![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does ubiquitous mean ? |
Bacteria are everywhere |
|

|
Growth characteristic of broth Turbidity- shake it up Pencil test |
|
|
Growth characteristic Ring with sedimentation |
|

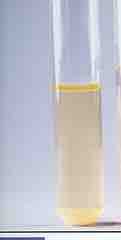
Name this growth characteristic of broth
|
Growth characteristic of broth Pellicle- entire surface is covered |
|
|
What does TSA stand for? |
Trypticase soy agar |
|
|
What does TSB stand for ? |
Trypticase soy broth |
|
|
Why do we invert TSA plates during incubation? |
So the water doesn't disinfect the bacteria that happens on the lid |
|
|
What is normal microbial flora ? |
bacteria which are found in or on our bodies on a semi-permanent basis without causing disease. |
|
|
Two examples of normal microbial flora? |
Resident flora Transient flora |
|
|
What is resident flora? |
Microbes that are always present |
|
|
What is transient flora? |
Microbes that live in or on your body for a period of time ( hours, days, weeks, months) then move on our die off. |
|
|
what does symbiosis mean? |
A close interaction between the two different organisms. |
|
|
What is mutualistic ? |
Both organism benefit "mutually beneficial" |
|
|
Example of mutualistic |
Escherichia coli synthesizes Vitamin k as well as vitamins of exchange. In exchange we prove warm environment |
|
|
What does commensalistic mean? |
One organism benefits, the other is neither helped nor harmed (positive or negative ) |
|
|
Example of commensalistic |
The presence of staphylococcus epidermis. |
|
|
What does opportunistic mean? |
Under normal conditions, microbe does not cause disease, but if conditions become conducive, it can cause disease |
|
|
Example of opportunistic |
Staphylococcus aureus found normally on skin cause no problems, but if it gets into a wound or burn it may become pathogenic. |
|
|
Mutualistic bacteria |
Escherichi coli |
|
|
Opportunistic Bactria |
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
More gram(+) bacteria or gram (-) bacteria ? |
Gram (+) bacteria |
|
|
Another example of bacteria that interacts in a mutualistic relationship |
Answer? |
|
|
Another example of bacteria that can be considered opportunistic ? |
E. Coli |
|
|
Advantage to acquire knowledge of the normal microbial flora? |
Better understanding of what's present or on our bosy |
|
|
If someone showers, why does that not get rid of all the bacteria that makes up your normal microbial flora? |
Microbes are always present so you never really get rid of them |
|
|
What is the purpose of preparing pour plates? |
To isolate individual bacterial colonies |
|
|
What is a pure culture ? |
A pure culture may originate from a single cell or single organism, in which case the cells are genetic clones of one another. |
|
|
What is a mixed culture ? |
mixed culture (one containing many species) |
|

Name this? |
Quebec colony counter |
|
|
Why do we temper agar tubes before bacterial inoculation? |
So that we don't kill the cells. |
|
|
How many are countable on a plate ? |
30-300 bacterial colonies |
|
|
What does NG stand for ? |
No growth |
|
|
What does TFTC? |
To few to count |
|
|
What does TNTC mean? |
To numerous to count |
|
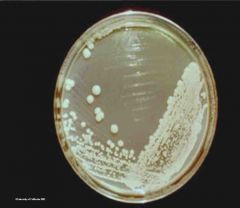
Name this type of plate ? |
Streak plate |
|
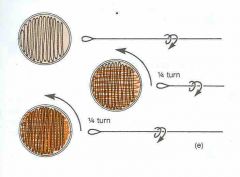
Name this type of plate |
Spread plate |
|
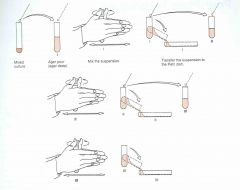
|
Pour plate |
|
|
Purpose of preparing a streak plate ? |
To isolate individual bacterial colonies |
|
|
Purpose of a spread plate ? |
To obtain a lawn of bacteria or "confluent growth" |
|
|
Difference between normal, transient & resident flora ? |
Normal- always there Transient- hours , days, weeks Resident - live there or reside there |
|
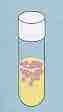
Name this oxygen requirement |
Aerobic/ top of solution |
|

Name this oxygen requirement |
Anaerobic- bottom of solution |
|
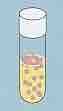
Name this oxygen requirement? |
Facultative- both |
|
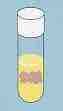
Name this oxygen requirement |
Microaerophilic- middle |
|

Name this? |
Gas pack |
|
|
What is the function of palladium crystals ? |
Reacts to make hydrogen and carbon dioxide which then creates a catalyst which creates the water |
|
|
Function of anaerobic indicator strip ? |
To determine if oxygen is present or not |
|
|
Function of fluid thioglycollate broth? |
Reducing medium |
|
|
Function of sodium thioglycollate? |
Reacts with molecular oxygen keeping oxygen levels low |
|
|
Resazurin? |
Anaerobic indicator |
|
|
Function of candle jar ? |
A candle jar in microbiology is used for anaerobiosis in which a lit candle is placed in an air tight jar and if it went out, it would be because it used up all the available oxygen. |
|
|
Normal atmospheric level of oxygen? |
21% |
|
|
Level of oxygen in Candle jar? |
16% |
|
|
Normal level of carbon dioxide |
6% |
|
|
Level of carbon dioxide in candle jar? |
3% |
|
|
TSA stabs? |
•1. Single stab with Inoculating needle – straight down, straight back up
•1. Micrococcus luteus |
|
|
TSA shakes ? |
1. Inoculate with Inoculating Loop - “shake” test tube so bacteria are equally distributed
•1. Micrococcus luteus |
|
|
Reason why we boil stabs, shakes and fluid thioglycollate broth? |
To remove dissolved oxygen |
|
|
Temperature classification of psycrophile ? |
•“Cold loving” •0 – 20 degrees C |
|
|
Temperature classification of mesophile? |
•“moderate temp loving” •20 – 40 degrees C |
|
|
Temperature classification of thermophile? |
•“heat loving” •40 – 100 degrees C |
|
|
What are thermoduric bacteria ? |
Thermoduric bacteria are bacteria which can survive, to varying extents, the pasteurisation process. Species of bacteria which are thermoduric include Bacillus, Clostridium and Enterococci. |
|
|
Thermal death point? |
•Temperature in which all bacteria and their endospores (if they have them) are killed within 10 minutes. |
|
|
Thermal death time? |
used to determine how long it takes to kill a specific bacteria at a specific temperature. |
|
|
Disinfectant ? |
antimicrobial agent designed to be used on inanimate objects |
|
|
Antiseptic? |
antimicrobial agent designed to be used on living tissue |
|
|
Bacteriostatic? |
Inhibits |
|
|
Bacteriocidal ? |
Kills |
|
|
Factors that determine ? |
•1. Time •2. Temperature •3. Degree of contamination •4. Sensitivity of the microbe •5. Concentration of antimicrobial agent •6. Presence of organic matter – blood, mucus, urine, etc |

