![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
schedule 1 are |
HIGHLY ABUSIVE : heroine/LSD/PCP. NO MEDICAL USE |
|
|
Schedule 2 drugs are |
High-MODERATE abuse potential: Morphine/Cocaine/Methadone/Methamphetamines. Accepted medical use WITH restrictions |
|
|
Schedule 3 drugs are: |
LESS potential for abuse: Steroids/codeine/hydrocodone with aspirin or tylenol/some barbs. YES! Accepted medical use |
|
|
Schedule 4 drugs are: |
Talwin/valium/xanax. Accepted medical treatment . LOW POTENTIAL of abuse but may lead to dependence. |
|
|
schedule 5: |
low potential / cough medicine with codeine . |
|
|
physical barriers oxycontin ER |
resists crushing and breaking / becomes a gel at exposure to water |
|
|
suboxone and embedea(morphine) use agonist/antagonist |
morphine is released over time. antagonist is not released unless its tampered with |
|
|
oxteca(IR oxycodone) - |
irritates nasal passages if snorted/ turns into gel if tries to inject |
|
|
prodrug opiod |
lacks effect until absorbed into the GI tract |
|
|
nociception : |
detection of a noxious stimulus |
|
|
nociceptor : |
peripheral nerve reception and transmission of pain stimuli |
|
|
Analgesia |
ABSENCE of pain w/o loss of consciousness |
|
|
somatic pain : |
sharp pain/ sharp localized pain/ stinging |
|
|
visceral pain : |
dull / aching / burning sensation
|
|
|
opium was orig used for |
constipation activity (immodium) |
|
|
Thebaine(anti convulsant) is the "new poppy" used because |
intermediates for semi sythetic opioids(codeine) / restrictions on old one |
|
|
we have endogenous opiod peptides that bind to the same receptors as cocaine they are : |
met-enkephalin (small peptides make this just 5 Amino acids) leu-enkephalin B-endorphin Dynorphin A
|
|
|
mu receptor for ?
THIS IS THE MAIN RECEPTOR for opiods but all do step 1 |
for analgesia. Has side effects of : physical dependence , tolerance, constipation, repiratory depression, euphoria, emeisis and sedation |
|
|
Kappa receptor is for? |
for analgesia. Side effects are: dysphoria/ diureses/sedation/miosis |
|
|
Delta receptor is for : |
analgesia? Side effects are respiratory depression, immune stim? |
|
|
what happens when it binds ? step 1 |
1. decreased release of NT. Why? because it blocks Ca+ which decreases neurotransmitter release (NTs like glutamate...) happens at pre synapse
|
|
|
step 2 when it binds where is it working and on what receptor ?
what do we get ? EPSP or IPSP |
it works on mu receptor and hyperpolarises the pain afferent - we get an efflux of K+. once Ca+ is decreased at pre synapse, K+ channels open and we have K+ efflux in post synapse which inhibits perception of pain. We get IPSP inhibitory post synaptic potential |
|
|
Indications for opioids |
pain/cough/diarrhea/acute pulmonary edema /anesthesia |
|
|
antidiarrheals : |
diphenoxylate + atropine (lomotil) loperamide (IMODIUM) limited BBB passage |
|
|
antitussives (cough) |
codeine dextramethorphan (3 isomer not an opioid ) |
|
|
The Opioid Receptor : are there many or just one spot for opoids to bind? Name the spots : 3 spots |
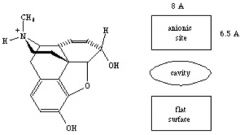
Many spots. Spots are at : anionic site -binds to charged N Cavity - accomodates piperdine ring Flat service- for binding on to aromatic ring Agonist and antagonist fit this receptor
|
|
|
What are the morphine rules? These structural features are found in all opioid analgesics (4) |
1.Tertiary N with small alkyl substituent 2.Quaternary Carbon -adjacent to an aromatic ring 3. Phenyl Group - or equivalent attached to quaternary carbon 4. 2 carbon spacer between quat carbon and 3 nitrogen |
|
|
morphine and related drgs SAR |
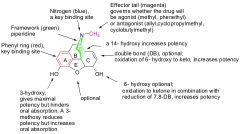
-CH3 will determine if its an agonist or antagonist -Double bond reduced, makes a ketone of -OH increases potency -The furan is optional but the nitrogen (3rd) is REQUIRED! -Piperdine increases activity -2 carbon spacer between D and C -3 hydroxy max potency but bad oral absorption -3 methoxy reduces potency but increases oral absorption |
|
|
Are derivatives stronger than parent morphine? Oxycodone is available PO t/f |
Yes, they are. -true it is available PO as percocet / tylox+APAP. Strength = to morphine. Unlike others, its for moderate pain |
|
|
Morphine is metabolized via --> Is it active or na? which is more potent glucoronidated ? |
-Glucoronidation -Yes, it is -WHEN THE RIGHT -OH is glucoronidated it is more potent than morphine |
|
|
Codeine PO- Hydrocodone- oxycodone - |
MOrphine pro drug. used for antitussive for moderate. Schedule 2 or 4 -comes as: Vicodin + APAP for moderate pain. Schedule 3 -comes as : SUSTAINED realease is oxycontin. Percocet , Tylox+APAP. Potent Mew agonist EQUAL TO MORPHINE Schedule 2 |
|
|
what metabolizes codeine ? |
CYP2D6--> metabolizes methyl off of Codeine. |
|
|
what is pruning of morphine? |
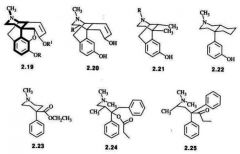
the fact that you can clip away at certain parts and have a useful analgesic. not as potent but active |
|
|
misc opiods (4) |
Nalbuphine (Nubain)- morphine nucleus. mixed agonist (kappa) antagonist at mew. kappa ligand
Morphinans: Ring E, the epoxide bridge, is missing. - called Levorphanol. Mew agonist.
Benzomorphans - ring E and C is missing. Pentazocine. ,mixed agonist/antagonist.
Oripavines- mew agonist / Etropine and Buprenorphine. Mixed partial agonist / antgaonist. ADD A RING
|
|
|
Morphianans |
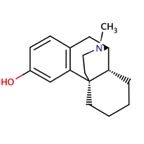
epoxide bridge missing. Ring E. Levorphanol |
|
|
Kappa ligands of the morphine family |
The groups on the nitrogen determine if its an agonist or antagonist. In Nalbuphine the cyclo butyl methyl group determines.These have ADVERSE EFFECTS. No ceilings but ad effects. Dysphoria and increased BP |
|
|
Oripavines are - |
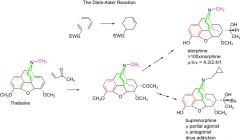
more rigid than morphine and bind well to receptor . Buprenorphine is used in substance abuse but too strong for humans. given to animals.mixed partial agonist at mu and kappa. Antagonist at delta.
Interestingly, When its cyclopropyl, its an antagonist at kappa and a partial agonist at mu. When its a methyl, its an agonist... |
|
|
Structures diverging from morphine :
Meperidine (demerol) - Fentanyl - Loperamide- |
-Irritates tissues IV/ Metabolite causes cns stimulation = seizures. -potent mu agonist. Some analogs are used in anesthesia. -anti-diarrheal: peripherally active mu agonist. DOes not cross BBB but it is diverging from morphine!! |
|
|
Fentanyl and its analogs. See similarities between Fen and mama Morphine... |
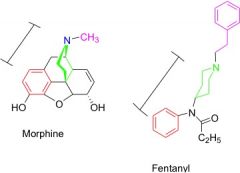
It is 80xs more potent than morphine! The amide is not 3 but has similar properties... Short duration/mu agonist / highly lipophilic (transdermal patch) |
|
|
Fentanyl has other analogs Which parts are worth looking at to see similarities?? |
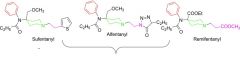
The amide next to the aromatic ring all very similar.... -anyl. These analogs of fentanyl are ultra short duration analogs used in anesthesia. |
|
|
Methadone is a - |
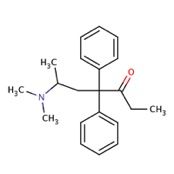
Strong full agonist. Its for withdrawl from heroine. Also a very good analgesic. The structure is different from morphine but just as strong. SLOW ACTION GIVES LONG HIGH |
|
|
Dezocine - |
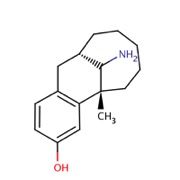
has unique structure. Diff from morphine. It is a mixed antagonist and agonist. has primary amine.. has ceiling effect not used alot.
|
|
|
Tramadol - Tapentadol- |
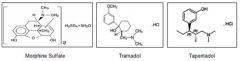
Tramadol has dual mechanism.Its a weak mu agonist and a weak inhibitor of 5HT and norepi reuptake. Little constipation and respiratory depression. Sch 4 now - Tapentadol - has dual MOA. Weak mu agonist and weak inhibitor of nor epi. Sche 2
|
|
|
Prescribing differences |
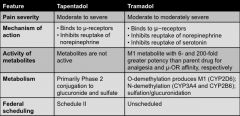
|
|
|
Strong full agonist none have ceiling effects except for |
Meperidine -- demerol adverse effects -- fentanyl hydromorphone levomorphone methadone morphine oxycodone oxymorphone
|
|
|
weak full agonist are |
codeine hydrocodone |
|
|
weak agonist reuptake inhibitors |
tramadol tapentadol |
|
|
Mixed agonist/antagonist summary |

DEF CANT INCREASE THE DOSE for these mixed ones. Oripavine -->animals
|
|
|
Adverse effects : |
-Dysphoria - feeling funky. -sedation-drowsy mental clouding -respiratory depression - dangerous (naloxone can reverse this and sedation quickly) -cough suppression- antitussive. tool advantage off-->put in cough syrups. -MIOSIS PIN POINT PUPILS -NVD -GI constipation
|

