![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the MCC of XP? |
1. Defect in DNA repair--- endonuclease |
|
|
From where do melanocytes originate? |
1. Neural crest |
|
|
What are the ssx of lentigo maligna? |
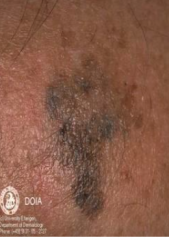
1. Irregular-shaped tan or brown macule 2. Enlarges to bizarre coloration, size, and shape 3. Noninvasive |
|
|
How do you tx lentigo maligna? |
1. Cryosurgery 2. Laser 3. 5-FU 4. Imiquod |
|
|
When does lentigo maligna become lentigo maligna melanoma? |
1. When there macule becomes palpable nodule |
|
|
What are the ssx of atypical melanocytic nevus? |
1. 5-10 mm or larger 2. Irregular macular lesion with various colors |
|
|
What is the lesion number risk associated with a dysplastic nevus? |
1. >3 lesions increases risk of melanoma from 3 to 43 times |
|
|
What are the ssx of a dysplastic nevus? |
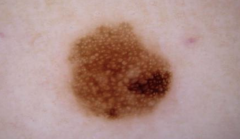
1. Variegated tan, brown, pink coloration 2. Macular 3. 5-12 mm with irregular borders 4. "Fried egg" |
|
|
What mutations lead to dysplastic nevi? |
1. CDKN2A tumor suppressor 2. p16 3. CDK4 |
|
|
What is the histology of a dysplastic nevus? |
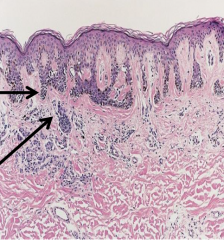
1. Elongated, clubbed rete ridges 2. Bridging of rate ridges 3. Should phenomenon 4. Lamellar concentric fibroplasia |
|
|
How do you tx dysplastic nevi? |
1. Excision 2. Photograph often 3. Sunscreen and monthly self-exam |
|
|
What are the ssx of dysplastic nevus syndrome? |
1. Melanoma in 1/2 degree relative 2. >50 melanocytic nevi 3. Dysplastic nevi on histologic exam |
|
|
What are the danger signs for skin nevi? |
1. Asymmetry 2. Border 3. Color 4. Diamter >6 mm |
|
|
What should you do if you see a suspected ABCD lesion? |
1. Bx--- punch or excisional 2. When in doubt, cut it out |
|
|
What are the MCC of melanoma? |
1. UV radiation exposure 2. CDKN2A on chromosome 9--- p16 and p14 proteins |
|
|
What are the ssx of acral lentiginous melanoma? |
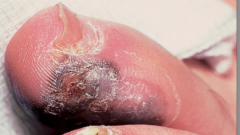
1. Brown or black macules on glabrous skin 2. MC on soles of foot/palm |
|
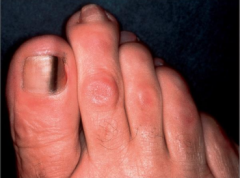
|
1. Hutchinson's sign--- black discoloration at proximal nailfold 2. Acral lentiginous melanoma |
|
|
What are the ssx of superficial spreading melanoma? |
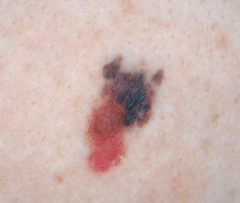
1. Slow growing brown or black macular lesion with irregular border 2. Macular/papular 3. Lower legs in women 4. Arise from pre-existing nevus |
|
|
What are the ssx of nodular melanoma? |
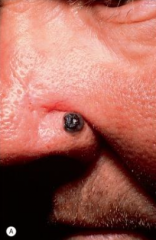
1. Brown or black papules that slowly and frequently ulcerates 2. Occurs denovo 3. More aggressive |
|
|
What are the ssx of amelanotic melanoma? |
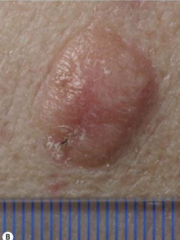
1. Nonpigmented variant 2. Can be confused with benign or less aggressive malignant tumors |
|
|
What are the dermascopic features suggestive of malignant melanoma? |
1. Atypical pigment network 2. Blue/whitish veil 3. Regression structures--- white or blue-gray areas |
|
|
What is Breslow's depth? |
1. Measured from granular layer to point of deepest invasion of tumor cells 2. Better than Clark's |
|
|
What is Clark's level? |
1. Describes depth of invasion 2. Level I- epidermis 3. Level II- from epidermis into papillary dermis 4. Level III- from epidermis and fill papillary dermis 5. Level IV- extend into reticular dermis 6. Level V- extend through dermis into underlying subQ fat |
|
|
What lesions have poorer prognosis in melanoma? |
1. Lesions on scalp, hands, and feet |
|
|
How do you tx malignant melanoma? |
1. Excision--- standard of care 2. Elective lymph node dissection 3. Chemo 4. Immunotx |
|
|
What is one independent predictor of survival for distant metastatic melanoma? |
1. LDH--- measured in stage IV |
|
|
When is sentinel node bx recommended in melanoma? |
1. T2, T3 T4 melanomas 2. T1b 3. Not shown to demonstrate overall benefit |

