![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is included in the integument
|
skin, nails, hair, sweat glands and sebaceous glands
|
|
|
the integument is __ % of total body weight
|
7-8
|
|
|
T/F the integument is the largest organ of the body
|
TRUE
|
|
|
how thick is skin
|
1.5 - 4 mm depends on abrasion
|
|
|
how much skin area wise
|
1.5-2 square meters
|
|
|
what are the function of the integument
|
Protection
Prevent loss of water Temperature regulation Metabolic regulation Immune defense Sensory receptors Excretion by means of secretion |
|
|
what are the __ layers of the integument
|
epidermis
dermis hypodermis( not actually part of integument) |
|
|
what main type of tissue is epidermis made of
|
Epithelial
|
|
|
what main type of tissue is dermis made of
|
connective
|
|
|
what main type of tissue is hypodermis made of
|
connective
|
|
|
what type of epithelial tissue are the epidermal layers made of
|
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
what are the layers of the epidermis from deep to superficial
|
bsglc
stratum basale statum spinosum stratum granulosum stratum lucidum statum corneum |
|
|
what cells are the pigment of the epidermis
|
melanocytes
|
|
|
what type of cells lose their nucleus and slough off the epidermis
|
keratinocytes
|
|
|
what types of cells are in the epidermis
|
keratinocytes
epidermal dendritic cells tactile cell (merkel cells) melanocytes |
|
|
what are the __ factors of skin color
|
3
blood - hemoglobin melanin - amount of pigment not amount of melanocytes carotene - carrots |
|
|
what is a nevus
|
mole or birthmark
overgrowth of melanin-forming cells harmless unless mutated and becomes malignant |
|
|
what are freckles
|
Yellowish or brown spots from excessive melanocyte activity, not increased melanocyte cells
|
|
|
Hemangioma
|
Proliferation of blood vessels
Bright red to deep purple in color |
|
|
Friction ridges (fingerprints)
|
Formed by large folds and valleys of the dermis and epidermis
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of the dermis
|
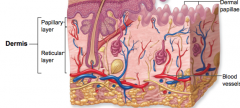
two layers
papillary layer reticular layer vascular innervated |
|
|
what type of connective tissue is the papillary layer of the dermis made of
|
areolar Connective tissue
|
|
|
what type of connective tissue is the reticular layer of the dermis made of
|
dense irregular connective tissue
|
|
|
what are striae and what causes them
|
stretch marks
torn collagen in the dermis |
|
|
what causes wrinkles
|
decreased flexibility and thickness of dermis
|
|
|
what are cleavage lines
|
orientation of collagen bundles
|
|
|
T/F a wound that is perpendicular to the cleavage lines are easier to close
|
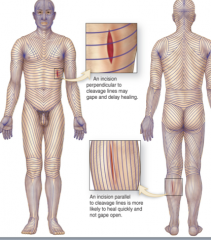
F
|
|
|
what is the structure of the hypodermis
|
areolar and adipose connective tissue
not considered part of teh integument |
|
|
what are the functions of the hypodermis
|
anchors skin to underlying structures
thermal insulation energy reservoir |
|
|
Know by heart
|
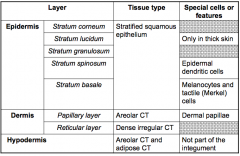
|
|
|
what are finger nails mostly made up of
|
Hard keratin
|
|
|
what are the structures of teh fingernail
|
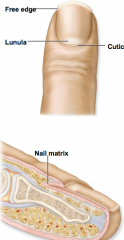
nail matrix
lunula cuticle free edge |
|
|
what are the __ types of hair
|
3
Lanugo vellus terminal |
|
|
where is lanugo hair found
|
fetal
|
|
|
where is vellus hair found
|
fine hair on most of the body
|
|
|
where is terminal hair found
|
head, pubic, armpit,facial hair
|
|
|
what are teh functions for hair
|
protection
sense touch reduce heat loss |
|
|
what is the structure of hair
|
foolicle root and shaft
keratin arrector pili muscle |
|
|
how fast does hair grow
|
2mm a week
|
|
|
what are the growth cycles of hair
|
active phase (2-7 yrs)
dormant phase (3-4month) |
|
|
what are some of teh reason for baldin
|
alopecia (hair thinning)
diffuse hair loss male pattern baldness |
|
|
what are the influences of male pattern baldness
|
genetic
hormonal testosterone causes terminal hair to be replaced by vellus |
|
|
what are the __ types of exocrine glands in the integument
|
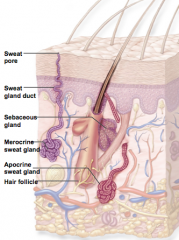
2
sebaceous(oil) sudoriferous(sweat) |
|
|
what do sebaceous glands produce
|
sebum
|
|
|
what are the __ types of sudoriferous glands
|
merocrine
apocrine |
|
|
where are mercrine glands foudn
|
most numerous
produce watery sweat |
|
|
where are apocrine glands found and what do they produce
|
axillary, nipple, anal, and genital areas
produce viscous sweat |
|
|
what cause acne
|
plugged sebaceous ducts
|
|
|
what are the three types of burns
|
first second and third degree
|
|
|
what does a first degree burn damage
|
epidermis
|
|
|
what does a second degree burn damage
|
epidermis and part of dermis
|
|
|
what does a 3rd degree burn damage
|
entire epidermis and dermis
|
|
|
what are th caharcteristics of basal cell carcinoma
|
most common
least dangerous originates in statum basale |
|
|
what cell type does squamous cell carcinoma come from
|
arises fro keratinocytes
|
|
|
characteristics of malignant melanoma
|
most deadly
arises from melanocytes ( usually presxisting mole) early detection is crucial |
|
|
what is the abcd rule of malignant melanoma recognition
|
A - assymetry
B - border C - color D - diameter |

