![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The only sugar available to fermenters growing in a Phenol Red Lactose Broth is lactose. Therefore, only bacteria capable of fermenting lactose will produce { } in this broth. |
Acid |
|
|
Utilization media are designed to test the ability of an organism to: |
Grow in the presence of a single essential nutrient |
|
|
Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide into |
Water and oxygen |
|
|
What is the function of the Durham tube inside a Phenol Red Tube? |
To indicate gas production |
|
|
The pH indicator bromthymol blue is used in the ( ) test. |
Simmons citrate agar |
|
|
The purpose of ferric citrate in the Bile Esculin Azide Agar is to |
Detect esculetin and form a dark brown color change |
|
|
True or False- in the Simmons Citrate Agar, lactose is the only carbon source |
False |
|
|
True or False- in the Phenylalanine test, the formation of a green color after incubation and addition of ferric chloride reagent indicates that phenylalanine has been deaminated |
True |
|
|
The alkali color of a Phenol Red broth is red and the acid color is |
Yellow |
|
|
A tube of TSB with 6.5% NaCl will be used for what test? |
Osmotic pressure test |
|
|
Describe a positive coagulase test |
Plasma is clotted |
|
|
What is a positive urea test and what does it mean |
A positive urea test has a bright pink tube and it is alkaline. Positve for amonia. |
|
|
The SIM tube tests for 3 things. What are they and how can you tell a positive test for each? |
1.Sulfur Reduction- (+) test is really dark, almost black 2. Indole Production- (+) test has a ring of pink at top 3. Motility- (+) test shows growth outside of stab line |
|
|
Describe A/A +G in TSI test |
Acidic- (+) for Glucose, Lactose or Sucrose Over same thing Has gas production |
|
|
Describe K/A +H2S |
Alkaline Over Acid- (+) for glucose then switched to peptone metabolism Sulfur indicated |
|
|
How can u tell a (-) starch test? |
After iodine is added there will not be a clear ring around bacteria |
|
|
What is meant by the term "beta hemolysis" |
Beta hemolysis means there is a complete hemolysis of RBC's |
|
|
When obtaining results of the antimicrobial sensitivity tests, the inhibition zone diameters will be measured in which units |
Millimeters |
|
|
The antibiotic sensitivity (susceptibility) test is known as |
Kirby-Bauer method |
|
|
The antimicrobial sensitivity test is a |
Disk diffusion test |
|
|
Name 3 components of the antimicrobial susceptibility test that are standardized |
1. Agar depth 2. Agar pH 3. 0.5 McFarland Standard |
|
|
Explain bacteriostatic |
They stop the growth, but don't kill |
|
|
How do u provide aerobic conditions for certain compartments of the Enterotube ll following inoculation |
Use the needle that came out of the middle of tube and poke holes in the plastic over the compartments that u want to have aerobic conditions |
|
|
In the Enterotube ll, a reagent must be added before reading the result of the... |
H2S/Indole chamber |
|
|
If 2 species are initially identified with the same numeric code using the Enterotube ll, then a confirmatory ( ) test is performed to differentiate betwn the 2 organisms. |
Voges-Proskauer |
|
|
True or False- the Enterotube is inoculated using the loop in your drawer |
False |
|
|
The Enterotube ll is used to identify a member of the family. .. |
Enterobacteriaceae |
|
|
What is a bacteria that grows into a clump of cells |
CFU- colony forming unit |
|
|
What is a countable plate |
Btwn 30 and 300 colonies |
|
|
What is the preferred method of urine collection |
Clean catch |
|
|
What is bactururia |
Presence of bacteria in urine |
|
|
What is Serial Dilution |
10- fold reduction in cells using water blanks |
|
|
What is OCD |
# of bacteria in original pt sample |
|
|
What is a volumetric loop |
Streaking tool made to hold a specific volume |
|
|
Modified streak plate with volumetric loop |

|
|
|
What is used for the salt tolerance test |
Osmetic Pressure Test- Osmosis Water moves through a cell membrane from high concentration to low concentration. |
|
|
What does the osmotic pressure test look for? What does a positive test look like? |
-Test looks for organisms that are halophiles. -Positive test shows little cloudy and settled at the bottom- TSB 6 1/2% salt -TSB control tube has some cloudy growth |
|
|
How to do Osmotic Pressure Test |
Inoculate saline medium tubes w/ Halobacterium broth using a sterile transfer pipette w/ 1mL of organism. Keep one uninoculated tube. Inoculate all tubes at 35+2degree C for 48 hours. Mix broth gently and check for turbidity, not color. |
|
|
What is important for control tube in osmotic pressure test (salt tolerance test) |
Plain TSB needs to be (+) when you compare contol to salt tube. If control tube is (-) then it's an invalid test. HAVE to HAVE (+) TSB control tube! |
|
|
What does Bile Esculin Agar test do? |
Differentiates different organisms. The bile in tube will select against gram (+). Gram (-) will grow. Add sodium azide to inhibit growth of gram (-). |
|
|
How does Bile Esculin Agar work? |
Test selects for Enterococcus. Use nutrient called esculin in tube. If bacteria wants to live in the tube it has to convert esculin into glucose and esculetin. Glucose goes away and esculetin is left in the tube. BLACK test tube is (+), no darkening of tube is (-). |
|
|
Phenol Red Broth |
Phenol Red broth is a differential test medium prepared as a base to which a carbohydrate is added. Included in the base medium are peptone and the pH indicator phenol red. An inverted Durham tube is added to each tube as an indicator of gas production. Keep one uninoculated tube for comparison. |
|
|
Test results for Phenol Red |
pH indicator is phenol red Red at neutral Yellow at acid-(+) We use lactose, dextrose, & sucrose (dextrose is same as glucose) |
|
|
PR results Yellow broth, bubble in tube |
Fermentation w/ acid and gas end products Symbol= A/G |
|
|
PR test results Yellow broth, no bubble in tube |
Fermentation w/ acid end products; no gas produced Symbol= A/- |
|
|
PR test results Red broth, no bubble in tube |
No fermentation Symbol= -/- |
|
|
PR test results Pink broth, no bubble in tube |
Degredation of peptone; alkaline end products Symbol= K |
|
|
Phenol Red pic |

|
|
|
Catalase test |
Catalase test is used to identify organisms that produce the enzyne catalase. It breaks down peroxide into water and oxygen (+) catalase= bubbles After adding peroxide don't forget to cover slide with lid of petri dish |
|
|
Citrate test |
Citrate tests to see if organism can break down citrate & convert it to pyruvate. pH indicator is bromothymol blue dye |
|
|
Citrate test results |
Blue tube is (+) Blue alkaline products were produced Green tube is (-) Uninoculated tube is also green |
|
|
Phenylalanine Deaminase Test |
To see if organism can use phenylalanine . Act of pulling off amino group is deamination. Pulling off a nitrogen group. Streak 2 slants |
|
|
Phenylalanine test results |

If u add ferric chloride and it turns dark green then it's positive. Negative has no reaction. |
|
|
Starch Hydrolysis (amylase test) |
Main nutrient is starch, bunch of glucose. Just need to pluck off glucose w/ amalase. Add iodine to starch agar after incubatio |
|
|
Starch Hydrolysis test before iodine |
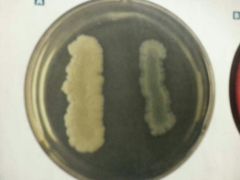
|
|
|
Starch Hydrolysis test after iodine |
Clear glow on left (halo) - (+) Right w/o clearing- (-) |
|
|
Urea Hydrolysis (urease test) |
This test is used to differentiate organisms based on their ability to hydrolyze urea w/ the enzyme urease. Use water and urease to break apart urea molecule. Urea is a byproduct of protein motabolism (waste product). Add pH indicator= phenol red |
|
|
Urea Hydrolysis test results |
Red- neutral Yellow- acidic (-) no urea hydrolysis Pink- basic (+) amonia building up in tube, rapid urea hydrolysis |
|
|
SIM Medium Sulfur reduction, indole production, motility |
》Motility- growing away from stab line (+) & dark brown (+) = motile Solid stab line= (-) for motility 》Sulfur- amino acid cysteine Iron (phyric sulfate) added to tube Black= (+) Not black= (-) for sulfur 》Indole Production- add reagent called Kovac's Cherry red= (+) indole test Nothing is (-) indole test |
|
|
Triple Sugar Iron 3 sugars- glucose, lactose, sucrose Glucose very small %- 0.1% Lactose- 1% Sucrose- 1% |
Peptone in tube (protein product) Iron in tube (sulfur test) pH indicator- phenol red All organisms use glucose to start Yello-ferment glucose, stays yellow if like lactose or sucrose Aerobically (only like glucose), slant back to orange Any bubbles or breaks- gas positive Black tube (+) for sulfur reduction but only happens in acidic conditions |
|
|
How to record triple sugar iron agar/ kligler iron agar |
Slant/butt A= acid/ yellow K= pink or red/ alkaline Black is H2S If black add +gas, +H2S |
|
|
Blood Agar |
Allows differentiation of bacteria based on their ability to hemolyze RBC's |
|
|
Blood Agar test results |
a-Hemolysis (alpha)= partial breakdown, green y-Hemolysis (gamma)= no break down B-Hemolysis (beta)= complete breakdown, clear |
|
|
B-HEMOLYSIS |
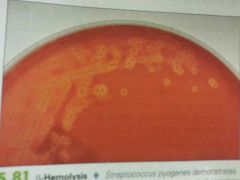
Clear |
|
|
a-Hemolysis |
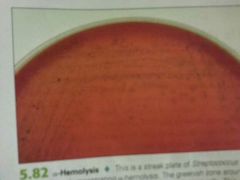
Green |
|
|
y-Hemolysis |
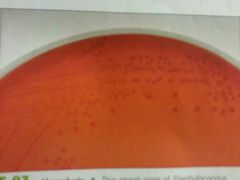
No breakdown |
|
|
Coagulase and Clumping Factor tests |

Coagulase tube test Remains liquid- coagulase (-) Solid- coagulase (+) Same for slide |
|
|
Enterotube ll |
Multitest system designed to identify enteric bacteria and other select oxidase-negative, Gram-neg bacteria |
|
|
Standard plate count (viable plate) Urine plate Yellow loop, blue loop |
Yellow loop= 10 microliter, .01 Blue loop= 1 microliters, .001 |
|
|
Standard plate calculation |
OCD= CFU/loop volume Make sure u put CFU's/ml at end CFU= # counting OCD= # looking for |
|
|
Urinary tract infections results |
*Greater than or = to 100,000 CFU's/ml is UTI *greater than or = to 10,000 to less than 100,000 CFU's/ml is possible UTI *less than 10,000 CFU's/ml is contamination (specimen collected or handled improperly) |
|
|
Antimicrobial susceptibility test: disk diffusion (kirby-Bauer) method |
Measure green circle in mm counting smallest lines |
|
|
The Enterotube ll is inoculated using |
A plated colony |
|
|
What is the Kirby-Bauer test |
It tests the susceptibility of microorganisms to antimicrobial agents |
|
|
Which test utilizes iodine reagent |
Starch |
|
|
Which of the following tests for amonia production |
Urea |
|
|
Clotted plasma is a (+) result for which test |
Coagulase |
|
|
Which test uses semisoft agar |
SIM |
|
|
The coagulase test is used to identify which species |
Staphylococcus |
|
|
What reagent is added to the SIM tube for the Indole test |
Kovac's Reagent |
|
|
Utilization media are designed to test the ability of an organism to |
Grow in the presence of a single essential nutrient |
|
|
The pH indicator bromthymol blue is used in the |
Simmons Citrate Agar test |
|
|
The purpose of the bile salts in the Bile Esculin Azide Agar is to |
Inhibit the growth of gram (+) organisms |
|
|
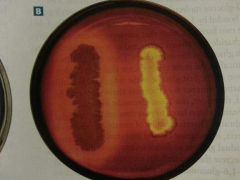
Bile Esculin Agar pic |

Left is bile esculin (+) |

