![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
amides have a pka of ___ a PC of ___ which is regarded as what? |
9 and pc of 0.02 which is LOW SLOW |
|
|
Amide has a pka of? partition coeff of ? |
8 and pc of 1 which is med |
|
|
class c has a pka of ? Partition Coefficient of ? class c has a ratio of 3/4/5:1 which means? |
7.9 and pc of 5 (high) It will distribute faster |
|
|
Drugs with LOW lipophilicity will : stay or disperse ? Lipophilicity depends on ? |
stay into area its injected into. -PKA |
|
|
Higher partition coeff will distribute into other tissues t/f - low PC will distribute to tissues well? |
True- has LONGER DURATION FALSE ! it won it will be metabolized right there and then. ALSO HAS SHORTER DURATION
|
|
|
Procaine/ESTERS has pka of ____ and short or fast onset? What about pc? |
pka of 9, has a slow onset and short duration of action and low PC |
|
|
Amides have a pka of ___ and what kind of onset and duration? Also what about pC? |
Amides have a faster onset, a pka of 9, a longer duration, and higher PC. |
|
|
name the three ester/procaine LAs use for : |
procaine, chlorprocaine, and tetracaine THE REST ARE AMIDES
PC |
|
|
Intermediate acting L/A |
Lidocaine/ Mepivacaine, Prilocaine have an intermediate DoA
LMP |
|
|
what drugs are long acting? |
tetracaine, bupivacaine, levobupivacaine,etidocaine and ropivacaine ARE LONG ACTING
TBLER |
|
|
WHICH ARE SHORT ACTING ALSO how do you increase its duration ? |
procaine/ chloroprocaine . increase by adding phenylephrine (vassoconstrictor) and/or by increasing the dose. less will go to cns since limit exit of drug via blood so less toxicity |
|
|
DOA is affected by |
-pka -ph -lipophilicity of drug - Rate of metabolismt |
|
|
two types of LA toxicities : |
Direct nuerotoxicity or systemic effects(effects on organs) -All local anesthetics go to cns toxicites are dose dependanet -when applied at high concentrations ALL CAN BE TOXIC TO NERVE TISSUE |
|
|
which are more toxic in the spine? |
chloroprocaine and lidocaine - toxicity is not related to sodium channel blockade. |
|
|
If you inhibit higher control you get ? how? |
convulsions -excitatory due to disinhibition - LA cause depression of cortical inhibitory pathways thus allowing unopposed excitatory activity. |
|
|
Lidocaine class 1 B antiarrythmic also intermediate acting LA. It is a amide or reverse amide of procaine ? |
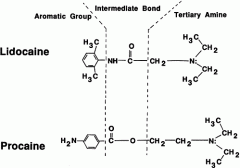
it is a reverse amide of procaine
|
|
|
Lidocaine is active parenteral or oral? has a fast onset and short or long duration? What is toxic about it ? |

parenteral and short duration - it is toxic when converted to monoethyl glycine xylidide via dethylation |
|
|
At high concentrations LAs can mess with na + calcium channels of the heart and cause toxic t/f. which drug is very cardiotoxic ? |
true. LA blocks sodium channels and at very high amounts can mess with calcium channels in the heart. Depress strength of cardiac contraction leading to hypotension. -bupivicaine. S enantiomer s better than the R which is more toxic. |
|
|
Ester type LAs are metabolized to PABA which can cause |
allergic reactions |

