![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adrenergic Agonists/Catecholamine pharmacophore |
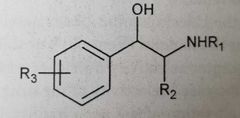
Primary or secondary amine 2 carbons away from substituted benzene ring.
Ethylamine chain essential to adrenergic activity
Ex: epinephrine, norepinephrine |
|
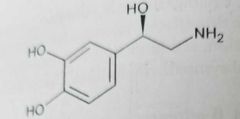
|
Norepinephrine (sympathomimetics, nonselective adrenergic agonist) Catechol group prone to oxidation
Alertness, increase heart rate and blood pressure, reduces blood flow to gastrointestinal system , releases glucose from energy stores |
|
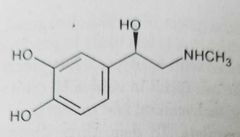
|
Epinephrine (sympathomimetics, nonselective adrenergic agonist)
Used to treat cardiac arrest and hypotensive crisis. Vasoconstrictor, ionotropic (increase contractility)/chronotropic (increase heart rate) |
|
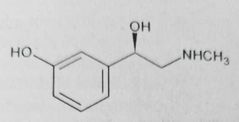
|
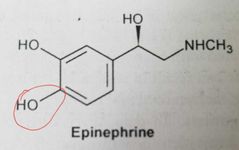
Phenylephrine (sympathomimetics, selective α-adrenergic agonist) Removal of para hydroxyl group increases α-receptor activity
Nasal decongestant. Maintain systemic blood pressure in hypotensive conditions
|
|
|
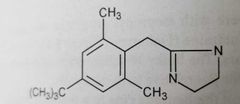
Oxymetazoline (sympathomimetics, selective α-adrenergic agonist)
Bulky para or meta substitution on benzene ring increases α activity
Nasal decongestant; vasoconstrictor in nasal mucosa |
|
|
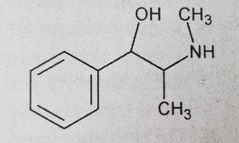
Pseudoephedrine (indirect sympathomimetics, α-agonist)
Removal of hydroxyls from catechol ring and addition of α-methyl group reduced direct receptor activity and increase indirect activity. Norepinephrine releasing Nasal decongestant |
|
|
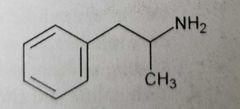
Amphetamine (indirect sympathomimetics) Removal of hydroxyls from catechol ring and addition of α-methyl group reduced direct receptor activity and increase indirect activity. Enhance catecholamine release in CNS. Used to treat ADHD |
|
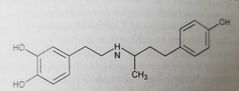
|
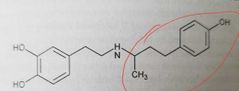
Dobutamine (sympathomimetics, selective β-adrenergic agonist) Bulky N-substitution increases β-receptor selectivity Used in acute heart failure. Ionotropic via β1 receptors - open calcium channels (enhanced contractility) |
|
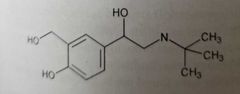
|
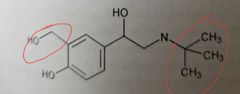
Albuterol (sympathomimetics, selective β-adrenergic agonist) Bulky N-substitution increases β-receptor selectivity
Alteration of meta hydroxyl group increases β2 selectivity over β1
Bronchodilator (activate β2 receptors)
|
|
|
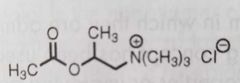
Bethanecol Selective muscarinic agonist used to treat postoperative urinary retention and abdominal distention |
|
|
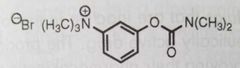
Neostigmine Reversible acetylcholine esterase inhibitor used to treat abdominal distention, urinary retention, and myasthenia gravis |
|
|
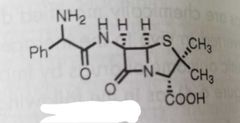
Ampicillin |
|
|
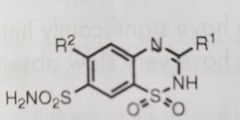
Benzothiazide
Thiazide diuretics |
|
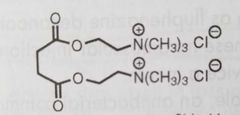
|
Succinylcholine chloride Nicotine antagonist used as depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent |
|
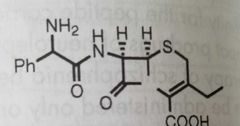
|
Cephalexin (cephalosporin antibiotic) |
|
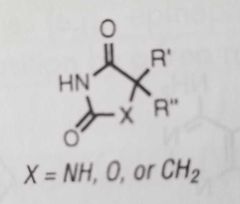
|
Antiepileptic agents Ex- phenytoin (X=NH) |
|
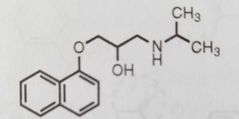
|
Propranolol
Nonselective β2 adrenergic antagonist
Used to treat hypertension and arrhymias (Substitution para to phenoxy position increase β1 selectivity) |
|
|
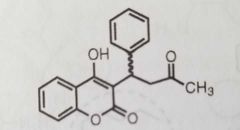
Warfarin Oral anticoagulant |
|
|
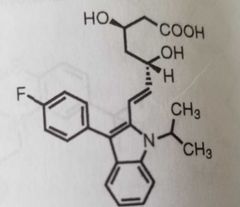
Fluvastatin Statin used to treat hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
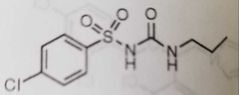
Chlorpropamide Used to treat diabetes |
|
|
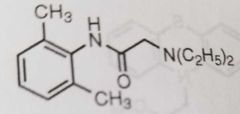
Lidocaine Local anesthetic |
|
|
Barbiturates Sedative hypnotics, antiepileptics, anesthetics |
|
|
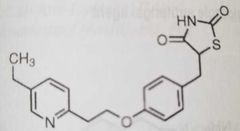
Pioglitazone Glitazone antidiabetic agent |
|
|
1,4-Benzodiazepines
Anxiolytics, antiepileptics, muscle relaxants |
|
|
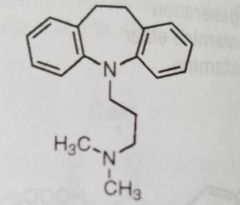
Imipramine Antidepressant |
|
|
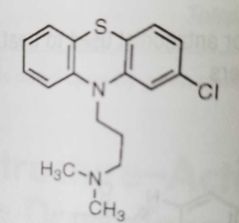
Chlorpromazine Antipsychotic agent |
|
|
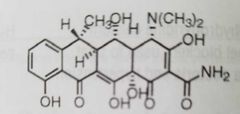
Doxycycline Antimicrobial agent |
|
|
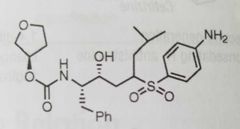
Amprenavir Antiviral and HIV protease inhibitor |
|
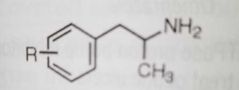
|
Phenylisopropylamines CNS stimulants (ex- amphetamine) |
|
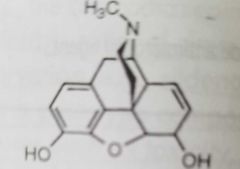
|
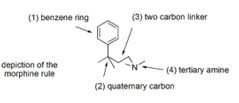
Morphine
Opioid receptor agonist Nearly all opioids and opiates have the morphine pharmacophore (above) |
|
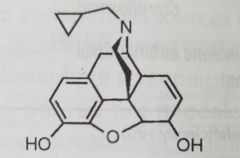
|
Naltrexone Opioid receptor antagonist |
|
|
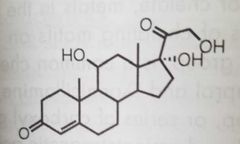
Hydrocortisone Adrenocorticoid |
|
|
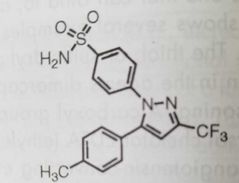
Celecoxib Selective COX-2 inhibitor |
|
|
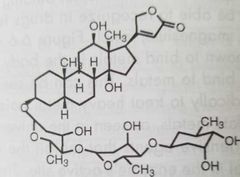
Digoxin Cardiac glycoside |
|
|
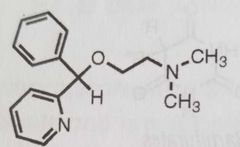
Diphenhydramine 1st gen ethanolamine ether antihistamine |
|
|
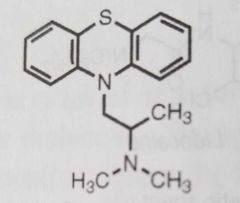
Promethazine 1st gen tricyclic antihistamine, H1 antagonist |
|
|
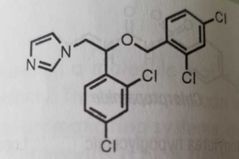
Miconazole Imidazole antifungal |
|
|
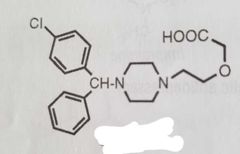
Cetirizine 2nd gen nonsedating H1 antihistamine |
|
|
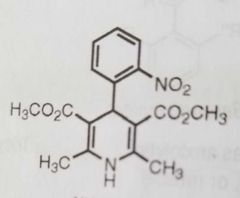
Nifedipine Calcium channel blocker used to treat angina pectoris and hypertension |
|
|
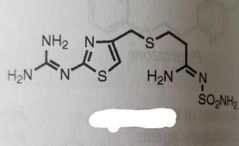
Famotidine H2 receptor antagonist used to treat peptic ulcers |
|
|
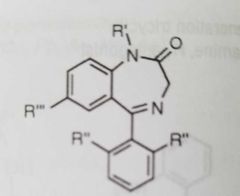
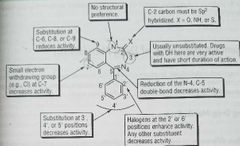
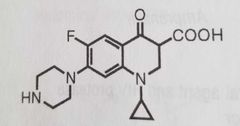
Ciprofloxacin
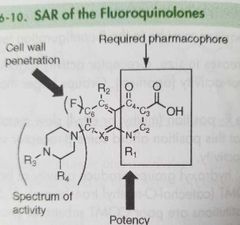
Quinolone antimicrobial Fluoroquinolones structure above: - c7 substituent: heterocyclic for gram neg activity. N for oral activity -x8 : N increases bioavailability; methoxy group increases stability to uv light -R1 and R2 groups affect gram pos potency |
|
|
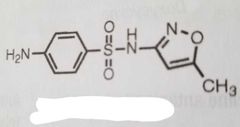
Sulfamethoxazole
Sulfonamide antimicrobial |
|
|
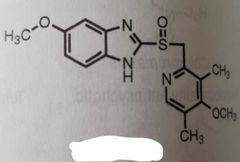
Omeprazole H+/K+ ATPase proton pump inhibitor used to treat peptic ulcers |
|
|
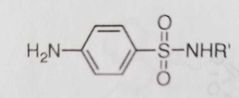
Sulfonamides with antimicrobial activity Acidity of sulfonamide group key to activity. Electron withdrawing R' group (ie- heteroaromatic ring) improves activity by enhancing acidity |
|
|
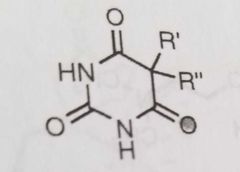
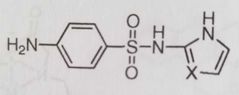
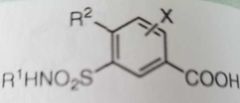
Sulfonamides with antidiabetic activity X= O, S, or N |
|
|
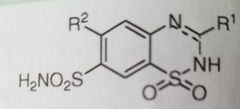
Sulfonamides with diuretic activity (Thiazide diuretics) Ex- hydrochlorothiazide |
|
|
Sulfonamides with diuretic activity (high ceiling diuretics) Ex-furosemide |

