |
|
|
Cell-Mediated Immunity
|
Cell-Mediated Immunity-
(1) SPECIFIC IMMUNITY (2) T-lymphocytes that DIFFERENTIATE into several subclasses of T cells (Helper T cell, Cytotoxic T cell etc) MAIN FUNCTION: (1) T cells produced a VARIETY of PROTEINS & TOXINS (2) to help eliminate SPECIFIC microbes or microbe infected cells |

