![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Immune Disorders
|
Hypersensitivities - IR to environmental antigens (allergens)
Autoimmunity - IR to self proteins Immune Deficiencies - failure to respond —> infection Transplantation Rejection - IR to foreign proteins in transplant |
|
|
AMI (Antibody mediated Immune Response)
|
Type I
IgE -(Classic, Anaphylactic, or Immediate) Type II - (Cytotoxic) Type III - (Immune Complex) |
|
|
CMI (Cell Mediated Immune Response)
|
Type IV -Tc and Th1 response to an antigen
(Cell mediated) |
|
|
Type I IgE
|
(Classic, Anaphylactic,
or Immediate) Mast cells verses environmental antigens (allergens) |
|
|
Type II (Cytotoxic)
|
IgG / IgM and complement verses cell surface antigen
|
|
|
Type III (Immune Complex)
|
IgG / IgM verses soluble antigen
|
|
|
Allergens : Type I (Anaphylactic) Reactions
|
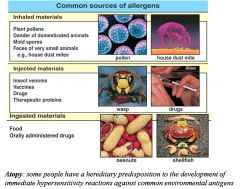
|
|
|
Type I (Anaphylactic) Reactions
STEPS |
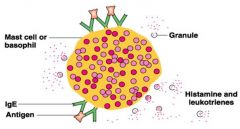
Initial allergen exposure induces IgE production
IgE “sensitizes” mast cells Fc of IgE attaches to mast cell surface receptor Subsequent allergen exposure Fc receptors cross linked Degranulation |
|
|
Type II (Cytotoxic) Reactions
|
IgG or IgM antibodies verses cell surface antigen
Presence of Ag-Ab complex activates complement Inflammation Complement activation causes cell lysis ( membrane attack complex) Damage by enzymes released by neutrophiles Ex: Transfusion Reactions Hemolytic Disease of Newborn Drug induced Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Mismatch of ABO Blood Group
|
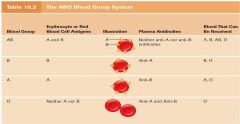
|
|
|
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
|
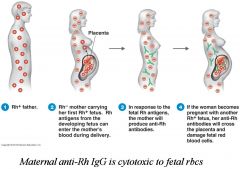
|
|
|
Drug-induced Thrombocytopenic Purpura
|
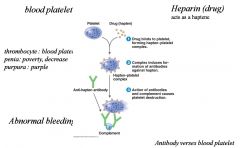
|
|
|
Type III (Immune Complex) Reactions
|
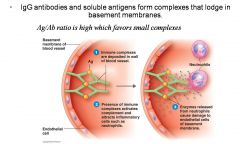
|
|
|
Allergic pneumonitis
|
bat guano
moldy hay pigeon breeders lung malt workers lung |
|
|
Type IV (Cell-Mediated) Reactions
|
Inappropiate CMI response (Tc or Ti cells)
1. Contact sensitivity Incitants adsorbed into skin act as haptenes 2. Allergy of Infection Ex: Tuberculosis Th1 (inflammatory) response (CMI) chronic inflammation Tubercule EX Poison ivy |
|
|
Haptens
|
|
|
|
Haptens
|
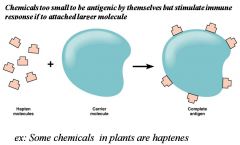
|
|
|
Contact Sensitivity
|
|
|
|
Contact Sensitivity
|
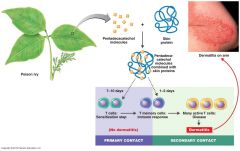
|
|
|
Autoimmunity
|
is loss of self-tolerance
|
|
|
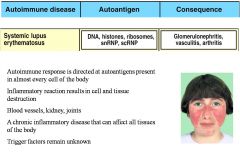
Autoimmune Diseases
|
IgG antibody against cell surface, matrix antigen, or receptor (type II)
IgG and soluble antigen Immune complex disease (type III) Tc and T inflammatory cells T-cell mediated disease (type IV) Note: there is no autoimmune disease in which IgE is produced against a self protein |
|
|
Type II : Cell Surface Receptor
|
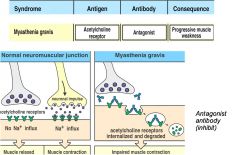
|
|
|
Type II : Cell Surface Receptor 2
|
|
|
|
Type III Immune Complex
|
|
|
|
Type II : Cell Surface Receptor
|
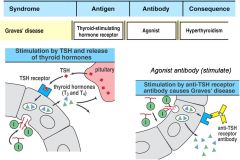
|
|
|
TYPE IV: T Cell Mediated
|
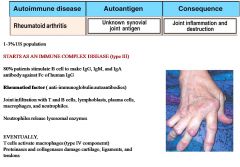
|
|
|
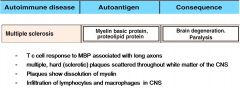
TYPE IV: T Cell Mediated
|
|
|
|
Diabetes 1
TYPE IV: T Cell Mediated |
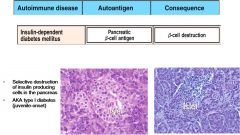
|
|
|
Acquired Immune Deficiencies
|
develop during an individual's life, due to
Infections HIV – AIDS Destruction of T4 lymphocytes (T helpers) no Th2, no AMI and no CMI Drugs Immunosuppressive therapy (transplant) - drugs inhibit recipients immune responses Chemotherapy (cancers) - drugs inhibit rapidly growing cells which include B and T lymphocytes Cancers B and T cell cancers - cancerous B and T cells do not respond properly |
|
|
AIDS Definition
|
Basis : HIV+/ CD4 T Cell Count / Clinical Catagory
CD4 ≥ 500 clinical category C CD4 200 - 499 clinical category B or C CD4 ≤ 200 clinical category A, B, or C Past AIDS definition: HIV+, CD4 count <200, clinical AIDS |
|
|
AIDS: Category A
|
Asymptomatic or persistent lymphadenopathy
|
|
|
AIDS: Category B
|
Persistent Candida albicans infections
|
|
|
AIDS: Category C
|
Clinical AIDS. CMV, TB, Pneumocystis, toxoplasmosis,
Kaposi's sarcoma (and other opportunistic infections) |
|
|
HIV Diagnostic Methods
|
Seroconversion takes up to 3 months
HIV antibodies detected by ELISA HIV antigens detected by Western blotting Plasma viral load is determined by PCR or nucleic acid hybridization |
|
|
HIV Transmission
|
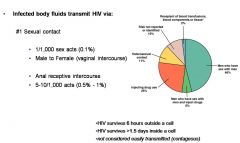
|
|
|
Other HIV Transmission
|
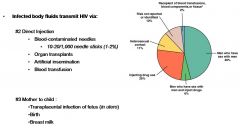
|
|
|
Chemotherapy
|
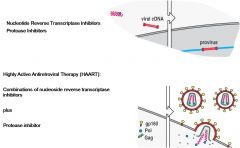
|
|
|
Diseases associated with AIDS
|
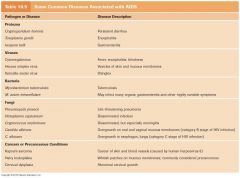
|
|
|
1983
|
Discovery of virus (HIV) causing loss of immune function.
|
|
|
Autograft
|
Use of one's own tissue
|
|
|
Isograft:
|
Use of identical twin's tissue
|
|
|
Allograft:
|
Use of tissue from another person
The fetus is an allograft that is protected from rejection |
|
|
Xenotransplantation
|
Use of non-human tissue
|
|
|
anti inflammatory
|
prednisone
Immunosuppression |
|
|
antimitotic —
|
— azathioprene (inhibits DNA replication)
|
|
|
Inhibit antigen activation of T and B cells
|
Immunosuppression
cyclosporine A and acrolimus (sirolimus) suppresses IL-2 no intestinal damage |
|
|
Graft verses Host Disease
|
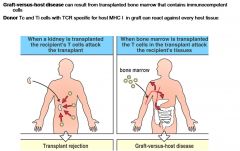
|

