![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What 2 things determine Colony morphology/appearance? |
Environmental factors and genetic makeup |
|
|
What are the 4 genetic makeup factors |
Color, size, shape, and texture |
|
|
What purpose do agar plates have in bacterial growth morphologies? |
Agar plates help with the organism identification process |
|
|
How does a colony form? |
When a single bacterial cell is deposited on a solid nutrient medium, it begins to divide. One cell makes two, two makes four, four make eight. Eventually a visible mass of cells, a colony, appears. |
|
|
In what 4 ways are color, size, shape, and texture of microbial growth determined? |
1. genetic makeup of the organism 2. nutrient availability 3. temperature 4. incubation |
|
|
The 5 basic categories of colony morphology |
1. colony shape 2. margin (edge) 3. elevation 4. texture 5. pigmentation (color) |
|
|
6 types of colony shape |
Punctiform, irregular, circular, rhizoid, spindle, filamentous |
|
|
5 types of margin |
1. Smooth round/entire (smooth with no irregularities) 2. undulate (wavy) 3. lobate (lobed) 4. filamentous 5. rhizoid (branched like roots) |
|
|
5 elevations of colonies
|
1. flat
2. raised 3. convex 4. pulvinate (very convex) 5. umbonate (raised in the center) |
|
|
colony counter
|
used to view subtle differences in colony shape and size
|
|
|
what 2 things allow greater observation of detail in a colony counter?
|
1. transmitted light
2. magnifying glass |
|
|
colony counter is best determined with ______.
|
reflected light
|
|
|
The grid in the colony counter background is a ______.
|
counting aid
|
|

Classify. |
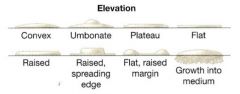
1. raised 2. raised, spreading edge 3. flat, raised margin 4. growth into medium |
|

Classify 2. |
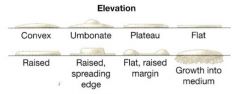
1. convex 2. umbonate 3. plateau 4. flat |
|

Classify. |
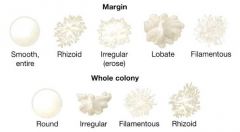
1. Smooth, entire 2. rhizoid 3. irregular (erose) 4. lobate 5. filamentous |
|
|
4 types of descriptions used to describe colony morphology: |
1. color 2. surface characteristics 3. consistency 4. optical properties |
|
|
2 types of surface characteristics |
1. shiny 2. dull |
|
|
6 types of consistency |
1. dry 2. moist 3.mucoid 4 . wrinkled 5. Smooth 6. rough |
|
|
3 types of optical properties
|
1. opaque 2. translucent 3. transparent
|
|
|
6 colonies studied in this lab
|
1. micrococcus luteus 2. corynebacterium xerosis 3. lactobacillus plantarum 4. mycobacterium smegmatis 5. bacillus subtilis 6. proteus miabilis
|
|
|
Colony elevation and texture are mostly easily observed with? |
Reflected light: hitting the growth at a low angle |
|
|
Colony opacity is best seen with? |
Transmitted light not reflected |
|
|
Purpose of an Agar slant |
•Agar slants are generally used for cultivation & maintenance of stock cultures
1.More difficult to contaminate compared to a plate 2.Do not dry out quickly 3.Require less media than plates
|
|
|
The usual shape of Agar slant growth. |
•Most slant growth = filiform -Dense,opaque growth with smooth edges |
|
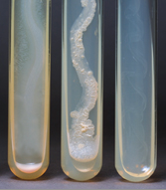
3 Agar slant growth patterns |
1.Spreading edge from motile organisms 2. Friable (crusty) growth –many 3. Translucent / transparent growth |
|
|
3 Growth Patterns in Broth |
•Pellicle: Organisms float on top of the medium & produce a membrane
•Sediment: Organisms sink to the bottom
•Flocculent growth: Organisms clump together |
|
|
Why do we not shake the test tube of nutrient broth before looking? |
•Do not agitate nutrient broth prior to looking… sediment becomes uniform fine turbidity! |

